STNA Module 4
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
topic: cardiovascular system
….
Note:
Veins are depicted blue, arteries are red in textbooks
Note: arteries
Blood is coming from the heart to the arteries (oxygenated and under pressure) and then depleted from there and then back with veins (deoxygenated)
Image: Heart
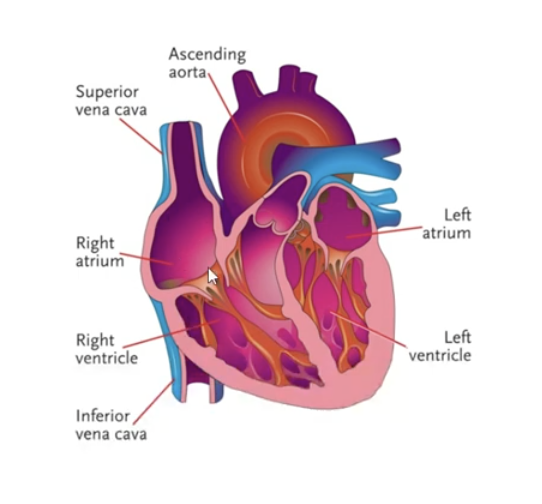
The heart has 4 chambers; list them and the positions (will be plural)
Top: atrium ( left and right )
Bottom: ventricles ( left and right )
Where does the blood get pumped out from the heart?
ascending aorta (artery)
time of cardiac cycle
60 seconds
Circulatory system (composition)
made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood
what does blood carry?
food, oxygen, and essential substances to cells
heart functions in how many phases?
2
diastole and systole
diastole
resting phase when blood fills up in the chamber
systole
contracting phase when ventricles pump blood
major functions of circulatory system / cardiovascular system (what do they supply)?
supply food, oxygen, hormones to cells
supply antibodies
Other major functions of circulatory system (cardiovascular system)
remove waste products
control body temp
aging (circulatory system) changes 3

How can NA assist with circulatory system?

Image: Important observations and reports for circulatory system

hypertension (HTN) (and measure)
high blood pressure, regularly measuring 140/90 mm Hg or higher (for elderly)
diuretics
medications that reduce fluid volume in body (water pill) (would allow more urination by pulling fluid from cells)
Image: plaque formation in arteries can build up high blood pressure
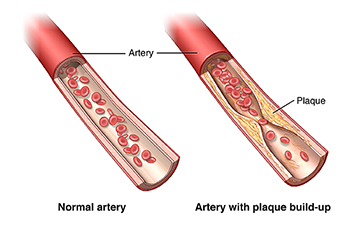
high cholesterol
excess fat circulating in blood stream which becomes plaque in arteries head to toe in various sections (years of build up)
(consumption milk cheese meat butter)
major cause of hyertension
atherosclerosis- hardening and narrowing of blood vessels ( such as build up of plaque)
symptoms of HTN
headache, blurred vision, dizziness; sometime nothing noticeable
normal blood pressure
140/90
normal pulse
60 to 100 bpm
Care for hypertension (2)
Regular trip to bathroom
Encourage residents to follow their diet and exercise programs. Measure blood pressure as directed (VS before giving medication)
angina pectoris
chest pain, pressure, or discomfort
Coronary artery disease CAD
blood vessels in coronary arteries (near heart) narrow and reduce blood flow to heart
result of CAD?
angina pectoris
guideline for angina pectoris (4— important to know the medication tablet)
encourage rest
nitroglycerin (dilator of blood) medication tablet or patch
only nurse should do it. tell them if resident needs help
residents avoid heavy meals, overeating, intense exercise, or cold humid weather
MI
myocardial infarction— heart attack
myo(muscle) cardial(heart)
death of heart muscle which is caused by block of blood flow to heart muscle
MI dead tissue area can be… (2)
large or small
result in serious heart damage or death
note
the closer the blockage is to the first or main branch of blood vessel, the more sever the MI and the parts that doesn’t get the supply of blood dies off
stroke is similar to heart attack…. as it is….
blockage in the brain
Care after heart attack/ surgery
low cholesterol, low fat, and sodium diet;
exercise program; medications for heart rate and blood pressure;
Avoid: smoking; cold temp; s
tress management
why a low salt (sodium) diet for heart attack care?
salt retains fluid; heart has to pump harder; strain on heart
Congestive heart failure CHF
failure of heart muscle to pump effectively due to damage
symptoms of CHF
coughing or gurgling (fluid in lungs)
Fluid won’t be able to get pumped back into heart so it builds up in lower body

