Human Biology Unit 1 - Scientific method, Cells, Tissues
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What are cells
. The basic structural and functional units of the body, that can perform life’s functions
. Composed of organelles, which maintain homeostasis . Have a large SA:V ratio to allow for nutrient absorption and waste removal
What processes do cells undergo?
. Respiration: breakdown of glucose to release energy for the cell
. Synthesis: building large molecules from smaller ones
. Growth: increase in size or number of cells
Cell Membrane (plasma membrane)
. The outer boundary of the cell that separates cytoplasm inside cell from neighbouring cells + extracellular environment
. controls which substances enter + leave a cell, made up of bilayer of lipids and proteins, contains cholesterol
. differentially permeable and semi permeable (permeable to some substances but not to others)
Cytoplasm
. Thick jelly like fluid within cell membrane that fills the space between cell membrane and organelles
. cytosol + organelles are suspended in, many substances are dissolved in
Cytosol
. The liquid component of the cytoplasm, 75-90% water
. Often has dissolved substances like salts + carbohydrates
. Other insoluble (in water) substances like protein + fats are suspended in
Nucleus
. ovoid/spherical, largest organelle
. contains genetic material (DNA)
. contains nucleolus + nucleoplasm
Function: responsible for maintaining integrity of DNA + controlling cellular activities (metabolism, growth and reproduction) by regulating gene expression
Ribosomes
. very small + spherical
. can be loose in cytoplasm or joined to other organelles (most) like ER (making rough ER)
. connect amino acids together to form proteins (protein synthesis)
Function (do their work in the cytoplasm): convert genetic code into an amino acid sequence, build protein polymers from amino acid monomers
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
. parallel membranes that extend through cytoplasm connecting cell membrane and nuclear membrane
. can be smooth: no ribosomes attached
. can be rough (most): ribosomes attached
. Function: provides a surface for chemical reactions to occur + channels can store and transport materials
. Forms supporting framework of cell
Golgi Apparatus/Body
. flattened membranes stacked one upon the other
Function: . modify proteins and package them in vesicles for secretion from the cell (exocytosis)
—> proteins that are made in ribosomes, pass through the ER to golgi apparatus
—> Edges of golgi apparatus then form vesicles (sacks of liquid containing protein) to secrete the protein out of the cell
Lysosomes
. small spheres that contain enzymes which break down proteins, lipids, nucleic acids and some carbohydrates
Function: break down materials taken into the cell or break down worn out organelles
Vesicle
. small membrane-bound sac that stores and transports materials into, out of or within the cell
Organelle
. a subcellular structure that has one or more specific jobs to perform in the cell
