turbines AGB
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
AGB purpose
transfers rotational power from the engine to various accessories/components
houses accessory drive and reduction gears
used during starting process to transfer starter rotation to rotate the engine
why should AGB be reliable
loss of AGB causes loss of every component attached to AGB
how much horsepower does the AGB take from the engine on high bypass engines
500
location of AGB depends on
engine design and aerodynamic needs
what drives AGB
HP rotor
what provides power to AGB
rotary power from engine
AGB location on turbojet
above or below compressor casing
AGB location on turbofan
below and/or side of fan case
AGB location on turboprop
back, front, bottom
prop reduction gearbox and governor at front
AGB location on turboshaft
front and/or back of engine
what does AGB power
Fuel pump
Hydraulic pump
Oil pump
Fuel control unit
Electrical generators
Starters (electric of pneumatic)
what component drives the AGB
starter (drives AGB therefore drives HP rotor)
hand crank mechanism
typical engine-to-AGB mechanical drive sequence
High pressure rotor > inlet gearbox > transfer gearbox > AGB
PT6 AGB
AGB at the rear - rotational energy powers gas generator section
prop reduction gears and prop governor at front - rotational energy comes from power section
what do gears do
AGB transmits power to drive accessories through gears
types of gears
spur
helical
bevel
spiral bevel
straight spur gear
Consists of a cylinder or disk with teeth protruding radially
Edge of each tooth is straight and aligned parallel to axis of rotation
Can only be meshed correctly when both shafts are parallel in direction
bevel gear
Used when direction of the shaft’s rotational output needs to be changed through an angle
types of bevel gears
straight, spiral, helical
straight bevel gear
straight and tapered teeth
simplest
spiral bevel gear
curved, oblique teeth
Transmit higher loads than straight bevel due to greater tooth area contact
helical bevel gear
Gradually engage at one end of the tooth maintaining contact until gears fully engage for smooth transfer of rotation and torque from the driving gear to the driven gear
what displacement do gears experience
axial displacement directly proportional to torque transmitted
how do we figure out propeller torque
measure engine power output (torque at turboprop propeller) to indicate propeller torque
HP rotor drives the AGB through a driveshaft system through 3 different gear drive designs
direct (bevel gear)
stub shaft
idler gear shaft
roller bearing
radial loads
ball bearing
thrust (axial) and radial (centrifugal) loads
what do bearings do
support length of engine shaft
number of bearings is determined by
length and weight of rotor shaft
how are bearings numbered
front to back
AGB lubrication
provide lubrication and cooling for all gears, bearings and splines
Oil protects corrosion-prone materials from oxidation
Must carry foreign matter away from bearings and gearbox that can cause wear and damage
ATA AGB
83
ATA PT6 AGB
72
maintenance
servicing AGB oil, inspect magnetic chip detector or leaking oil
shear shaft
Shear shaft is subjected to a torque force exceeding maximum rating
Will snap if under force exceeding maximum rating and prevent damage to AGB and components
drive pad
Where each component is installed on the AGB
If AGB pad seal leaks, each pad has a dedicated drain line to safely drain away oil
magnetic chip detector
captures ferrous metal particles
magnetic chip detector types
electric - warning light cockpit
passive - maintenance must inspect AGB oil
engine hand-turn access
for maintenance only
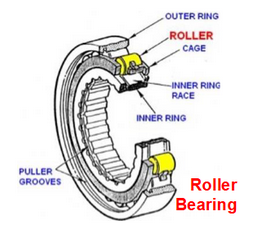
roller bearing
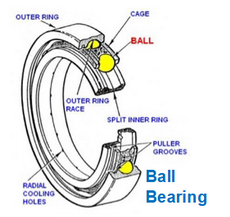
ball bearing

helical bevel gear
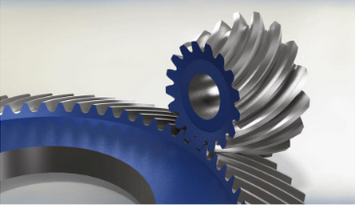
spiral bevel gear
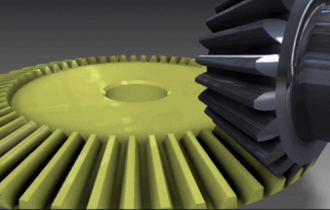
straight bevel gear

straight spur gear
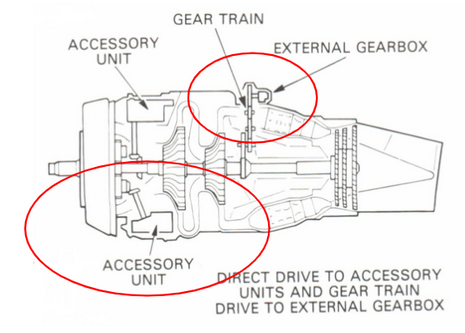
internal/external AGB
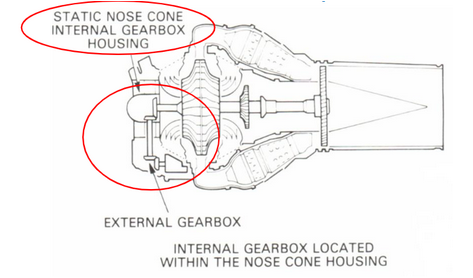
internal/external AGB
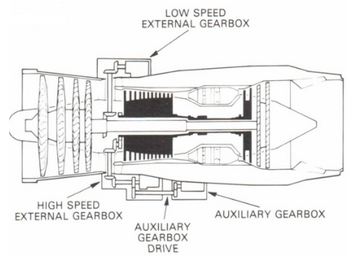
auxiliary AGB
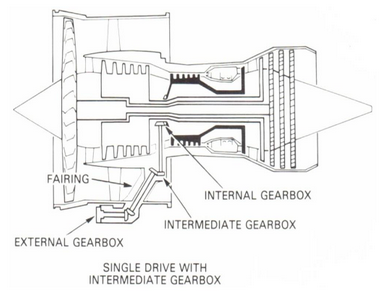
intermediate AGB