2.5 The determination of equilibrium market prices
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
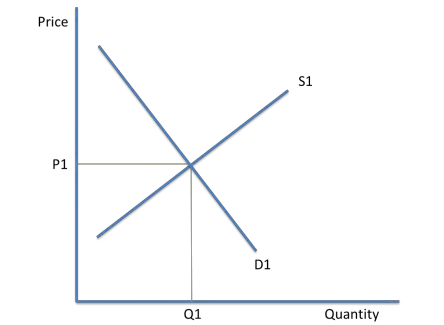
Equilibrium price and quantity
This is when supply meets demand. On the diagram, this is shown by P1 and Q1.
At market equilibrium, price has no tendency to change, and it is known as the market clearing price.
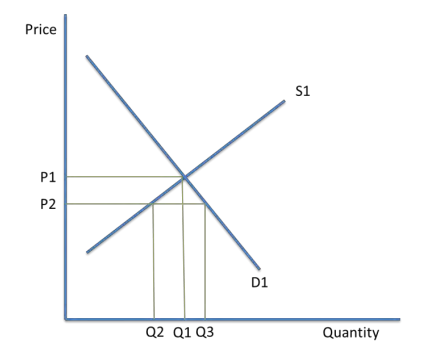
Excess Demand
At Q2, price is at P2 which is below market equilibrium. Demand is now greater than supply, which can be calculated by Q3-Q2. This is of disequilibrium. The demand price does not equal the supply price, and the quantity demanded does not equal the quantity supplied.
This is a shortage in the market. This pushes prices up and causes firms to supply more. Since prices increase, demand will contract.
Once supply meets demand again, price will reach the market cleaning price, P1
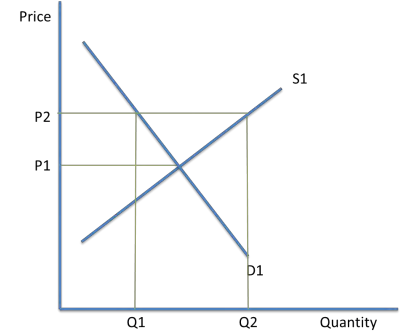
Excess Supply
This is when price is above P1
Supply is now at Q2 and demand is at Q1. There is a surplus of Q2-Q1. Price will fall back to P1 as firms lower their prices and try to sell their goods. The market will clear and return to equilibrium.
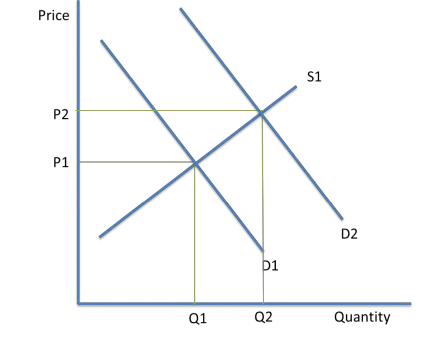
New Market Equilibrium
When the demand or supply curve shift due to the PIRATES or PINTSWC reasons, new market equilibriums are established.
For example, if there was an increase in the size of the population, demand would shift from D1 to D2.
Price would increase to P2 and suppliers would supply a larger quantity of Q2. A new market equilibrium is established at P2 Q2.