. Suspended in cytoplasm
Mitochondria
. sphere/elongated organelle spread through cytoplasm
. contains circular DNA
. Has double membrane: outer smooth membrane, inner folded membrane (folds = cristae)
. Function: folds allow greater SA for chemical reactions to occur
. releases energy for cell through cellular respiration (occur at cristae, where chemical energy is broken down to form ATP)
Nuclear Pores
. allows molecules to pass through the nucleus
Nuclear Membrane (nuclear envelope)
. separates DNA from the cytoplasm, is double membraned (2 lipid bilayer membranes) + contains pores/gaps
. Controls which substances move through nucleus
Nucleolus
. located inside nucleus
. composed mainly of RNA
. nucleolus and DNA suspended in jelly like nucleoplasm
. involved in manufacture of ribosomes
Centrioles
. pair of cylindrical structures involved in mitosis (reproduction of cell)
. usually located near nucleus
Cilia and Flagella (similarities)
. Fine projections that beat back and forth to either move cell or move substances over the cells surface
Cilia
. lots of short projections that look like hair
. eg: in trachea to move mucus towards the throat
Flagella
. one or two longer projections
. eg: sperm cell tail allows sperm cell to swim
Cytoskeleton
. framework of protein fibres that give cell its shape + assists cell movement
. consists of microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments
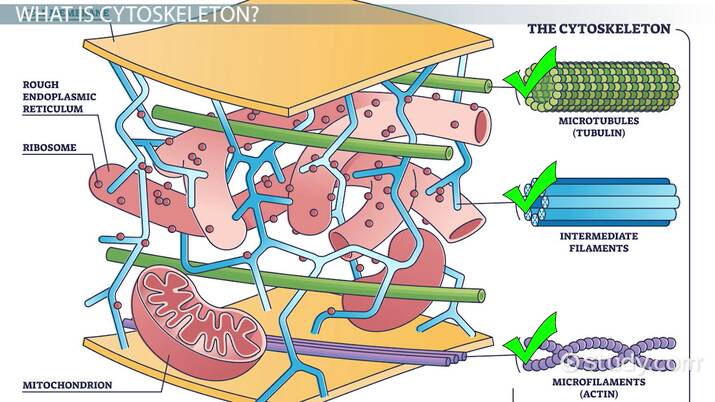
Inclusions
. chemical substances that aren’t part of the cell structure but are found in the cytoplasm
. eg: haemoglobin (RBCs), melanin (skin, hair, eye cells)
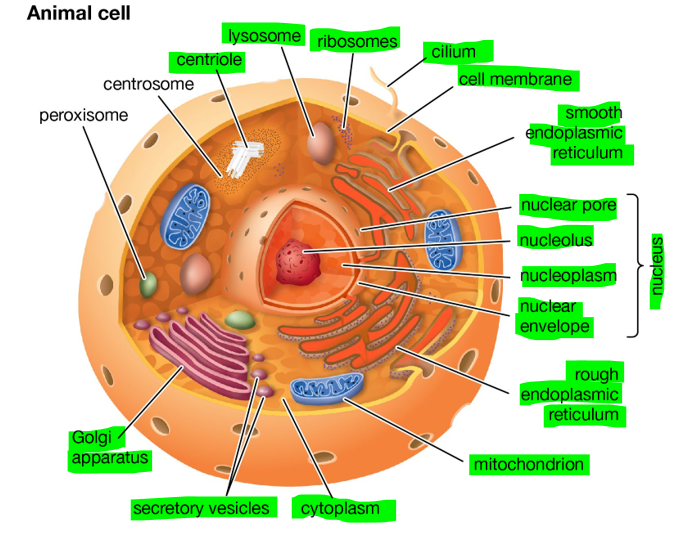
Labelled Animal Cell Diagram
Functions of the Cell Membrane (NO?)
. Physical barrier
. Separates cytoplasm from extracellular fluid around it
. Regulation of materials entering + exiting the cell
. Movement of ions and nutrients into cell
. Movement of wastes out of cell
. Release of secretions
Cell Membrane Sensitivity
. membrane detects any changes in the extracellular environment
. eg: an increase of glucose in blood
Cell membrane Support
. membrane is attached to the cytoskeleton which supports the structure of the cell
. cells are attached to one another via the membrane giving rise to tissues
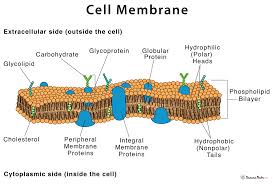
Describe the Cell Membrane Composition
. the design of the composition = the fluid mosaic model
—> as many molecules are located in the cell membrane and are constantly in motion
. Composed of a double layer (bilayer) of phospholipids (are molecules made up of lipids with a phosphate group attached)
—>phospholipid molecules have a hydrophilic + polar head and hydrophobic + non-polar tail (tails are repelled by water and forced to face inwards away from the watery environment, while heads face outwards as they are attracted to the intra+extracellular fluids)
—>hydrophilic molecules can’t cross the hydrophobic tail layer, keeping the 2 (intra + extra) fluids separate
