9.2 Phloem transport
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/20
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
1
New cards
Translocation
The movement of organic compounds from sources to sinks
2
New cards
Source
Where organic compounds are synthesised (photosynthetic tissues)
3
New cards
Sink
Where the compounds are delivered to for use or storage - includes roots, fruits and seeds.
4
New cards
How are sugars transported?
As sucrose
5
New cards
Cells in the phloem
Sieve element cells, companion cells, parenchymal cells and schlerenchymal cells
6
New cards
Sieve element cells
Long and narrow cells that are connected to form the sieve tube.
7
New cards
Properties sieve element cells
* Connected by sieve plates at their transverse ends, which are porous to enable flow between cells
* Have no nuclei and reduced numbers of organelles to maximise space for translocation
* Have thick and rigid cell walls to withstand the hydrostatic pressures which facilitate flow.
* Have no nuclei and reduced numbers of organelles to maximise space for translocation
* Have thick and rigid cell walls to withstand the hydrostatic pressures which facilitate flow.
8
New cards
Companion cells
Provide metabolic support for sieve element cells and facilitate the loading and unloading of materials at source and sink
9
New cards
Properties companion cells
* Possess and infolding plasma membrane which increases SA:vol ratio to allow for more material exchange
* Have many mitochondria to fuel the active transport of materials between the sieve tube and the source or sink
* Contain appropriate transport proteins within the plasma membrane to move materials into or out of the sieve tube.
* Have many mitochondria to fuel the active transport of materials between the sieve tube and the source or sink
* Contain appropriate transport proteins within the plasma membrane to move materials into or out of the sieve tube.
10
New cards
Phloem vs. xylem in roots of monocotyledon
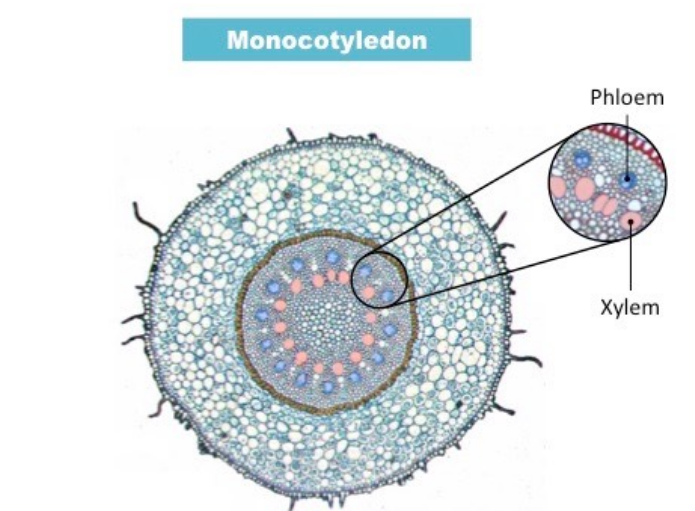
11
New cards
Phloem vs. xylem in roots of dicotyledon

12
New cards
Xylem vs. Phloem in stem of monocotyledon
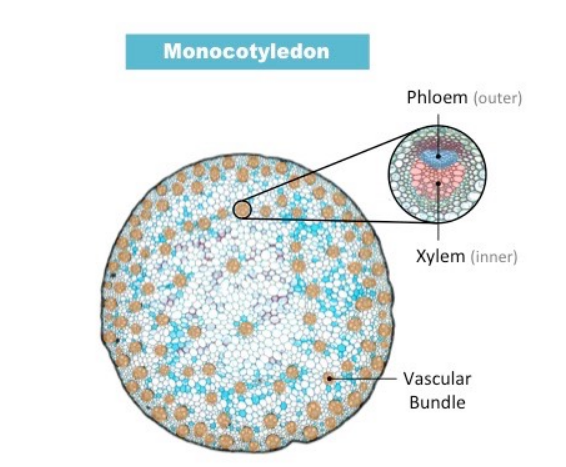
13
New cards
Xylem vs. Phloem in stem of dicotyledon
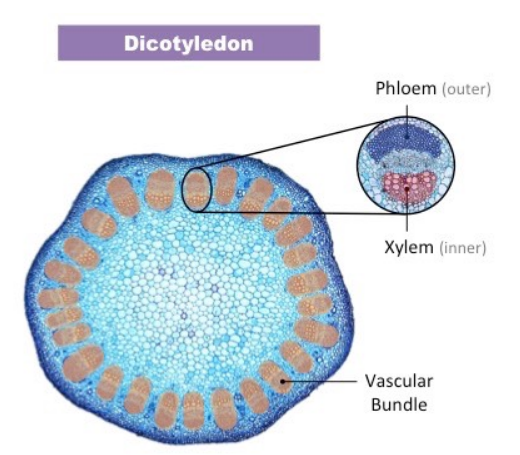
14
New cards
Plasmodesmata
small channels that directly connect the cytoplasm of neighboring plant cells to each other, establishing living bridges between cells
15
New cards
How are organic compounds loaded onto phloem?