can medications help control CHF?
yes
guidelines for CHF
medications
toilet
follow diet— high potassium can help with dizziness
rest
intake and output of fluid measure
weigh residents
ROM
Extra pillow for breathing— elevate head of bed
Peripheral vascular disease PVD
fatty deposits in blood vessels that harden (peripheral meaning around hands, feet, etc)
symptoms of PVD
cool arms and legs
swelling in hands and feet
pale or bluish hand and feet
bluish nail
ulcers on legs and feet
pain when walking
treatment of PVD
quit smoking, medications, exercise, surgery
topic: respiratory system
…..
Image: respiratory system
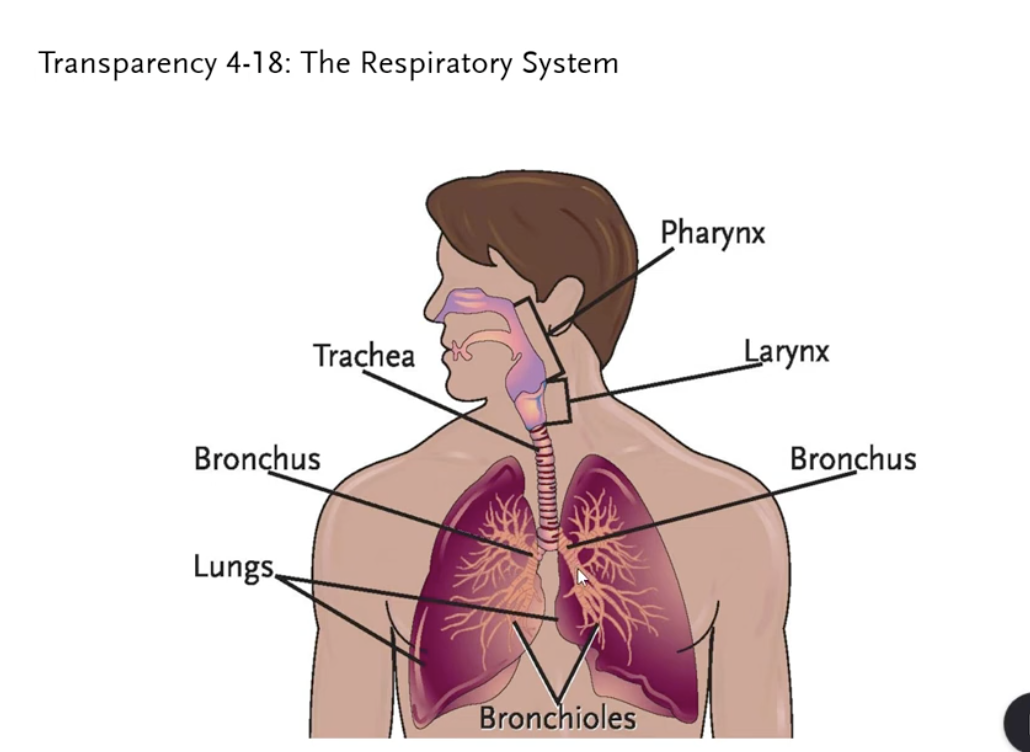
inspiration
breathing in
expiration
breathing out
respiration
inspiration + expiration
Respiratory system function (2)
bring oxygen into body
eliminate carbon dioxide produced by body
Normal changes of respiratory system (due to age)
loss of strength (lung)
decreased lung capacity
decreased oxygen in blood
weakened voice
NAs can help residents by
avoid exposure to polluted air (like smoke or pollens)
rest
exercise and movement
deep breathing exercises
positions into ease breathing (high fowlers—sitting upright)
Image: observations for respiratory system

chronic obstructive pulmonary COPD
lung disease that makes it difficult to breath
is COPD chronic?
yes
two types of COPD
chronic bronchitis and emphysema
COPD resident has high risk of what?
pneumonia
COPD residents may have….
fear of suffocation—> not sleep
poor appetite due to lack of sleep
COPD symptoms
cough or wheeze (chronic)
trouble breathing
shortness of breath
pale,cyanotic, reddish-purple skin
confusion
weakness
appetite loss
fear and anxiety
Image: Observations for COPD


