Zoology Exam 3
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
phylogenetic trees are factual evidence of evolutionary past
true/false
false; phylogenetic trees are consdiered hypothesis of evolutionary past. They are not 100% certain and many phylogenetic trees can be formed from one source of concrete data.
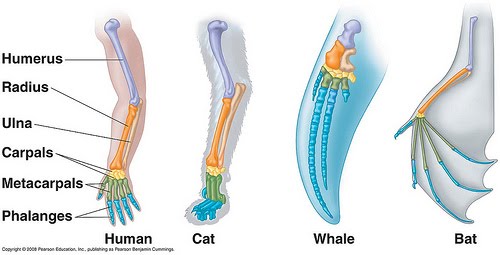
homologous characters
different versions of the same structure when comparing one species to another
can be used to make a phylogenetic tree
apart of the understanding of the morphological species concept
ex: forlimbs of bats, birds, and humuns are homologous bc they have the same basic bone structure (ulna, radius, humerus, digits)
same origin, different function
analogous characters
independently evolved characteristics
different morphology across species
different genetic basis
ex: bird wing vs bat wing are analogous as flight structures, performing the same function
not used to make a phylogenetic tree
different origin, same function

what are some possible traits that phylogenetic trees can be made out
definition of ecology:
study of interactions between different organisms, as well as organisms within their enviornment
life history (definition & qualities):
an individual’s pattern of development, growth, maturation, reproduction, and life span
life history patterns have evolved to suit varied enviornments & ecological roles
aspects: birth size, growth, age at sexual maturity, reproductive rate & effort, survival at different ages & sizes, overall lifespan
life history trade-offs:
energy and resources can go toward survivorship or reproductive mechanisms
survival and reproduction have an inverse relationship
the more energy spent invested in reproduction, the less energy spent on survival
the more offspring produced, the lower the quality of offspring
fecundity definition
an animal’s reproductive rate
the more fecund the animal, the higher their mortality
more sexually reproductive organisms die faster
ex: bunnies have high fecundity; they are very fecund
Definition of Semelparity
one big reproductive yeild for the entire lifetime
salmon, spiders, insects
Iteroparity
multiple reproductive events during life
majority of animals
Definition of Population
individuals within a speies that live in a given area, potentially able to breed
heterogenous enviornments
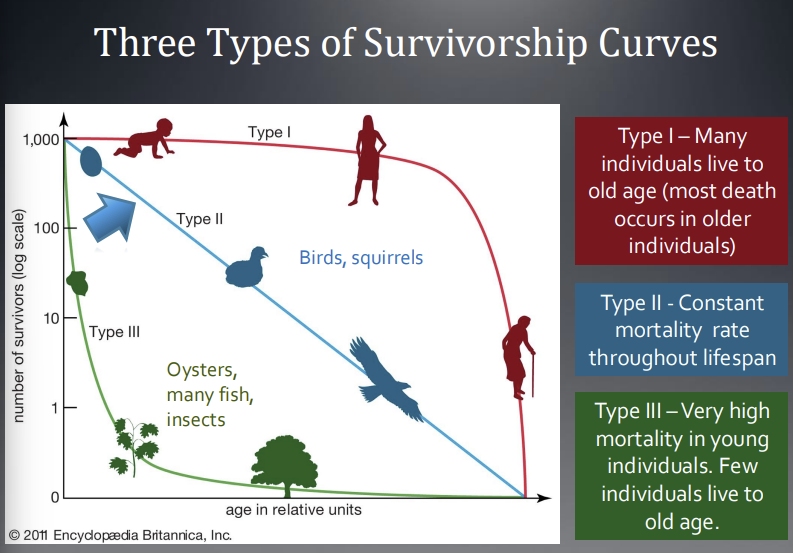
3 Types of Survivorship Curves
Type I, Type II, and Type III
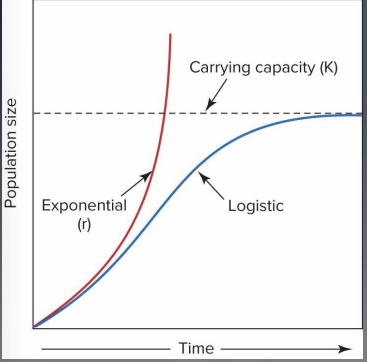
important figure: Exponential growth (R), Carrying Capacity (K), & Logistic Growth
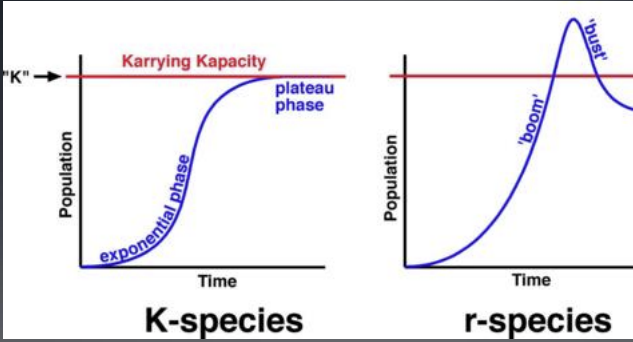
important figure: Carrying Capacity Firgues of R & K selected species
Fundemental Niche vs Realized Niche
Fundemental niche refers to the [abiotic] conditions that a species can survive in without competition
potiential habitat & resources
Relaized Niche refers to the [abiotic +biotic] conditions that a given species actually lives in including competition factors
actual habitat & resources
3D niche of a fish
salinity, pH, and temperature
niche partitioning
species occupying unique niches to minimize competition
different breeding areas, different nesting, different insect resources
competitive exclusion principle
competition is short-term.
if 2 species don’t parition & compete instead, one species will outdo the other to the point of extinction
specialist vs generalist species