💊Estrogen and Progesterone
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
estrogen
What hormone is produced by the ovaries and placenta with receptors in the vagina, uterus, ovaries, mammary glands, vascular epithelium, hypothalamus, prostate, and bones?
Clinical Uses:
• Menopausal Hormone Therapy (HT)*
• Contraception*
• Gender Affirming Hormone Therapy (GAHT)*
• Osteoporosis
• Primary hypogonadism
• Dysmenorrhea/Amenorrhea
• Hirsutism
• Acne
*in combination with progesterone
progesterone
What hormone is produced by the ovaries and placenta with receptors in the uterus, ovaries, mammary glands, brain, cardiac, and bones?
Clinical Uses:
• Menopausal hormone therapy (HT)*
• Contraception*
• Gender affirming hormone therapy (GAHT)*
• Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
• Infertility
• Prematurity prevention
• Endometrial carcinoma and hyperplasia
*in combination with estrogen
estrogen
Hormone effects:
-maintains body temperature
-delay memory loss
-prepare glands for future milk production
-stimulate maturation of ovaries and uterus, maintain a thick vaginal lining
-preserve bone density
-regulate liver’s production of cholesterol (reducing LDLs)
progesterone
Hormone effects:
-immune system (increase anti-inflammatory agents)
-lower blood pressure
-reduce breast tenderness and cyst formation
-inhibit uterine contractions during pregnancy
-protect the cervix from infection
Estrogen Contraindications
• History of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE)
• History of stroke or myocardial infarction (MI)
• Pregnancy
• Vaginal bleeding without cause
• History of liver disease
• History of estrogen dependent tumors or breast cancer (except when indicated)
Estrogen Drug Interactions
Major substrate of CYP3A4 and CYP1A2; inducers or inhibitors of these CYP enzymes lead to altered levels
-includes many antibiotics/antiseizure medications
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs)
Drugs: Tamoxifen, Toremifene, Raloxifene, Bazedoxifene
MOA: estrogen receptors in some tissues and antagonists
Tamoxifen/Toremifene
Which SERMs inhibit cell growth in the breast (breast cancer therapy), protect against osteoporosis and lower lipids
ADR: hot flashes, increased risk of endometrial cancer, blood clots
Raloxifene
Which SERM inhibits cell growth in the breast (breast cancer therapy), protects against osteoporosis and lower lipids
ADR: hot flashes, blood clots
*No risk for endometrial cancer
Bazedoxifene
Which SERM is used in combination with conjugated estrogens in menopausal hormone therapy to reduce the effects of estrogen, prevent vasomotor symptoms (hot flashes) and osteoporosis?
Progestin
Which hormone (in combination with estrogen) has adverse effects of breast tenderness, abdominal discomfort, depression, and increased risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women?
Menopausal Hormone Therapy (HT)
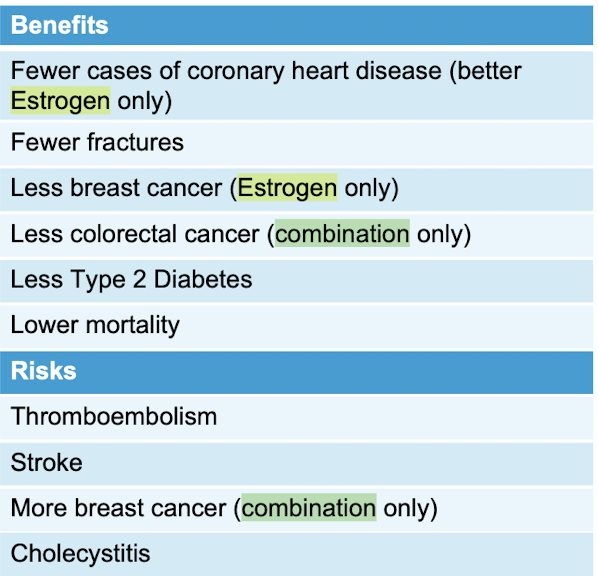
Risks vs. Benefits of ___________
Menopausal Hormone Therapy (HT)
Benefit to risk profile of ________ was best for patients:
50-59yo for short duration of therapy (<10 years)
-assess each patient individually; drugs can be immediately stopped or tapered
Progestin
Which hormone is used in Menopausal Hormone Therapy (HT) to counterbalance effects of estrogen and protect against uterine cancer?
*NOT used in women who have undergone hysterectomy
endometrial hyperplasia
What condition involves overgrowth of the tissue lining the uterus (endometrium)?
endometriosis
What condition involves tissue from the endometrium that extends and implants outside the uterus such as ovaries and outer wall of the uterus?