Cell Membrane’s Phospholipid bilayer diagram

Types of Membrane Proteins: 1. Peripheral proteins
. are attached to one side of the membrane only
Types of Membrane Proteins: 2. Integral Proteins
. are located through the membrane
—> many are responsible for transporting ions + small molecules across the membrane
—> these substances are polar (a molecule where electrons aren’t shared equally between atoms, creating a slightly positive end and a slightly negative end on the molecule) or are moving against their concentration gradient (L to H)
Proteins
. large molecules within the cell membrane
. only 2% of membrane are proteins but 55% of cell’s weight is due to the proteins
. Include: receptor proteins, channel proteins, carrier proteins, cell-identity markers
Receptor proteins
. communicate, transmitting info about extracellular stimuli into the cytoplasm
—> certain molecules outside cell bind to receptor proteins which influences changes within cell
—> only one type of receptor protein will bind to one molecule (site specific)
—> Eg: the insulin hormone which is secreted from the pancreas binds to a receptor protein which allows the cell to absorb greater amounts of glucose to aid respiration
—> the limited number of receptor proteins influences the rate of cellular activity
Channel Proteins
. proteins that form pores for specific molecules to pass through
. Transports small, polar, water soluble molecules (Na, Ca, Cl) - large molecules (glucose) can’t pass through
. this (passive) process occurs via facilitated diffusion
. proteins found in the cell membrane that allow substances to pass into and out of the cell
Carrier proteins
. Bind to molecules (eg glucose) and change shape to transport them across the cell membrane and into cell’s cytoplasm
. can be facilitated diffusion (moving molecules w/ concentration gradient) + active transport (against gradient)
—> protein changes its own shape
—> are specific
—> the number of carrier proteins limits the intake of molecules into the cell
—> substances such as hormones will trigger carrier proteins binding to molecules
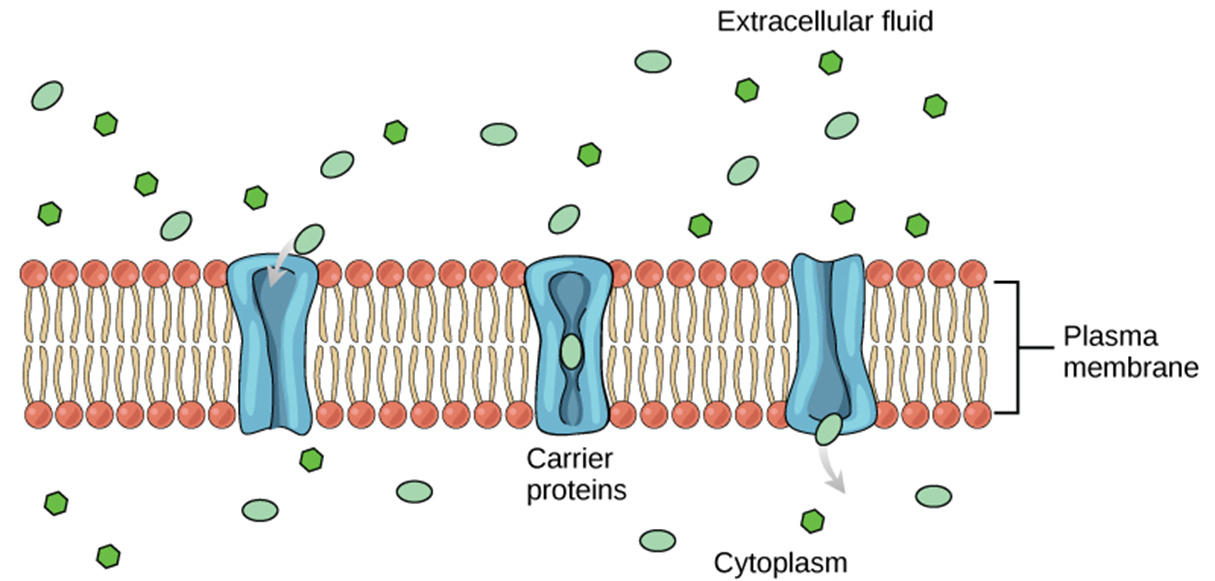
Cell-Identity Markers
. serve as recognition markers for the body’s immune system
. the body’s immune system recognises these cells and thus these cells won’t be destroyed
Cell Membrane Diagram
Cell Membrane: Semi/selective/differentially permeability
. ability to allow only certain molecules in or out of the cell
. cells must exchange materials such as nutrients + gases with their environment by allowing them to pass through their membrane
—> lipid bilayer permeable to: few small uncharged molecules (O2, CO2)
—>Impermeable to: large, polar/ionic compounds
What 3 main components make up the cell membrane
Phospholipid bilayer
Cholesterol
Membrane proteins
Cholesterol Molecules in the Cell Membrane
. wedged between the phospholipid molecules
. provide flexibility + improve the structural integrity of the membrane, helping the membrane keep its shape
Function 1 of the Cell Membrane (YES?)