aveoli
air sacs attached to bronchioles (can’t be regenerated)
(has blood vessels)
emphyzema
type of COPD caused by prolonged smoking, by over-inflating the lung and alveoli
Note: asmtha
Bronchioles cross-section similar to arteries
inflammation that tightens the bronchioles making it hard to breathe (Bronchitis— mucous build up in it)
note
emphyzema patients have damaged lungs so they are used to running on lower oxygen levels. Giving too much oxygen during therapy can trigger respiratory arrest
Topic: endocrine system and diabetes
,,,,,
image: Endocrine system
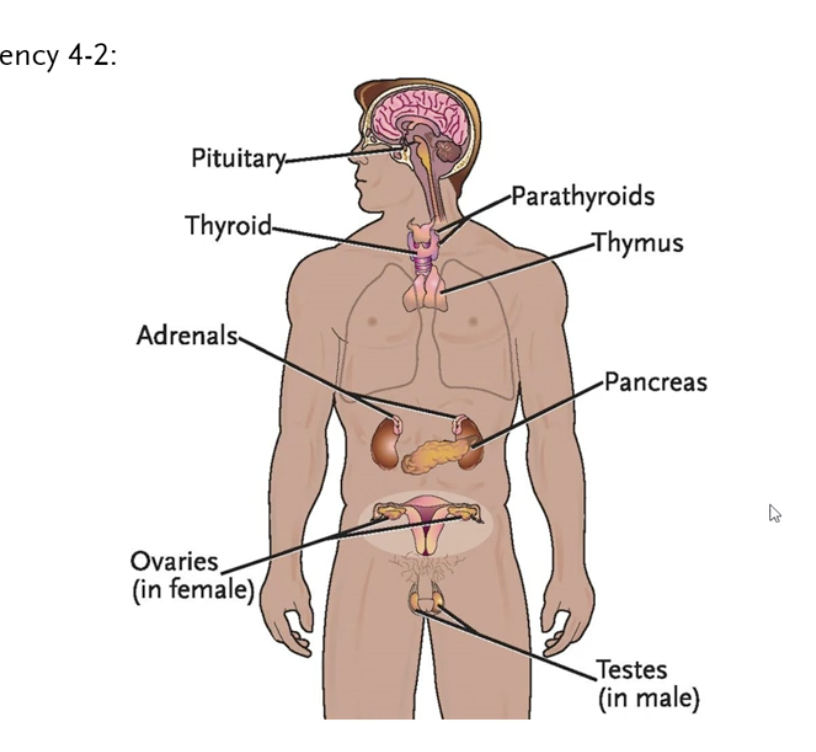
Endocrine system
Made up of different glands
glands
organs that produce and secrete different hormones
Hormone
chemical substance that the body usses
what does pituitary gland secrete (an example)? What is another function?
oxytoxin— for uterus contraction (labor)
commands other glands on when to produce the hormones
Thyroid gland (in charge of?)
metabolism
parathyroids
regulate calcium in blood stream
thymus (usage)
before adolescence—> growth for puberty
after puberty if shrinks
adrenal glands (secretes?)
epinephrine (fight or flight response— dilator of blood vessels)
Norepinephrine (vasoconstrictor)
Cortisol—secreted under stress, decreases the immune system
pancreas (secrete)
insulin (brings blood sugar down)
glucose (sugar-not hormone)
ovaries (secrete)
estrogen
progesterone
testes (secrete)
testosterone
how are hormones carried to organs?
blood
what does hormones achieve?
maintain homeostasis
growth and development
blood sugar levels
calcium and phosphate levels
reproduction
burning food (calories) for energy
Normal age change in endocrine system

NAs help the endocrine system by

Image: observations


polydypsia
excessive thirst
polyphagia
excessive hunger
polyuria
excessive urination
symptoms of diebetes (some signs)
polyphagia, polydypsia, polyuria
diabetes
pancreas produces little insuline or no proper use of insulin
insulin
hormone that converts glucose from blood into cell for energy
pre diabetes
blood glucose level are above normal but not high enough
gestational diabetes
appears in pregnant women who never had diabetes before but who have high glucose level during pregnancy
diabetes; what can glucose do?
glucose can collect in blood causing circulatory problems
type 1 diabetes
found in children and young adults; pancreas produces little to no insulin. Managed with daily injections of insulin or pump and special diet. Blood testing must be done.
which is more common, type 1 or 2 diabetes?
type 2
type 2 diabetes
Either body produce little to no insulin or fails to properly use insulin. Insulin resistance. It develops slowly and mildly. Develops after 35 (typically); the risk of getting this type increases with age.
signs of diabetes


Diabetes complications
circulatory system change—→ stroke, MI, poor circulation
Damage to eye/blindness
leg foot uclers/ wound infections
insulation reactions and biabetic ketoacidosis
image: diabetic guidelines

topic: vital signs
……
normal pulse rate
60-100 bpm (beats per minute)
normal respiratory rate
12-20 respirations per minute