-tissue responds to estrogen and can cause abdominal and back pain, abnormal bleeding leading to infertility and spontaneous abortion
Tx: surgery or drug therapy
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone agonists (GnRH) MOA
Drugs: Leuprolide (Leupron) IM, Nafareline (Synarel) intranasal
act on pituitary gland to increase LH and FSH (estrogen and progesterone) causing negative feedback loop that lowers levels of estrogen/progesterone, mimics menopause shrinking endometrial tissue and used in prostate cancer (decreased testosterone)
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone agonists (GnRH) ADR
Drugs: Leuprolide (Leupron) IM, Nafareline (Synarel) intranasal
ADR: menopause like symptoms: hot flashes (relieved with B6 and vitamin E supplements), vaginal dryness, headache, bone loss (limit therapy to <6 months, test bone density)
Combined Oral Contraceptives (COCs) MOA
estrogen + progestin; inhibit ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, alter endometrium
Dosing: 28 day cycles (monophasic, biphasic, triphasic, quadriphasic regimens), extended and continuous cycles possible with monophasic only (to skip periods)
Benefits: improve menstrual symptoms, reduce migraines frequency, decrease risk of certain cancers, reduces iron deficiency anemia, acne reduction
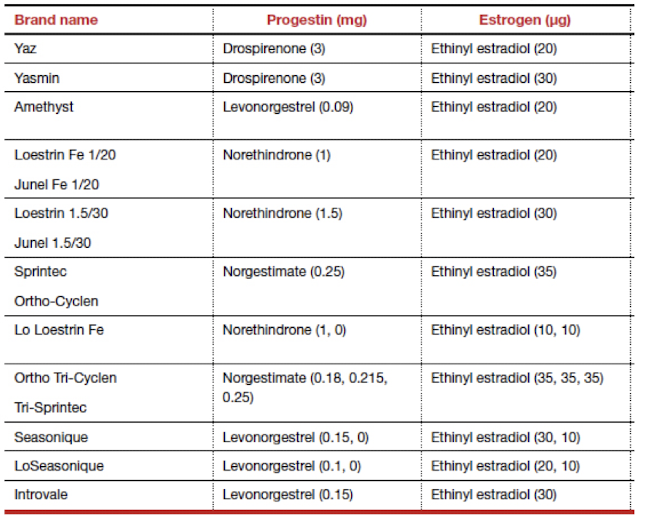
Progestin
Which oral contraceptive is less effective and only works at thickening of the cervical mucus and alteration of endometrium (does not inhibit ovulation)?
*minipill
Combined Oral Contraceptives (COCs) Contraindications
Absolute:
Thromboembolic risk (history/risk factor)
abnormal liver function
known or suspected breast cancer
undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding
known or suspected pregnancy
smokers >35yo
Relative: Hypertension; Cardiac disease; Diabetes; History of cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy, Gallbladder disease; Epilepsy; Migraine
CYP3A4 inducers
What drug class ↓ reduces the effects of oral contraceptives?
ie. HIV medications, antiseizure medications, St. John’s wort
decrease
Oral contraceptives ______ effects of Warfarin, Insulin and hypoglycemic agents
*increase dose of these medications
increase
Oral contraceptives ______ effects of
Theophylline
Tricyclic Antidepressants (ie. Amitriptyline, Doxepin)
Diazepam
*Lower dose of these medications
24 to <48 hours
If one hormonal pill has been missed _______, take the late/missed pill as soon as possible, continue taking the remaining pills at the same time (OK to take two pills on the same day), no additional contraceptive protection is needed
>48 hours
-take the most recent pill as soon as possible and discard any other missed pills
-use back-up contraception (condoms)/avoid sexual intercourse until hormonal pills have been taken for 7 consecutive days
-consider emergency contraception if hormonal pills were missed during the first week and unprotected intercourse occurred in previous 5 days
Oral Contraceptives: two or more consecutive hormonal pills have been missed in ______
Implant (Nexplanon)
Pros: >99% effective, long lasting (5 years), cramps often improve, often no bleeding after 1 year, can become pregnant right after removal, lower risk of endometrial/ovarian cancer and PCOS
Cons: irregular bleeding/spotting, must be removed by a clinician, may cause mood changes
Copper IUD (Paraguard)
Pros: >99% effective, long lasting (12 years), can become pregnant right after removal, lower risk of endometrial/ovarian cancer and PCOS
Cons: may cause cramps and heavy monthly bleeding, spotting between monthly periods, rare injury to uterus during placement, must be removed by clinician
Levonorgesterel (IUD)
Pros: >99% effective, long lasting (3-8 years), may improve cramps, can make monthly bleeding more regular, can become pregnant right after removal, lower risk of endometrial/ovarian cancer and PCOS
Cons: may cause spotting first few months, rare injury to uterus during placement, must be removed by clinician
Patch (Ortho Evra)
Pros: 93% effective, can make monthly bleeding more regular and less painful, can become pregnancy right after stopping
Cons: can cause site irritation, estrogen may interact with testosterone, may cause spotting first few months
Use: 3 weeks on, one week off
Ring (Annovera, NuvaRing)
Pros: 93% effective, monthly/yearly options, can make monthly bleeding more regular and less painful, private, one size fits all, can become pregnant right after removal