Acts as a physical barrier:
. separates intracellular fluid (cytoplasm) from extracellular fluid
Function 2 of Cell Membrane
Regulates the passage of materials:
. controls movement of materials in + out of cell
Function 3 of Cell Membrane
Able to sense changes:
. cell membrane is first part of cell affected by any changes in extracellular fluid, containing receptor proteins that can respond to changes in the extracellular fluid very quickly
Function 4 of Cell membrane
Helps to support the cell:
. contains structural molecules that give cell shape + allow it to join with other cells
. internal part of the membrane is attached to the microfilaments of cell’s cytoskeleton, giving support to the whole cell
Simple diffusion
. movement of certain substances directly through the lipid bilayer (alcohol, oxygen, CO2)
. passive process, no energy required
. substances move from high concentration to low concentration
—> eg: oxygen into cells, carbon dioxide out of cells
What does the rate of diffusion depend on?
The concentration gradient: greater difference in concentration between the 2 regions of the substance, the greater the rate of diffusion
The size and nature of the diffusing molecule: smaller molecules diffuse faster than large ones
The distance over which diffusion takes place: shoter=greater rate of diffusion
The area over which diffusion takes place: larger surface area=greater rate of diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
. type of passive transport in which the molecules move from the region of higher concentration to the region of lower concentration assisted by a channel or carrier protein
—> as some molecules are too large to diffuse through the cell membrane on their own (amino acids + glucose), the molecule uses a protein within the cell membrane + is moved into or out of the cell
. rate of facilitated diffusion is dependent on the amount of proteins being used
. is specific
Active Transport
. the movement of molecules or ions across a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration (against the concentration gradient)
. carrier proteins used to transfer molecules from outside of cell into cell
. cell must use energy (ATP)
Vesicular Transport
. a cellular process responsible for moving (large) molecules across and within cells using membrane-bound sacs called vesicles
. an active process
. maintains homeostasis and communication between cells by the release of neurotransmitters in nerve cells
Vesicular transport: Endocytosis
. the movement of molecules into the cell via vesicular transport
. the membrane surrounds the substance + then pinches off to form a vesicle which then is suspended in cytoplasm
. eg: engulfing bacteria by white blood cells
Endocytosis: Pinocytosis
. entering of liquid substances
. The process by which a cell takes in small molecules and fluids from the extracellular fluid into the cytoplasm
—> when the cell takes in the fluid, it’s stored in a tiny vesicle provided by the cell membrane
Endocytosis: Phagocytosis
. entering of solid substances
. Process by which phagocytes (living cells) ingest other cells or particles, including foreign substances, microorganisms and apoptotic cells
—> these phagocytes rise the membrane to an internal compartment called the phagosome
Vesicular Transport: Exocytosis
. the movement of substances out of the cell via vesicles
—> substances move from the golgi towards cell membrane via a vesicle, then fuses with cell membrane and its contents escapes into the extracellular environment
Active vs Passive Transport
Active: requires energy (ATP) to move molecules across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient (L to H)
Passive: doesn’t require energy and moves molecules down their concentration gradient (H to L)
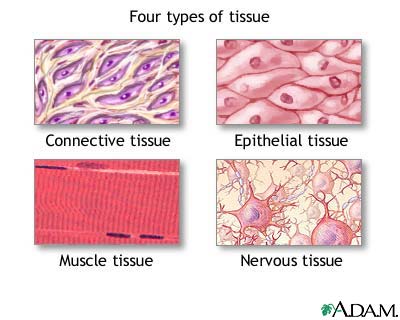
Tissue types: Muscular tissue
. contractile tissue
3 types:
Skeletal muscle: tissue that’s attached to bones, voluntary, allows for movement
Smooth muscle: supports internal organs, involuntary (moving substances down our pipes), found in the walls of hollow organs (intestines) and passageways (veins)
Cardiac muscle: makes up the walls of heart, involuntary
Tissue Types: Epithelial Tissue (MORE NEEDED?)
