Unit 3 part 1
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
bony thorax, respiratory system, mediastinum
What are the 3 divisions of chest anatomy?
Bony thorax
what is the division of chest anatomy that is the protective framework?
Respiratory system
what is the division of chest anatomy that contains the lungs and airways?
Mediastinum
what is the division of chest anatomy that is the space between the lungs?
Bony thorax
-Sternum (breastbone)
-Clavicles (collarbones)
-Scapulae (shoulder blades)
-12 pairs of ribs
-12 thoracic vertebrae
manubrium
upper portion of the sternum
body
middle portion of the sternum
Xiphoid process
lower, narrow portion of the sternum
True
True or False: The Bony Thorax provides protection for the thoracic viscera
Respiratory System
Division of Chest anatomy who's purpose is to move air into & out of lungs(breathing)
Oxygen (O2) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
The respiratory system exchanges gaseous substances between air and blood; what are the two gases?
pharynx/larynx and trachea
the two most superior divisions of the respiratory system
Bronchi and lungs
the two most inferior divisions of the respiratory system
Diaphragm
primary muscle of inspiration
Pharynx (upper airway)
Passageway for air located posterior to the nose, nasal cavities, & mouth - just anterior to the cervical spine
3
how many divisions in the Pharynx
Pharynx
What extends downward to the larynx before connecting to the trachea & esophagus
Nasopharynx
uppermost portion of the pharynx; located behind nasal cavities
False
True or False: The nasopharynx is a passageway for food and water
Swallowing
soft palate elevates to block food or saliva from going up into the nasopharynx
uvula
part of soft palate hanging down in the back of your throat; boundary between nasopharynx & oropharnyx
adenoid tonsils
Masses of lymphatic tissue forming a protective ring around the nose and upper throat(in the nasopharynx)
Eustachian tubes
narrow tubes that lead from the middle ear to the nasopharynx
oropharynx
Mid potion of the pharynx
-located directly behind the mouth
False
True or False: The oropharynx is a passageway for both air & food/liquid (at the same time)
palatine tonsils
what lymphatic tissues are in the oropharynx
laryngopharynx
Lower portion of the pharynx
-located above & superior to larynx
-passageway for both air & food/liquid(not at the same time)
True
The laryngopharynx opens anteriorly to larynx/trachea - breathing
Larynx (Voice Box)
Cartilaginous structure located on anterior neck suspended from hyoid bone - upper margin @C3 & lower margin @ C6
Adam's Apple
thyroid cartilage
cricoid cartilage
A firm ridge of cartilage that forms the lower part of the larynx.
-inferior to the thyroid cartilage
Vocal cords
2 strong bands of tissue stretched between thyroid & cricoid cartilages
glottis
The opening between the cords is called the _______
Epiglottis
uppermost cartilage that flips down & covers the laryngeal opening & trachea to prevent aspiration of food/liquid
Larynx
What part of the respiratory system is shown?
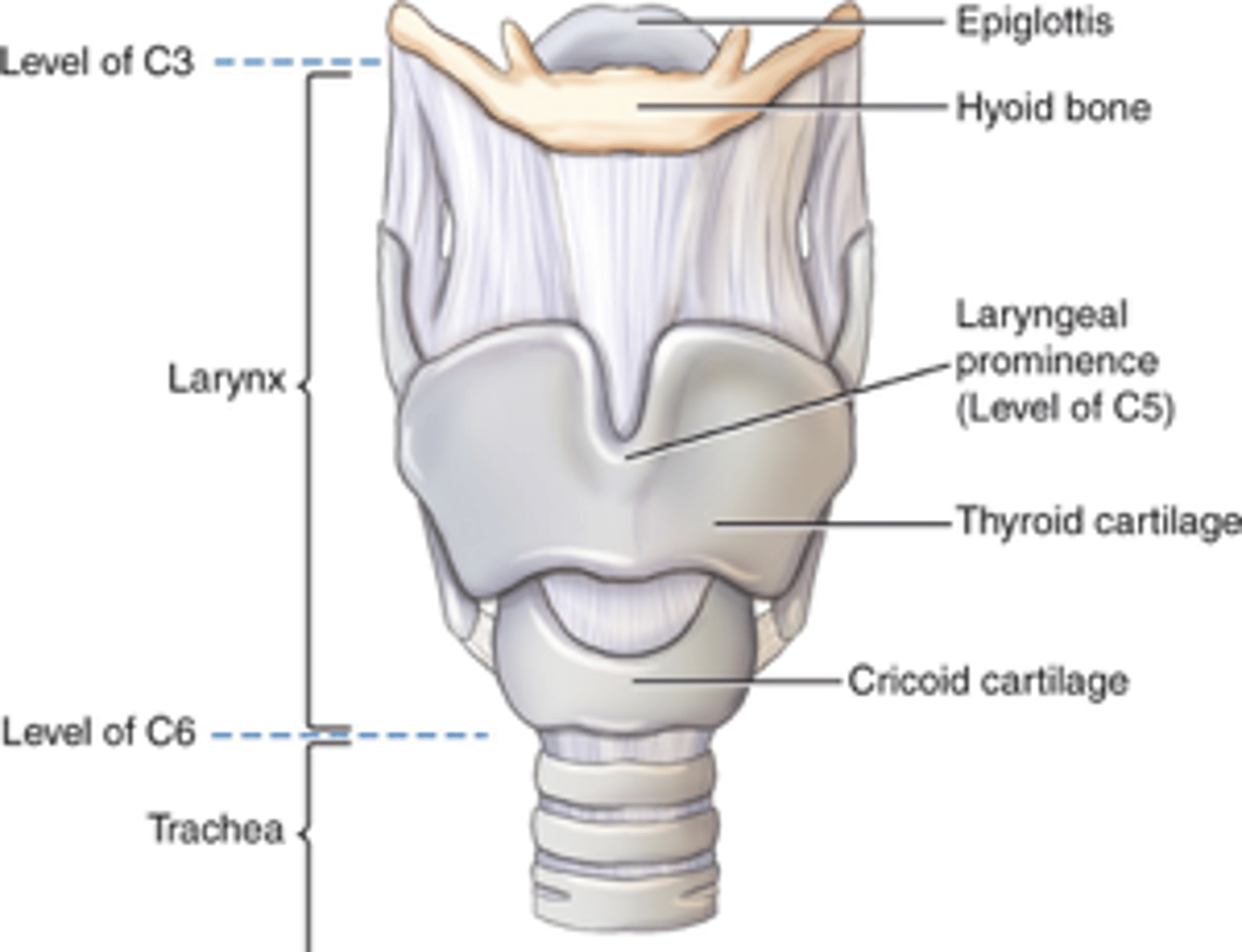
Trachea
Extends down from larynx to primary bronchi just anterior to the esophagus
Trachea (windpipe)
Fibrous muscular tube held open by approximately 20 C-shaped pieces of cartilage
Thyroid, parathyroids, and thymus
What are the 3 endocrine glands lining the Trachea?
