B4 - Community Level Systems
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:13 PM on 2/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
Ecosystem
All living organisms and physical conditions present in an area
2
New cards
Habitat
Area where an organism lives
3
New cards
Population
Total number of organisms within one species
4
New cards
Community
All large living organisms in an area that all rely on eachother
5
New cards
Producer
Organism that make their own food through the process of photosynthesis
6
New cards
Consumer
Organism that has to eat other organisms to gain energy
7
New cards
Abiotic factor
Non-living (Physical) component of an ecosystem
\
\
EG; light intensity, temperature, soil pH
\
EG; the woodland ecosystem, the amount of rainfall received and the temperature of the ecosystem
\
\
EG; light intensity, temperature, soil pH
\
EG; the woodland ecosystem, the amount of rainfall received and the temperature of the ecosystem
8
New cards
Biotic factor
Living components of an ecosystem
\
EG; plants, animals, microorganisms, disease
\
EG; in a woodland ecosystem, the presence of beech trees, squirrels, and hedgehogs and population numbers
\
EG; plants, animals, microorganisms, disease
\
EG; in a woodland ecosystem, the presence of beech trees, squirrels, and hedgehogs and population numbers
9
New cards
Competition
Two or more organisms competing for a resource
EG; food, space
EG; food, space
10
New cards
Nitrifying bacteria
Converts ammonia into nitrates
11
New cards
Nitrates
Plants use these from the soil to make proteins
12
New cards
Denitrifying bacteria
Converts nitrates into nitrogen in the air
13
New cards
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Lives in the roots of plants. They combine nitrogen from the air with oxygen to make more nitrates. The plant can use them. This type of bacteria form a mutualistic relationship with the plant.
14
New cards
Why is the nitrogen cycle needed?
shows how nitrogen is recycled in ecosystems
\
require nitrogen to produce proteins and nucleic acids, DNA RNA
\
78% of the atmosphere is nitrogen but organisms **cannot** access nitrogen in form
\
Instead, they rely on certain **bacteria** to convert nitrogen into **nitrogen-containing compounds**, which is taken up by plant
\
require nitrogen to produce proteins and nucleic acids, DNA RNA
\
78% of the atmosphere is nitrogen but organisms **cannot** access nitrogen in form
\
Instead, they rely on certain **bacteria** to convert nitrogen into **nitrogen-containing compounds**, which is taken up by plant
15
New cards
Dentivore
Small animal which breaks down organic matter into small pieces
\
They break it down into smaller pieces, so increasing the surface area for decomposes speeds up the process of decomposition.
\
EG; dung beatles, earth worms and woodlice
\
They break it down into smaller pieces, so increasing the surface area for decomposes speeds up the process of decomposition.
\
EG; dung beatles, earth worms and woodlice
16
New cards
Decomposer
Organisms that gain their energy by feeding on dead or decaying matter, Feed on waste left by detritivores
\
Microorganisms that are used to break down human and plant waste. They break down complex compounds into simple soluble ones, that can be absorbed.
\
They cause decay by releasing enzymes on to the dead animal or plant
\
Microorganisms that are used to break down human and plant waste. They break down complex compounds into simple soluble ones, that can be absorbed.
\
They cause decay by releasing enzymes on to the dead animal or plant
17
New cards
Aerobic conditions that affect decomposition
With oxygen. Oxygen is needed for microorganisms to respire and carry out decomposition
18
New cards
Moist environment that affect decomposition
Water present. Micro-organisms need water to carry out decomposition, not enough will prevent decomposition.
19
New cards
What are the differences between a decomposer and a dentrivore
==Decomposers;==
microorganisms that include bacteria and fungi.
feed on dead animals, plants. detritivores
\
Feed on their waste by secreting digestive enzymes to break down their cells.
\
They use some of the nutrients from this waste material to grow and reproduce.
\
carbon dioxide, water & mineral ions such as nitrates are released into the environment. Plants take these mineral ions up through their roots to build chemicals such as proteins.
\
@@Detritivores@@
include maggots, some worms & beetles.
\
start the decay process by eating dead animal and plants and producing waste material.
\
It is this waste material that the fungi and bacteria are then able to feed upon to complete the decay process and return the nutrients to the soil.
microorganisms that include bacteria and fungi.
feed on dead animals, plants. detritivores
\
Feed on their waste by secreting digestive enzymes to break down their cells.