Cons: may cause spotting the first few months, can increase vaginal discharge, estrogen may interact with testosterone
Shot (Depo-Provera)
Pros: 96% effective, works for up to 15 weeks each time, decreases monthly bleeding, private for user, helps prevent uterine, endometrial, ovarian cancer and PCOS
Cons: may cause spotting between periods, weight gain, depression, hair or skin changes, changes in libido, side effects may last up to 6 months after stopping; caution about bone density changes/increased fracture risks with long-term use (>2 years)
Use: injection every 3 months (13 weeks)
Gender Affirming Hormone Therapy (GAHT)
Drugs: Estradiol (estrogen) + Spironolactone, Finasteride or Dutasteride (androgen blocker) ± Medroxyprogesterone acetate (Progestin)
MOA: Development of female secondary sex characteristics, suppression/minimization of male secondary characteristics
ADR: increased risk of VTE, DVT, PE, gallstones, elevated liver enzymes, weight gain, high triglycerides, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, high prolactin/prolactinoma, type 2 diabetes, breast cancer, changes in emotional and social functioning
Gender Affirming Hormone Therapy (GAHT)
Expected effects:
• Breast development (3-6 months, 2-3 years max)
• Redistribution of facial and body fat (3-6 months, 2-5 years max)
• Reduction of muscle mass (3-6 months, 1-2 years max)
• Reduction of body and facial hair (1-3 months, 1-2 years max)
• Change in sweat and odor patterns
• Arrest and possible reversal of scalp hair loss (1-3 months, 1-2 years max)
• Reduction in erectile function (1-3 months, 3-6 months max)
• Changes in libido (1-3 months, 1-2 years max)
• Reduced or absent sperm count (variable onset)
• Reduced testicular size (3-6 months, 2-3 years max)
Drugs: Estradiol (estrogen) + Spironolactone, Finasteride or Dutasteride (androgen blocker) ± Medroxyprogesterone acetate (Progestin)
Copper IUD (Paraguard)
MOA: prevents fertilization through inhibiting sperm maturation and motility and implantation through foreign-body reaction
ADR: menstrual changes, pain, cramping
Emergency contraceptive, most effective option (99.9%)
Copper IUD (Paraguard)
What is the most effective emergency contraceptive option (99.9%) if used within 5 days and continued contraceptive action for up to 10 years?
Challenges: not FDA approved for EC, expensive, inaccessible care
Ulipristal (Ella)
MOA: progesterone agonist/antagonist that blocks endogenous progesterone from binding, delaying LH surge to delay or inhibit ovulation
ADR: headache, dysmenorrhea, abdominal pain, nausea (repeat dosing if vomit within 3 hours)
Emergency Contraceptive; prescription 1x 30mg oral dose, effective up to 5 days after unprotected intercourse; upper weight efficacy <85kg (187lb)
Levonorgesterel (Oral)
MOA: progesterone analog that binds to progesterone receptors to decrease surge in LH and delay or inhibit ovulation
ADR: heavier menstrual bleeding, abdominal pain, nausea (repeat dosing if vomit within 2 hours)
Available OTC as Plan B One-Step®, Next Choice One Dose®, Next Choice®, AfterPill, My Way, Take Action ($40-50)
Emergency contraceptive; most effective within 3 days;
upper weight efficacy <70kg (154lb)
Levonorgesterel (IUD)
MOA: progesterone analog that binds to progesterone receptors to decrease surge in LH and delay or inhibit ovulation; thickening cervical mucus and interferes with sperm maturation and function
Benefit: continued contraception; Challenge: timing and access to implantation
Skyla®, Kyleea®, Mirena®; Emergency Contraceptive; must be implanted within 5 days
Levonorgesterel (Oral)
-BMI 25-29.9: risk of pregnancy is 1.5x higher
-BMI >30: risk of pregnancy is 3x higher
-upper weight efficacy 70kg (154lbs)
Consideration regarding weight for which emergency contraceptive?
Ulipristal (Ella)
-BMI >30: risk of pregnancy is 2x higher
-upper weight efficacy 85kg (187lb)
Consideration regarding weight for which emergency contraceptive?
Combination Progestin/Estrogen (Yuzpe)
MOA: interferes with ovulation, fertilization, and implantation, 2 doses, 12 hours apart (oral contraceptive with ethinyl estradiol + levonorgestrel or norgestrel)
ADR: less effective than levonorgestrel alone, more adverse effects (nausea/vomiting)
Emergency contraceptive; not commonly used anymore, not FDA approved*
Mifepristone
MOA: synthetic steroid acts as a progesterone antagonist/partial agonist, blocks the LH surge to block/delay ovulation, oral 10-25mg
Can prevent pregnancy OR cause abortion (within 5 days vs. >5 days)
Emergency contraceptive; not FDA approved*