thyroid
produces and secretes hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and appetite
parathyroid glands
store & secretes hormones; helps to maintain blood calcium levels
thymus
helps body produce antibodies & aids in immunity
AP Upper Airway X-ray
What X-ray is shown
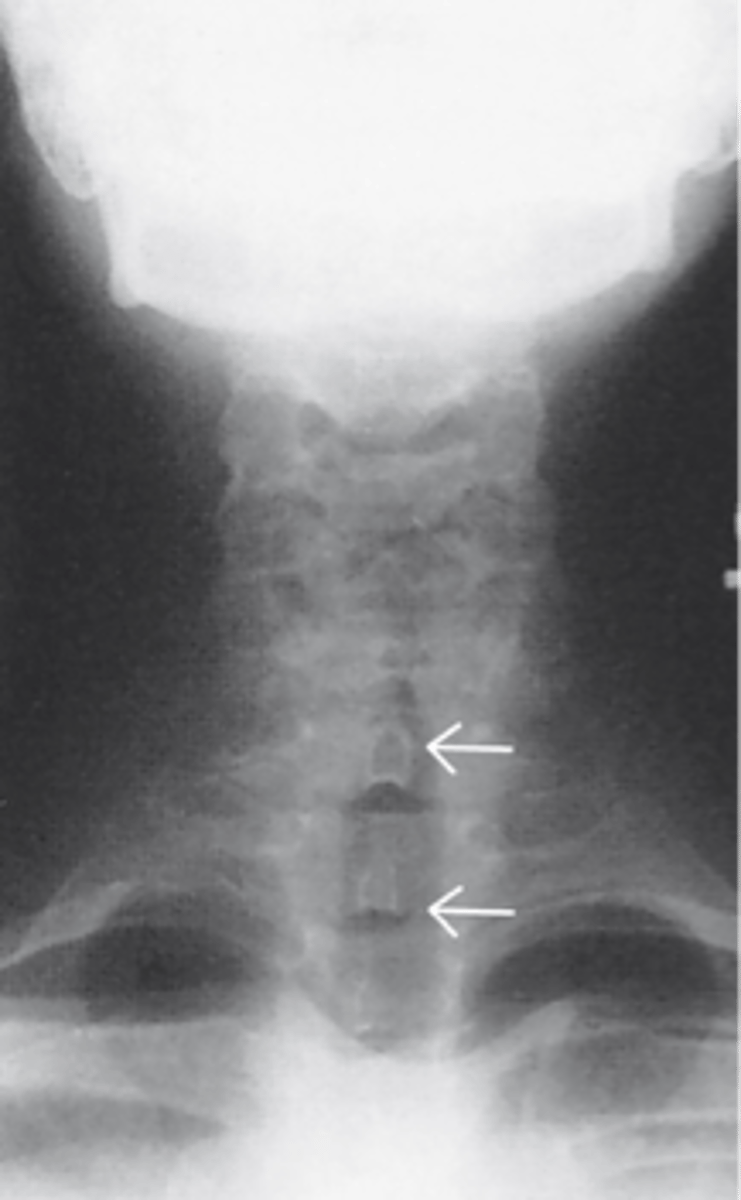
Lateral Airway X-ray
What X-ray is shown? (more common than AP in upper airway x-ray imaging)
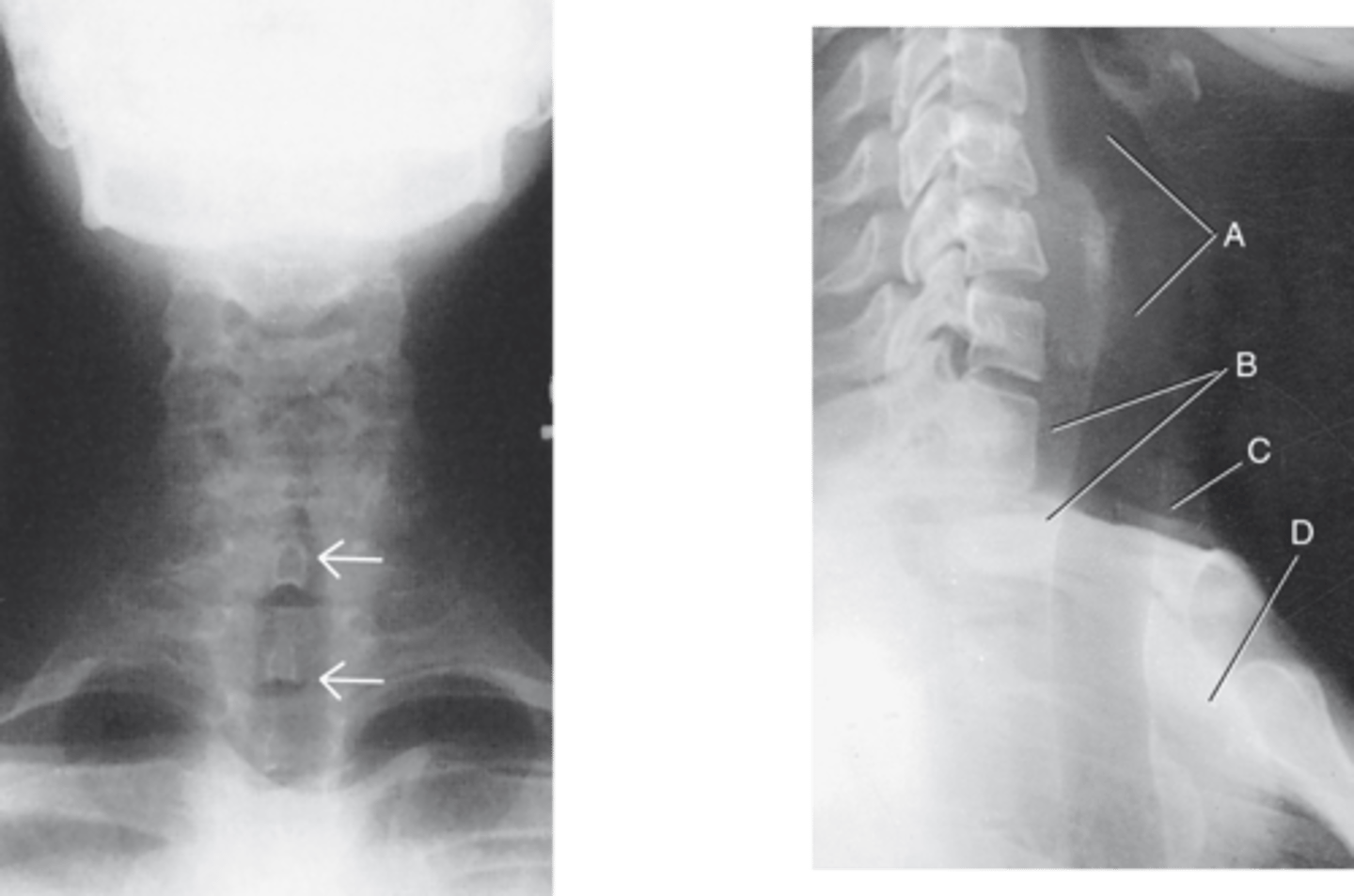
Bronchi (Bronchial Tree)
-2 Primary (“main stem”) bronchi (R & L)
-5 secondary bronchi
Carina
ridge of lowest tracheal cartilage where the trachea divides into R & L primary bronchi
3
how many secondary bronchi are there for the right lung?
2
How many secondary bronchi for the Left lung?
True
True or False: Both primary and secondary bronchi have cartilage similar to the trachea to keep them open
Bronchioles
Secondary bronchi subdivide into smaller ___________ that spread through each lobe of the lungs
Alveoli
Bronchioles terminate in very small air sacs called _______
Alveoli
What are surrounded by a capillary network of blood vessels - oxygen & carbon dioxide exchanged through diffusion between air sacs & capillaries
False
True or False: Bronchioles have cartilage like primary & secondary bronchi
Lungs
Located on either side of the heart in the thoracic cavity and protected all around by the rib cage
Parenchyma
spongy, elastic tissue
-lungs are composed of this tissue
pleura
Each lung is contained in a double-walled membrane sac called the ______.