. bricks on a wall appearance
. lines surface
. eg: skin, the lining of GI tract
Tissue Types: Connective Tissue
. provides support and structure
. cells are spread far apart in an extracellular matrix
. eg: bone, cartilage, blood
Tissue types: Nervous Tissue
. composed of neurons
. neurons carry information to parts of the body by electrochemical messages known as action potentials
The 4 Tissue Types Appearance
Osmosis
. the movement of water from an area of low solute (high water) concentration to an area of high solute (low water) concentration, through a selectively permeable membrane
—> special type of diffusion involving water
—> occurs via channel proteins in cell membrane (aquaporins)
—> from dilute to concentrated solutions
—> passive process, no energy required
Aquaporins
. integral membrane proteins, which are water-selective, that facilitate the movement of water by osmosis
. water channels
. water molecules can travel through aquaporins + semi-permeable membrane
—> water moves through cells most rapidly in tissues that have aqauporins
Osmotic pressure
. the pressure created by water moving across the membrane due to osmosis, to create equilibrium
—> the higher solutes in solution = higher osmotic pressure
—> pressure needs to be applied to halt osmosis
Isotonic solution
. a solution that has the same solute concentration as another solution
. no net movement of water particles + overall concentration on both sides of cell membrane remains constant
—> rate of water movement in and out is equal
—> cell = normal size
Hypertonic solution
. a solution that has a higher solute concentration (lower water) than another solution
On the outside: concentrated solutes outside
—> water particles will move out of cell, causing crenation + cell shrinking
Hypotonic solution
. a solution that has a lower solute concentration (higher water) than another solution
On the outside: dilute solutes outside
—> water particles will move into cell, causing cell to expand (swell) and eventually lyse (burst)
Solvent
. a substance, often water, in which a solute is dissolved
Solute
. a substance that can be dissolved in a solvent
Tonicity
. the ability of an extracellular solution to make water move into or out of a cell by osmosis
. a solution’s tonicity is related to its osmolarity
Osmolarity
. the total concentration of all solutes in the solution
. solution with low osmolarity has fewer solute particles per litre of solution
. solution with high osmolarity has more solute particles per litre of solution
—> when solutions of different osmolarities separated by membrane permeable to water, but not to solute, water move from side with lower osmolarity to higher
Hypotonic solution osmolarity
. extracellular fluid has lower osmolarity than the fluid inside the cell
. net flow of water will be into the cell
. solute concentration inside cell = higher
Hypertonic solution osmolarity
. extracellular fluid has higher osmolarity than cell fluid
. water diffuses out of cell
isotonic solution osmolarity
. extracellular is the same osmolarity as the cell
. no net movement of water in and out, amount transported into cell = amount transported out
Surface Area to Volume Ratio for Diffusion Efficiency
. smaller cells have a larger SA:V ratio, which allows faster diffusion
. as a cell grows, its volume increases faster than its SA, reducing efficiency
Why are cells small?
. a high SA:V ratio ensures efficient exchange of nutrients and waste
. large cells struggle to get enough oxygen + nutrients
. cells divide instead of growing too large to maintain efficiency
How do you increase reliability
. repeat trials
How do you increase validity
. control ..
How do you increase accuracy
. use right equipment, use equipment correctly
Examples of Endocytosis
Phagocytosis: White blood cells engulfing bacteria
Pinocytosis: absorption of nutrients in the small intestine
Examples of Exocytosis
Nerve signal transmission/neurotransmitter release
Hormone (insulin) secretion
Mucus and Enzyme secretion: stomach cells secrete digestive enzymes to break down food