\
They use some of the nutrients from this waste material to grow and reproduce.
\
carbon dioxide, water & mineral ions such as nitrates are released into the environment. Plants take these mineral ions up through their roots to build chemicals such as proteins.
\
@@Detritivores@@
include maggots, some worms & beetles.
\
start the decay process by eating dead animal and plants and producing waste material.
\
It is this waste material that the fungi and bacteria are then able to feed upon to complete the decay process and return the nutrients to the soil.
20
New cards
Warm temperatures in decomposition
allows for the enzymes involved in the decomposition are working optimally. Oxygen is needed for the microorganisms to respire and carry out respiration.
21
New cards
Condensation
Process in the water cycle, turned from gas to liquid
22
New cards
precipitation
Process in the water cycle, water droplets in clouds get heavier and fall as rain, snow, hail or sleet
23
New cards
Perlocation
Process in the water cycle. Water trickles through gaps in soil and rocks
24
New cards
Transpiration
Loss of water vapour from plants directly into the atmosphere
25
New cards
Evaporation
Process in the water cycle, sun heats a body of water and forms a water vapour instead of a liquid which forms moist warm air
26
New cards
The water cycle
Energy from the sun comes down and causes a body of water to evaporate, this can be from oceans or lakes. There is also an evaporation of water the leaves of plants which is called transpiration. We have taken water from the earth’s surface and evaporated it into water vapour into the air.
\
As all this water vapour accumulates in the sky, it will start to condense into clouds which can then be blown from one region to another.
\
Until, at some point the water will fall back down to earth in the form of rain, snow, hail or sleet which we call precipitation.
\
Now, the water has fallen back onto earth the cycle can then repeat.
\
As all this water vapour accumulates in the sky, it will start to condense into clouds which can then be blown from one region to another.
\
Until, at some point the water will fall back down to earth in the form of rain, snow, hail or sleet which we call precipitation.
\
Now, the water has fallen back onto earth the cycle can then repeat.
27
New cards
Mutualism
Relationship in which both organisms benefit
28
New cards
Parasitsm
Relationship in which the parasite gains and the host is harmed
29
New cards
Photosynthesis
The Carbon Cycle
Process by where producers make food for themselves-
\
carbon dioxide and water react to form glucose and oxygen which ==removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere== (ONLY WAY)
\
Carbon dioxide is combined with water to make the sugar glucose, photosynthesis uses light energy and is only carried out by plants
Process by where producers make food for themselves-
\
carbon dioxide and water react to form glucose and oxygen which ==removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere== (ONLY WAY)
\
Carbon dioxide is combined with water to make the sugar glucose, photosynthesis uses light energy and is only carried out by plants
30
New cards
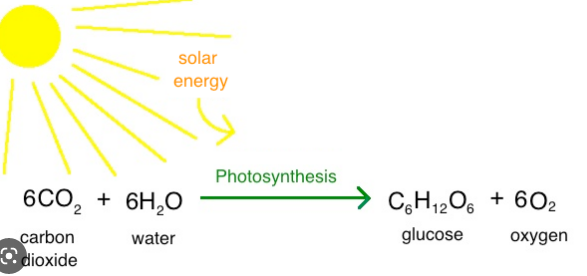
Photosynthesis equation
Carbon dioxide + water > Glucose + oxygen
31
New cards
Respiration
The Carbon Cycle
All living organisms respire to transfer energy from chemical stores in food - happens in mitochondria - ==releases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere==
All living organisms respire to transfer energy from chemical stores in food - happens in mitochondria - ==releases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere==
32
New cards
Combustion
The Carbon Cycle
Reaction in which a substance burns in oxygen. ==releases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere==
Reaction in which a substance burns in oxygen. ==releases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere==
33
New cards
Food chain
A sequence of organisms who are independent on each other for food as a source of energy, the arrows represent the transfer of energy
34
New cards
How does light affect the plant?
Light is required for photosynthesis., without light plants are unable to grow food of their own which reduces their growth
\
tthe greater the light availability, the greater the growth of a plant.
\
Plants have evolved to grow successfully in different light intensities.
\
For example in areas of low light, plants often have larger leaves in order to absorb as much light as possible!
\
tthe greater the light availability, the greater the growth of a plant.
\
Plants have evolved to grow successfully in different light intensities.