Right lung
Which lung is 1'' shorter due to liver and composed of 3 lobes (superior, middle, inferior)
fissures
Lobes are separated by _________
True
True or False: Superior lobes larger than the other lobes; left superior lobe is the largest
Parietal Pleura
Outer layer of pleural sac that lines the inner chest wall & diaphragm
Visceral (pulmonary) pleura
Inner layer of pleural sac that lines the lung surface & into the fissures
Pleural cavity (space)
between parietal & visceral pleura; contains lubricating fluid that allows for movement during breathing
Trachea (windpipe)
Label: A
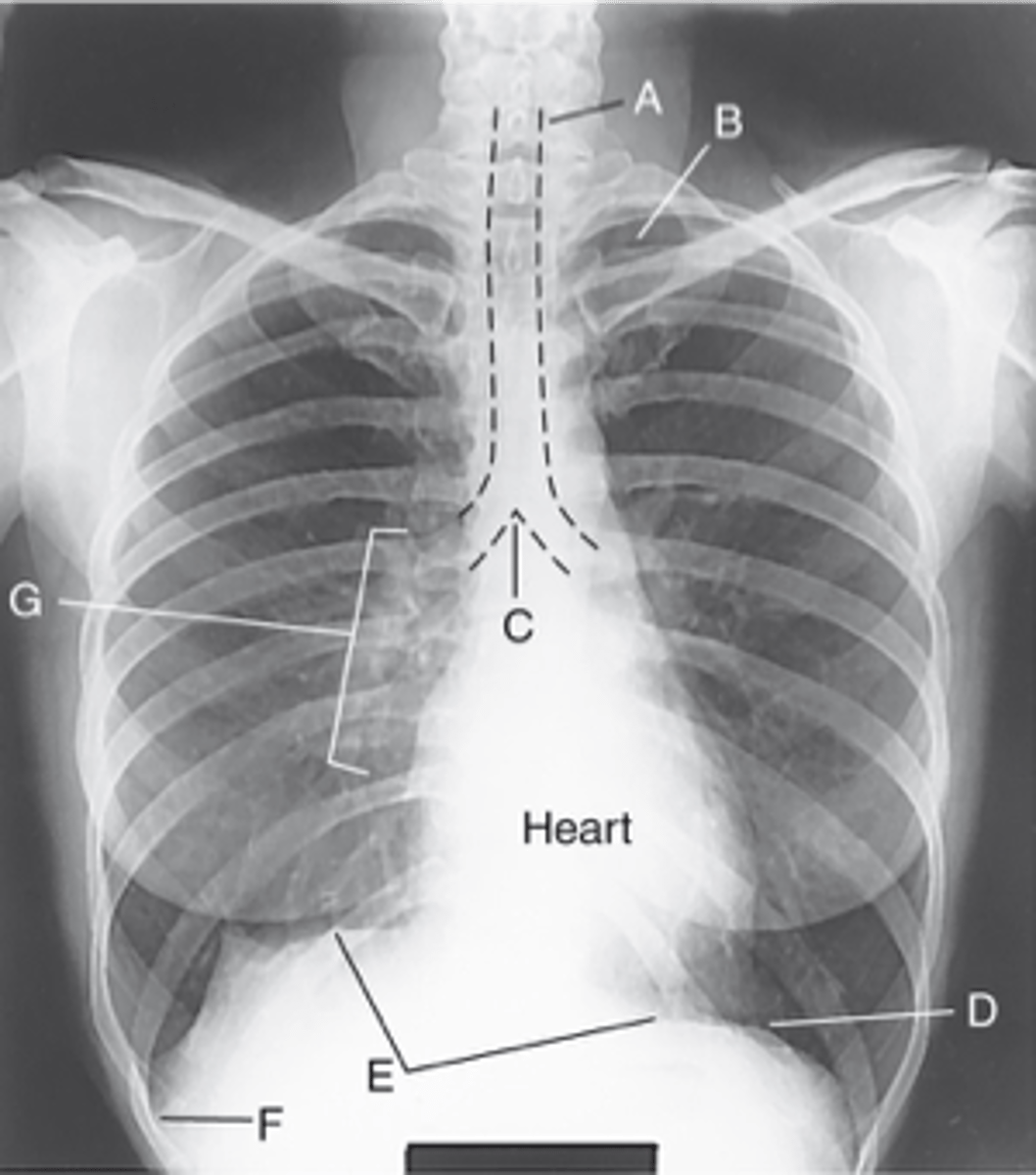
Apices
Label: B
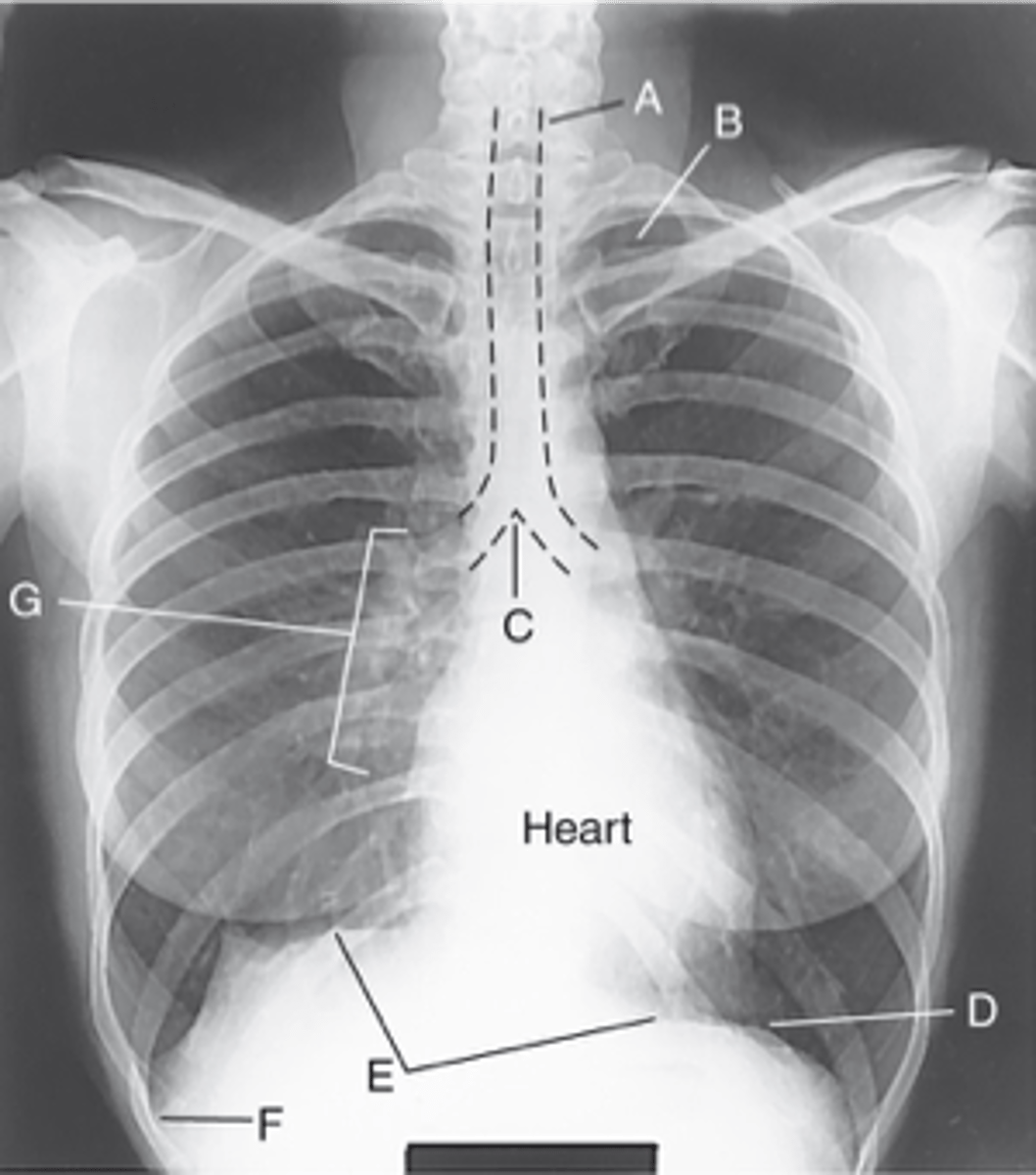
Carina
Label: C
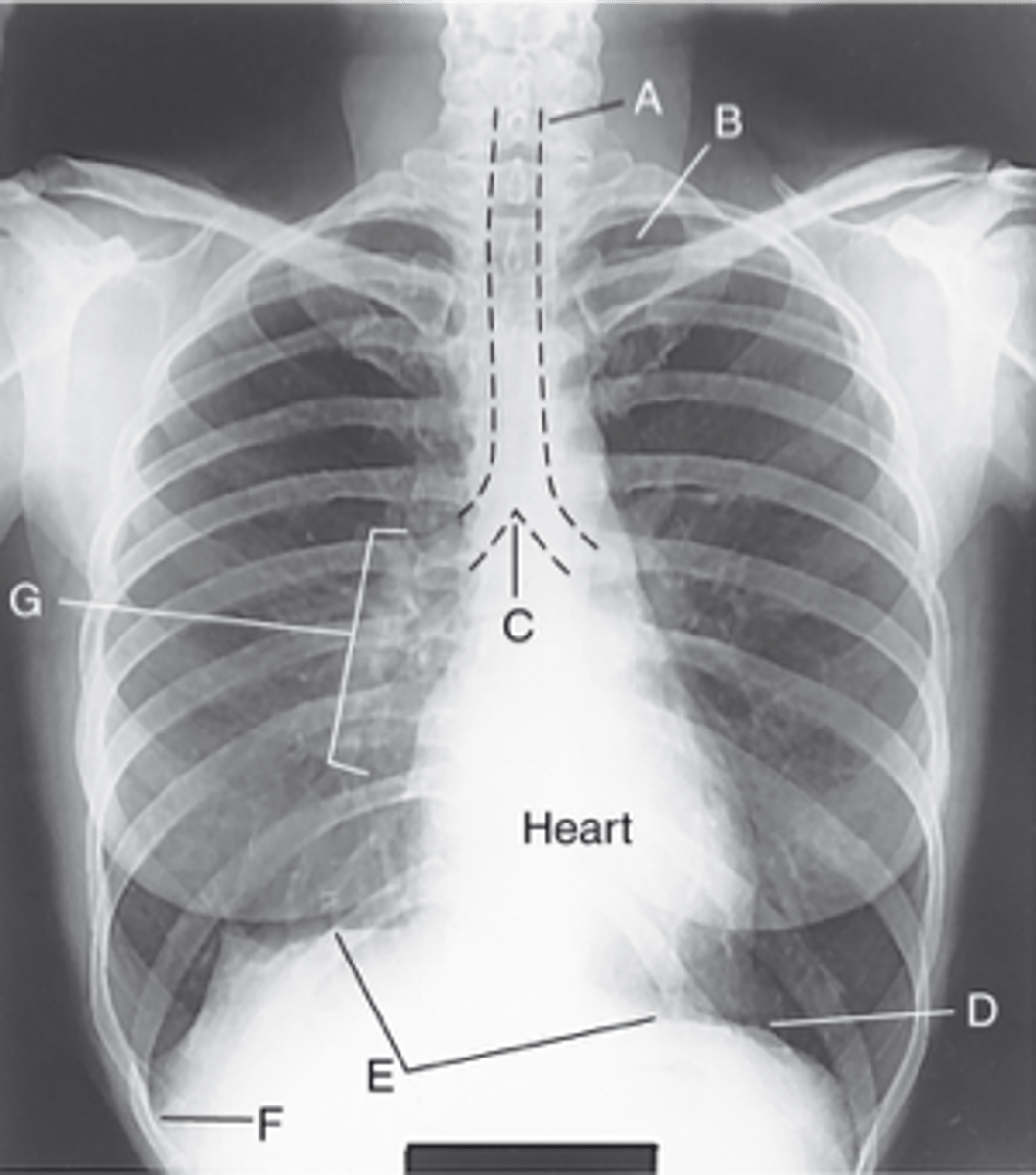
Bases
Label: D
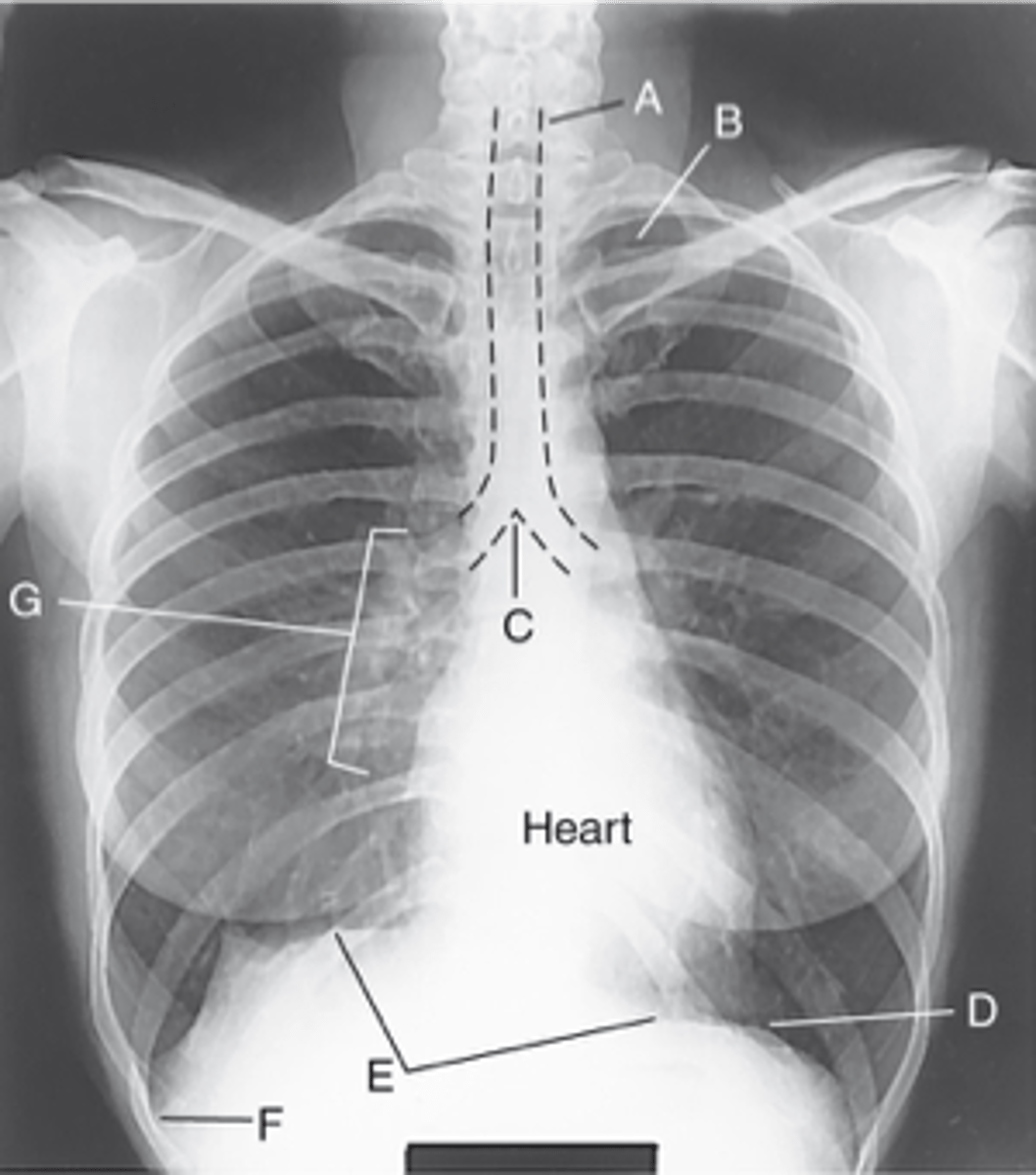
R & L hemidiaphragm
Label: E
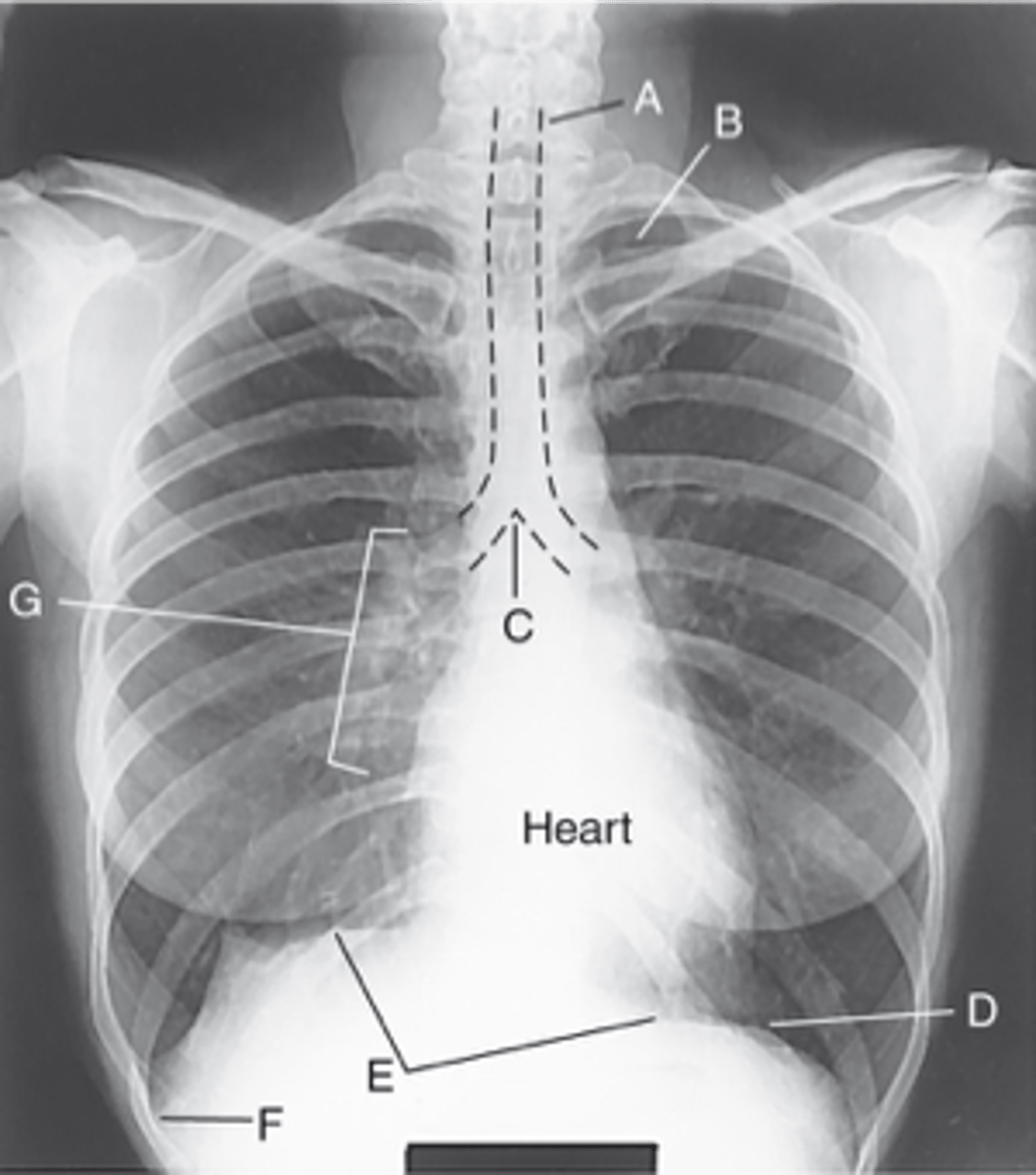
Costophrenic Angle
Label: F
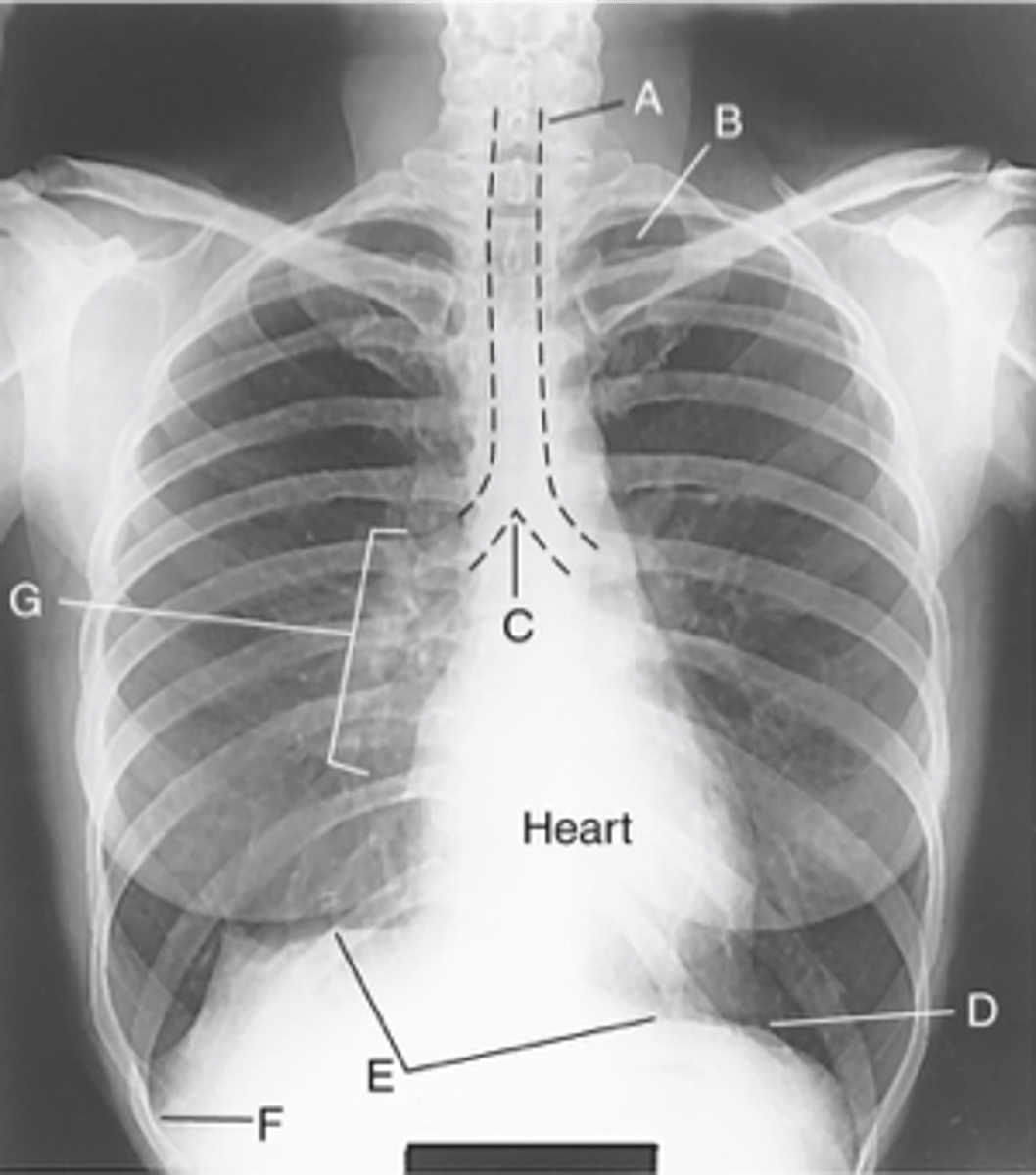
Hilum
Label: G
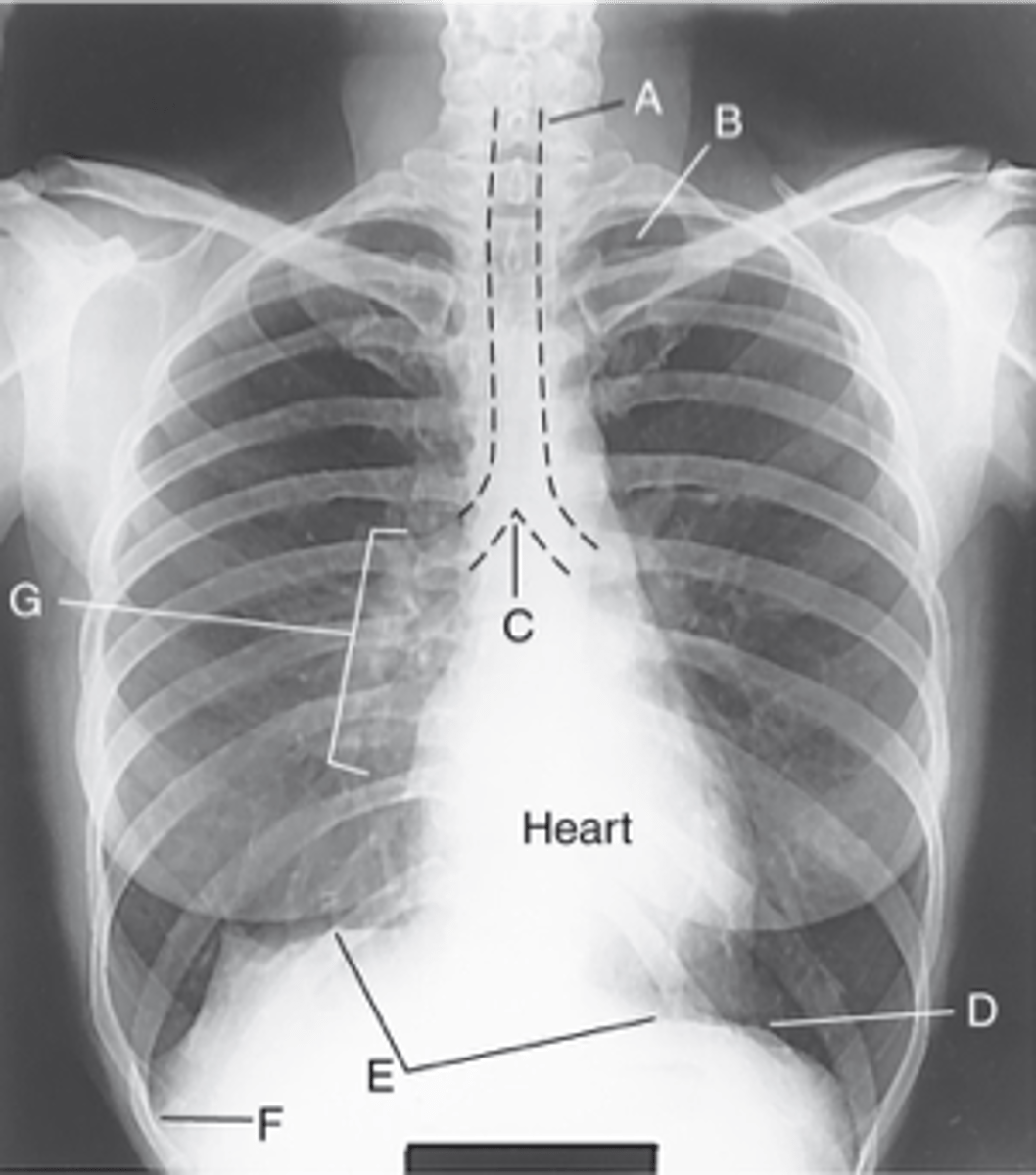
Apices
rounded upper area of lung above clavicles
Bases
lower concave area of lung resting on diaphragm
Costophrenic Angle