By companion cells
* Materials can pass into the sieve tube via interconnecting plasmodesmata (symplastic loading)
* Alternatively, materials can be pumped across the intervening cell wall by membrane proteins (apoplastic loading)
* Materials can pass into the sieve tube via interconnecting plasmodesmata (symplastic loading)
* Alternatively, materials can be pumped across the intervening cell wall by membrane proteins (apoplastic loading)
16
New cards
Apoplastic loading
* Hydrogen ions are transported out of phloem by proton pumps (needs ATP)
* Hydrogen ions build up creating a conc. gradient
* Hydrogen ions passively diffuse back into the phloem cell via co-transport protein, which requires sucrose movement
* This results in the sucrose being loaded into the phloem
* Hydrogen ions build up creating a conc. gradient
* Hydrogen ions passively diffuse back into the phloem cell via co-transport protein, which requires sucrose movement
* This results in the sucrose being loaded into the phloem
17
New cards
Mass flow in source
* The active transport of solutes makes the sap hypertonic
* Therefore water from the xylem flows into the phloem via osmosis
* This increases the hydrostatic pressure in the phloem
* This pressure forces sap to move towards areas of lower pressure
* Hence phloem transports solutes away from source and towards sink
* Therefore water from the xylem flows into the phloem via osmosis
* This increases the hydrostatic pressure in the phloem
* This pressure forces sap to move towards areas of lower pressure
* Hence phloem transports solutes away from source and towards sink
18
New cards
Mass flow at sink
* Solutes are unloaded by companion cell into sink
* Causes sap to become hypotonic
* Consequently water moves back into xylem
* Therefore hydrostatic pressure at sink is always lower than pressure at source
* This will cause phloem sap to move from source to sink
* Causes sap to become hypotonic
* Consequently water moves back into xylem
* Therefore hydrostatic pressure at sink is always lower than pressure at source
* This will cause phloem sap to move from source to sink
19
New cards
How do Aphids drink sap from phloem?
* Have mouth piece that pierces the plant’s sieve tube to allow sap to be extracted
* Penetration of stylet is aided by digestive enzymes
* Even with a hole in stem, sap will continue to flow due to pressure
* Penetration of stylet is aided by digestive enzymes
* Even with a hole in stem, sap will continue to flow due to pressure
20
New cards
Measuring phloem transport
* a plant is grown in a lab with radioactive CO2
* The leaves will convert CO2 into radioactive sugars
* Aphids will feed from the sap
* The sap can then be analyzed for the presence of radioactive sugars
* The rate is calculated by finding the time taken for the radioisotope to be detected at different positions along the plant’s length.
* The leaves will convert CO2 into radioactive sugars
* Aphids will feed from the sap
* The sap can then be analyzed for the presence of radioactive sugars
* The rate is calculated by finding the time taken for the radioisotope to be detected at different positions along the plant’s length.
21
New cards
Factors affecting translocation rate
* Rate of photosynthesis
* Rate of respiration
* Rate of transpiration
* Diameter of sieve tubes
* Rate of respiration
* Rate of transpiration
* Diameter of sieve tubes