\
For example in areas of low light, plants often have larger leaves in order to absorb as much light as possible!
35
New cards
Describe how temperature can affect animals and plants
Temperature has its greatest effect on the **enzymes** that control metabolic reactions. Enzymes work better if the temperature is at the optimum
\
Plants develop more rapidly in warmer temperatures as enzymes can work more quickly!
\
Plants develop more rapidly in warmer temperatures as enzymes can work more quickly!
36
New cards
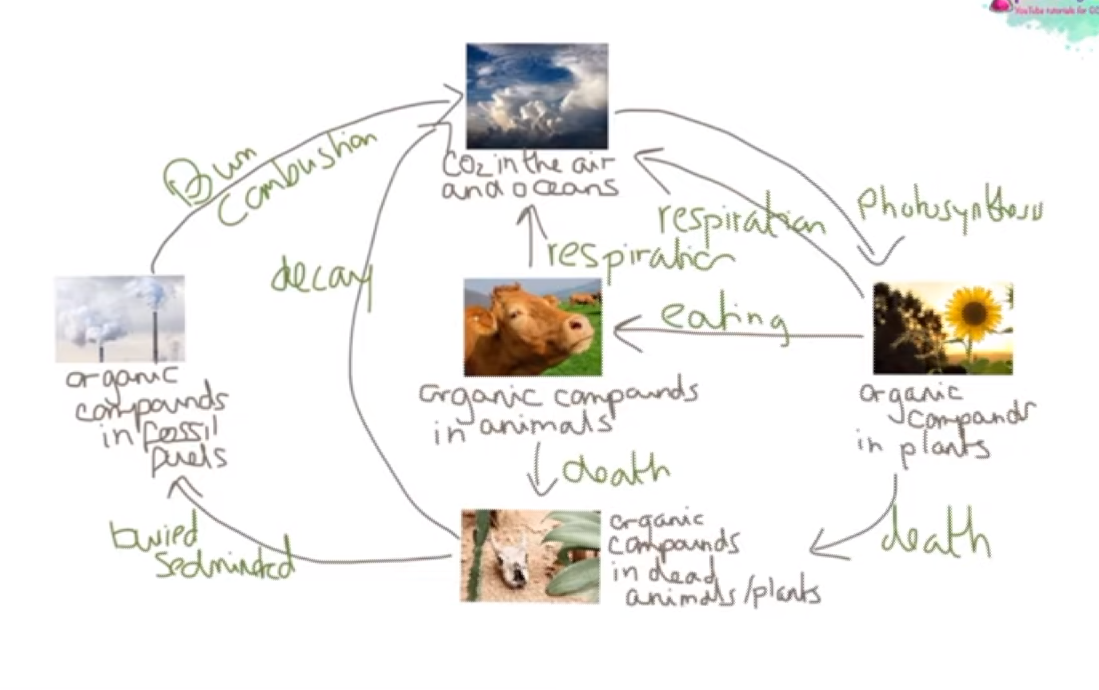
The Carbon Cycle
Starts with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
\
Photosynthesis takes in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into biological molecules like glucose.
\
This carbon can do two things; it can either be passed back into the atmosphere via respiration or passed onto animals who eat the plants who then respire to release carbon dioxide.
\
However, when these plants and animals die, these organisms decay by micro-organisms that live in the warm, moist aerobic conditions of the soil. This will break them into smaller pieces until all the carbon has been released as carbon dioxide during microbial respiration.
\
However, if the dead organisms avoid being decayed like this and are instead decayed in anaerobic conditions (NO OXYGEN) then they may slowly be converted into fossil fuels like oil, natural gas or coal.
\
These fossil fuels are then burned by humans which release carbon dioxide (Combustion)
\
Photosynthesis takes in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into biological molecules like glucose.
\
This carbon can do two things; it can either be passed back into the atmosphere via respiration or passed onto animals who eat the plants who then respire to release carbon dioxide.
\
However, when these plants and animals die, these organisms decay by micro-organisms that live in the warm, moist aerobic conditions of the soil. This will break them into smaller pieces until all the carbon has been released as carbon dioxide during microbial respiration.
\
However, if the dead organisms avoid being decayed like this and are instead decayed in anaerobic conditions (NO OXYGEN) then they may slowly be converted into fossil fuels like oil, natural gas or coal.
\
These fossil fuels are then burned by humans which release carbon dioxide (Combustion)