lower corner of each lung where diaphragm meets ribs
Hilum
central lung area where bronchi, blood & lymph vessels, & nerves enter/leave each lung
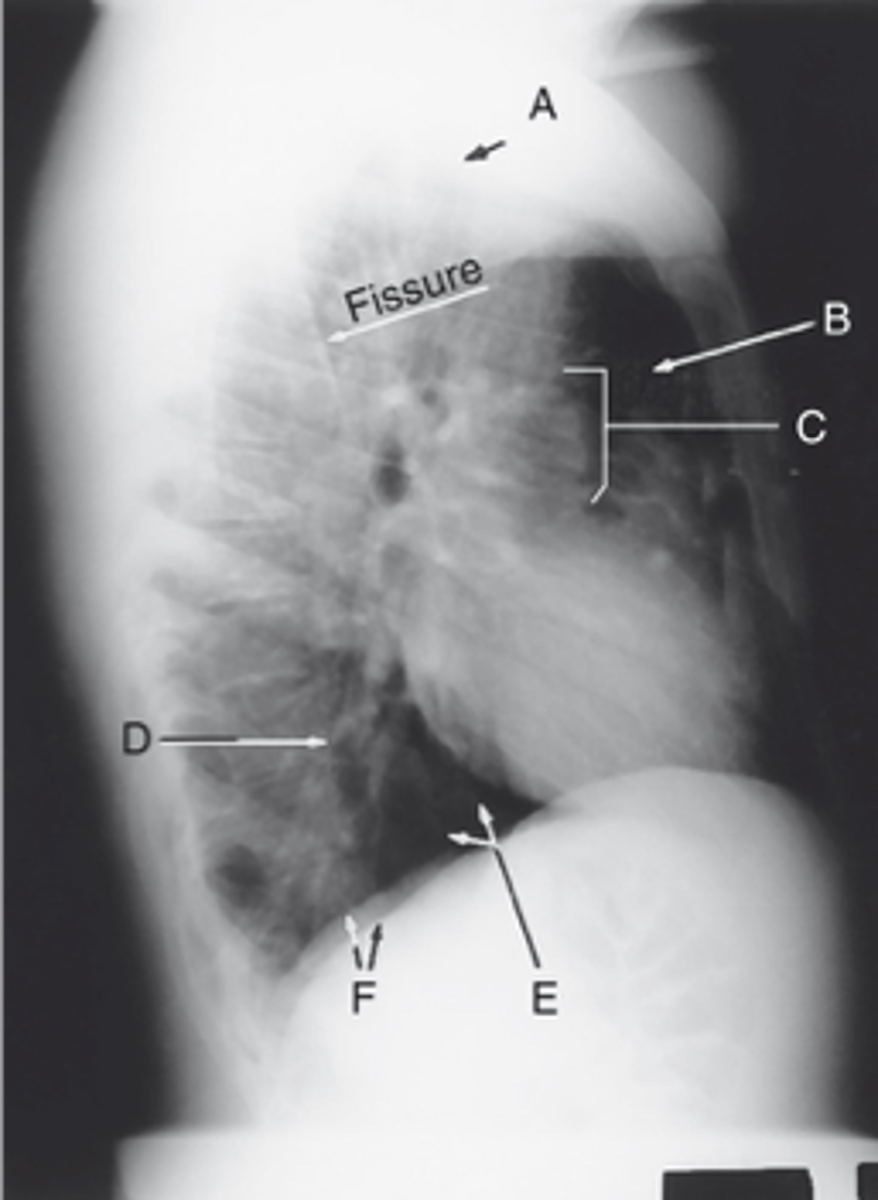
Apex
Label: A
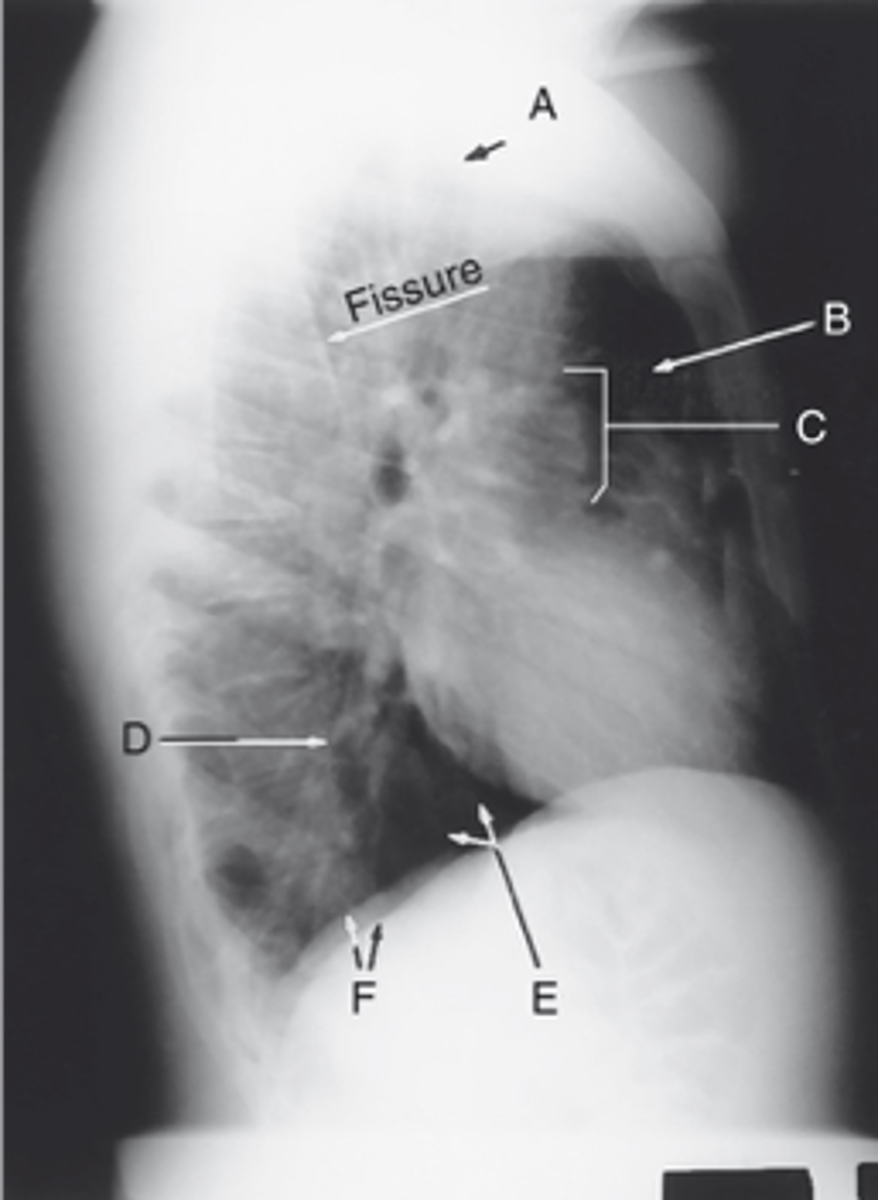
Upper lobe of lung
Label: B
_____ ____ __ ____
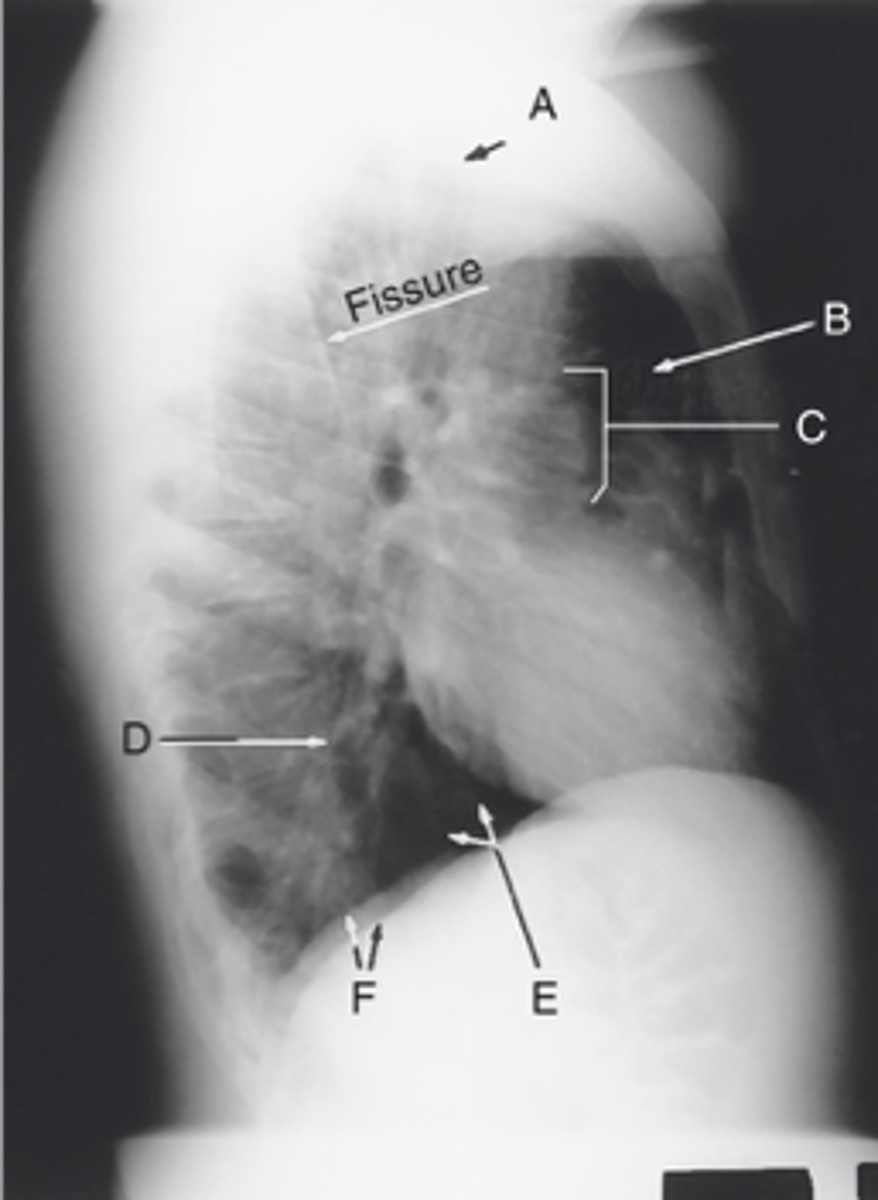
Hilum
Label: C
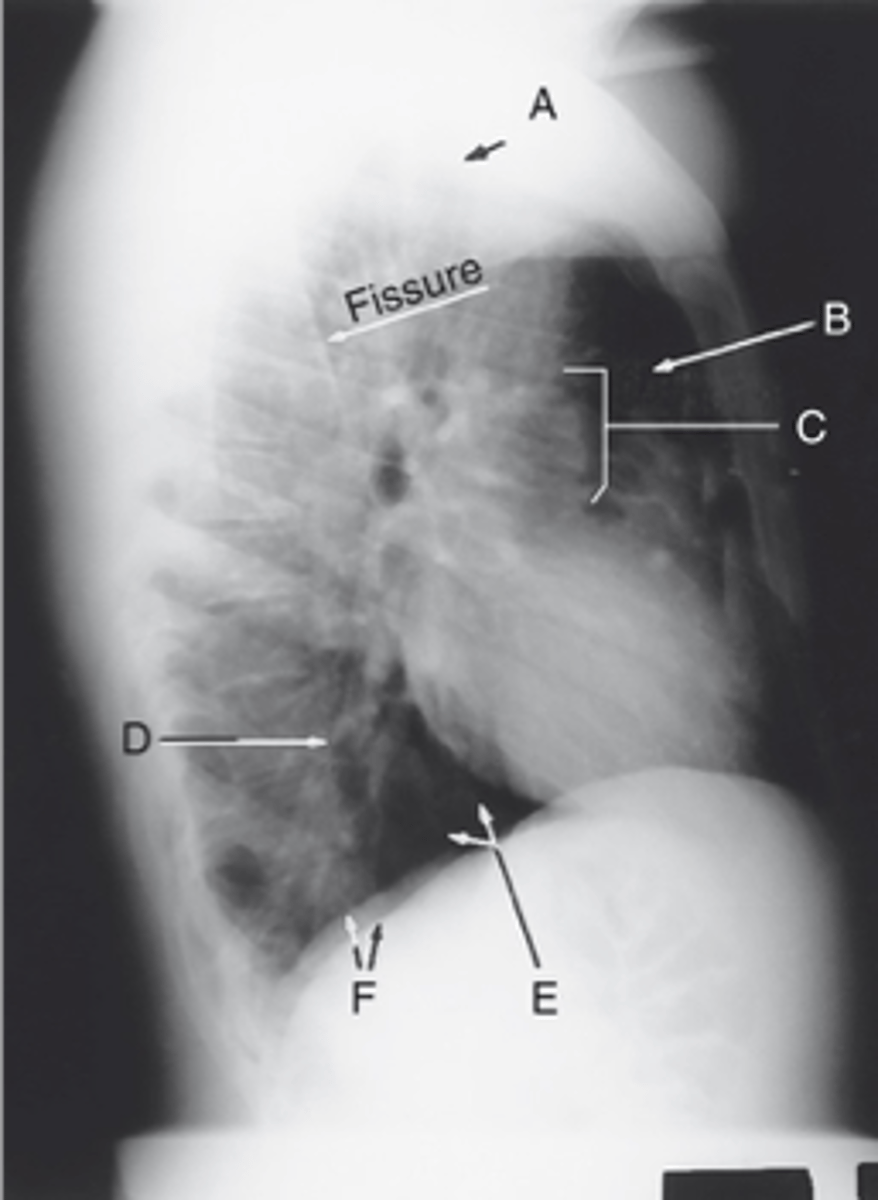
Lower lobe of lung
Label: D
_____ ____ __ ____
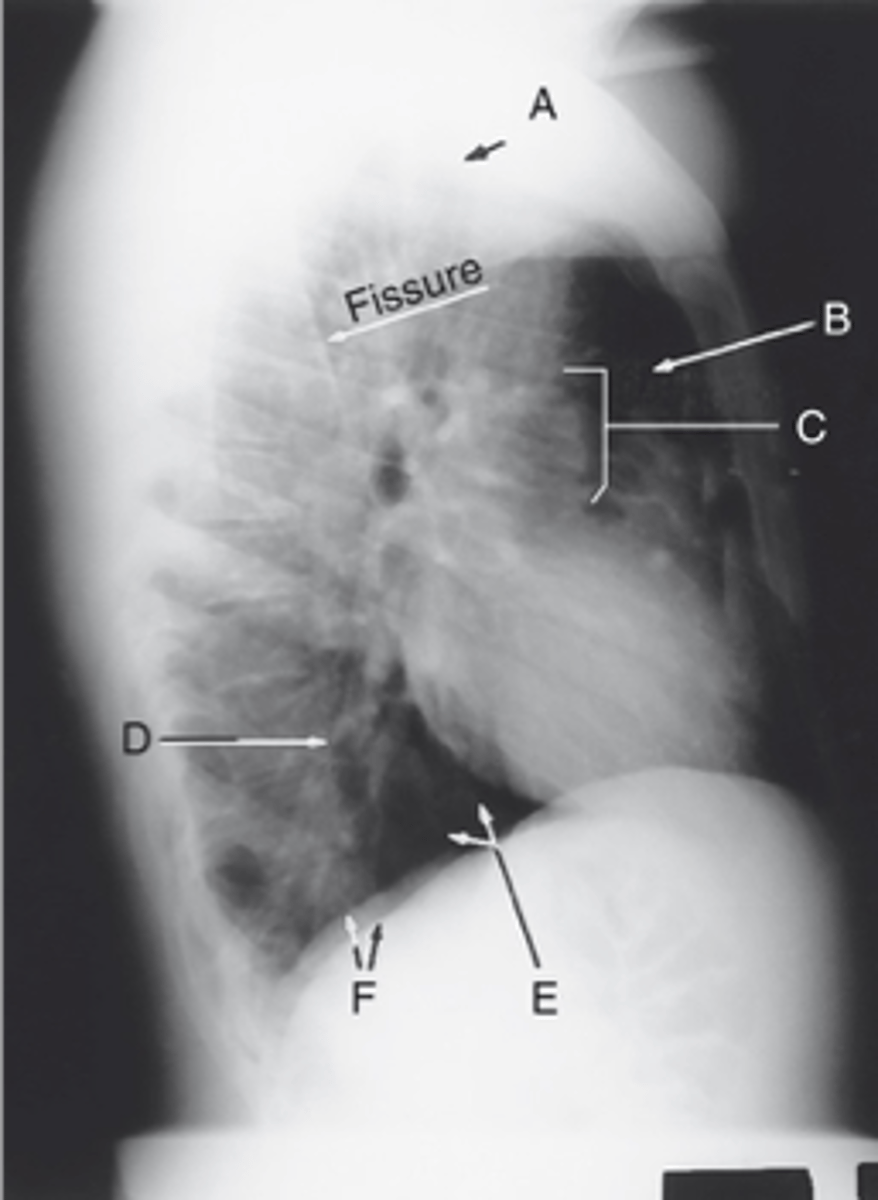
Base of the lung
Label: E
____ __ ___ ____
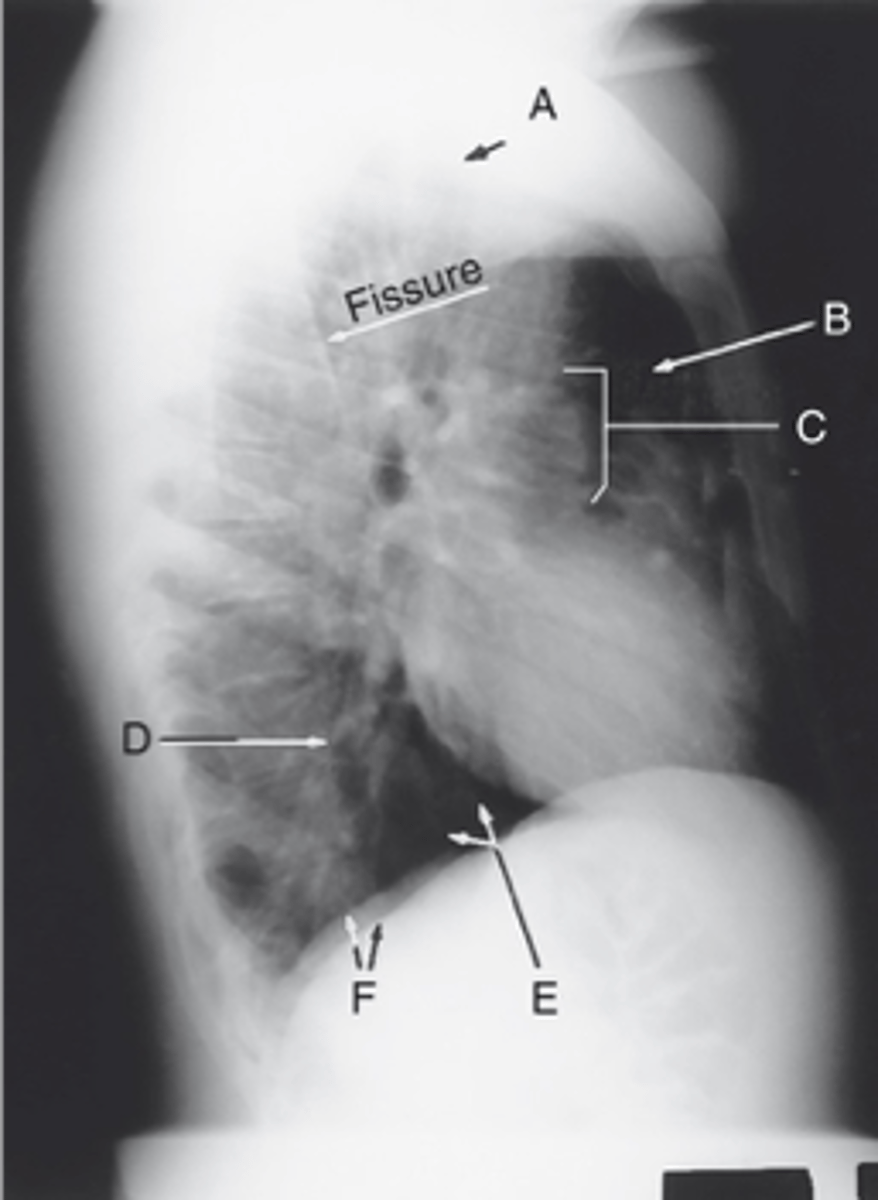
R & L hemidiaphragm
Label: F
_ & _ _____________
Mediastinum
Medial portion of thoracic cavity between lungs; has four structures
True
True or False: The trachea and Esophagus are two of the four structures in the mediastinum
Thymus gland
This gland is one of the four structures in the mediastinum
-large in infancy up to puberty
heart and great vessels
The trachea, esophagus, thymus gland, and lastly the _____ ___ _____ _______ are the four structures of the mediastinum
ascending, arch, descending
the aorta is is divided into three, what are they?
Superior Vena Cava (SVC)
receives blood from the head and arms and chest and empties into the right atrium of the heart
Inferior Vena Cava (IVC)
largest vein in the human body, returns blood from portions of the body below the heart
pulmonary arteries
the vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs
pulmonary veins
carry the oxygenated blood from the lungs into the left atrium of the heart
Pneumothorax
air or gas pressure in the pleural cavity resulting in a collapsed lung
Pleural Effusion
accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural cavity
hemothorax
blood in the pleural cavity
pleurisy
an inflammation of the pleura that produces sharp chest pain with each breath
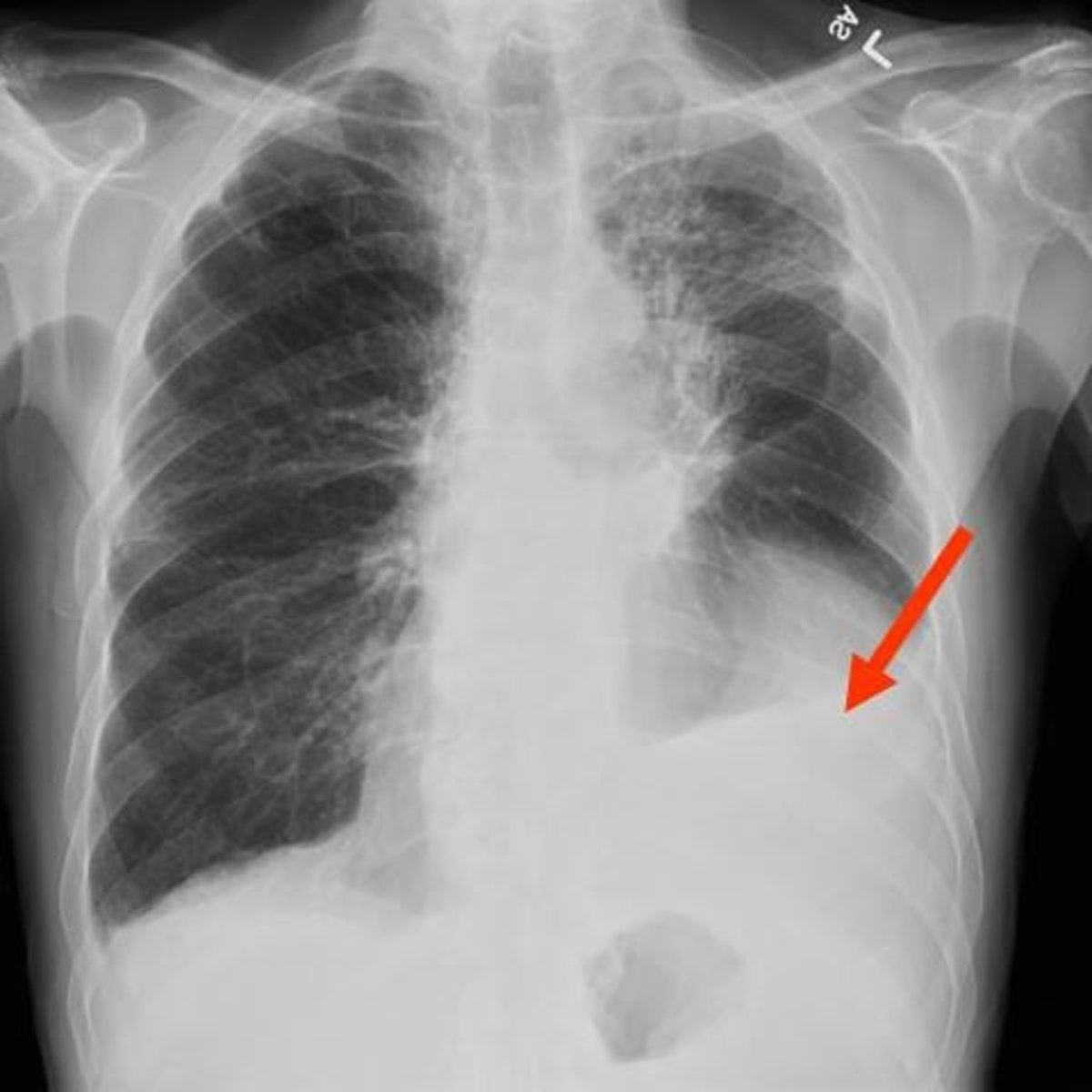
pleural effusion
Which common lung pathology is shown?
landscape(crosswise)
the IR is placed _________ on a hypersthenic body habitus
False
PA Chest is only done portrait (lengthwise) on a sthenic body habitus
Portrait (lengthwise)
PA Chest is done __________ on both hyposthenic and asthenic body habitus - long lungs
4
How many divisions in the respiratory system? (Know each of them)