Lesson 20: Muscular system anatomy
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What special terminology is used for muscle cell organelles?
Plasma membrane: sarcolemma
cytoplasm: sarcoplasm
endoplasmic reticulum: sarcoplasmic reticulum
muscle cells: muscle fibers.
What are the two main types of muscle tissue based on structure and function?
Striated muscle and smooth muscle.
Which muscles are classified as striated muscles?
Skeletal muscle and cardiac (heart) muscle.
What characterizes striated muscles?
high organization of actin and myosin filaments. With vertical striation
What characterizes smooth muscle compared to striated muscle?
Poor organization of actin and myosin filaments and absence of vertical striations.
What is the embryological origin of muscle tissue?
Mesoderm.
Is muscle tissue vascularized and innervated?
Yes, muscle tissue is both vascularized and innervated.
What are the four special properties of muscle tissue?
Electrical excitability, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity.
What is electrical excitability in muscle tissue?
The ability to respond to stimuli by generating muscle action potentials.
What types of stimuli can trigger muscle action potentials?
Autorhythmic electrical signals and chemical stimuli such as neurotransmitters, hormones, and pH changes.
What is contractility?
The ability of muscle tissue to contract forcefully when stimulated.
What is extensibility?
The ability of muscle tissue to stretch within limits without being damaged.
What is elasticity?
The ability of muscle tissue to return to its original length and shape after contraction or extension.
What is a muscle fiber in skeletal muscle?
A long
cylindrical
multinucleated
cell formed by the fusion of myoblasts.
Associated with bones
Where are nuclei located in skeletal muscle fibers?
At the periphery, just beneath the sarcolemma.
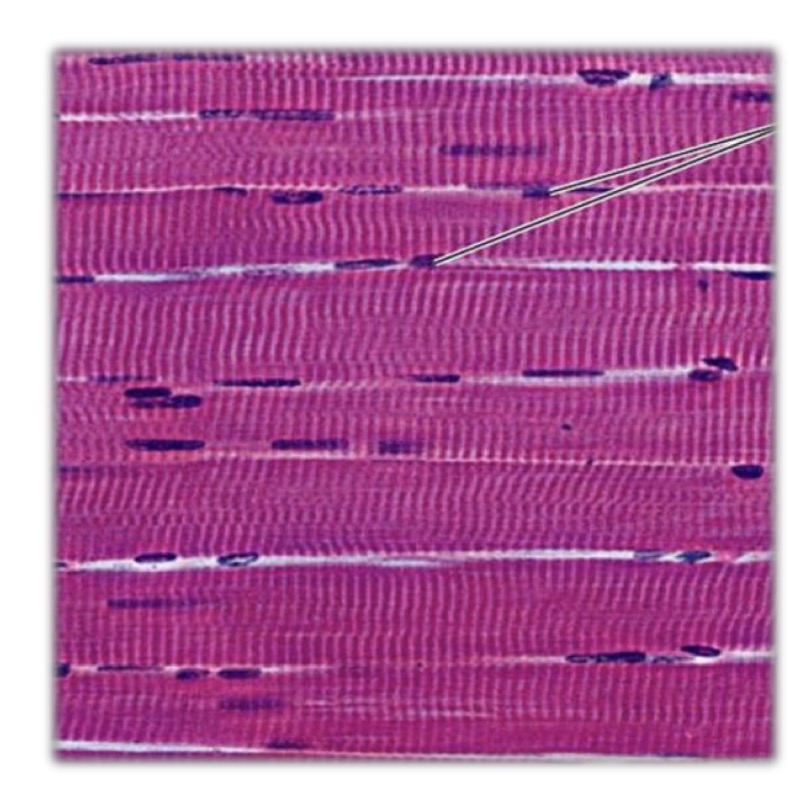
Can skeletal muscle fibers divide?
No, they grow by hypertrophy, not by mitosis.
Type of contraction
Short term forceful contractions
What type of control does skeletal muscle have?
Voluntary control.
Where are skeletal muscles located?
They are associated with bones.
What connective tissue layers organize skeletal muscle?
Epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium.
What is the epimysium?
A dense connective tissue sheath surrounding the entire muscle. Attached through tendons to the muscle
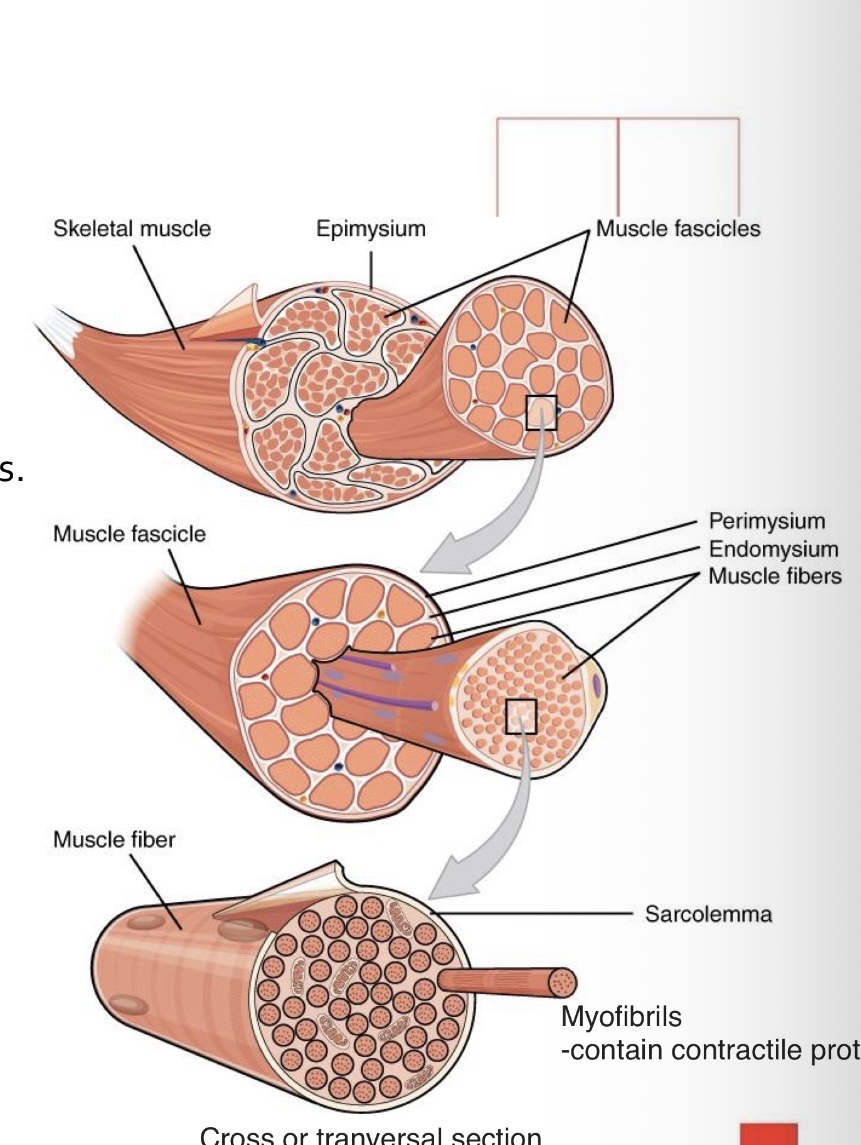
What is the perimysium?
Intermediate Connective tissue surrounding muscle fascicles.
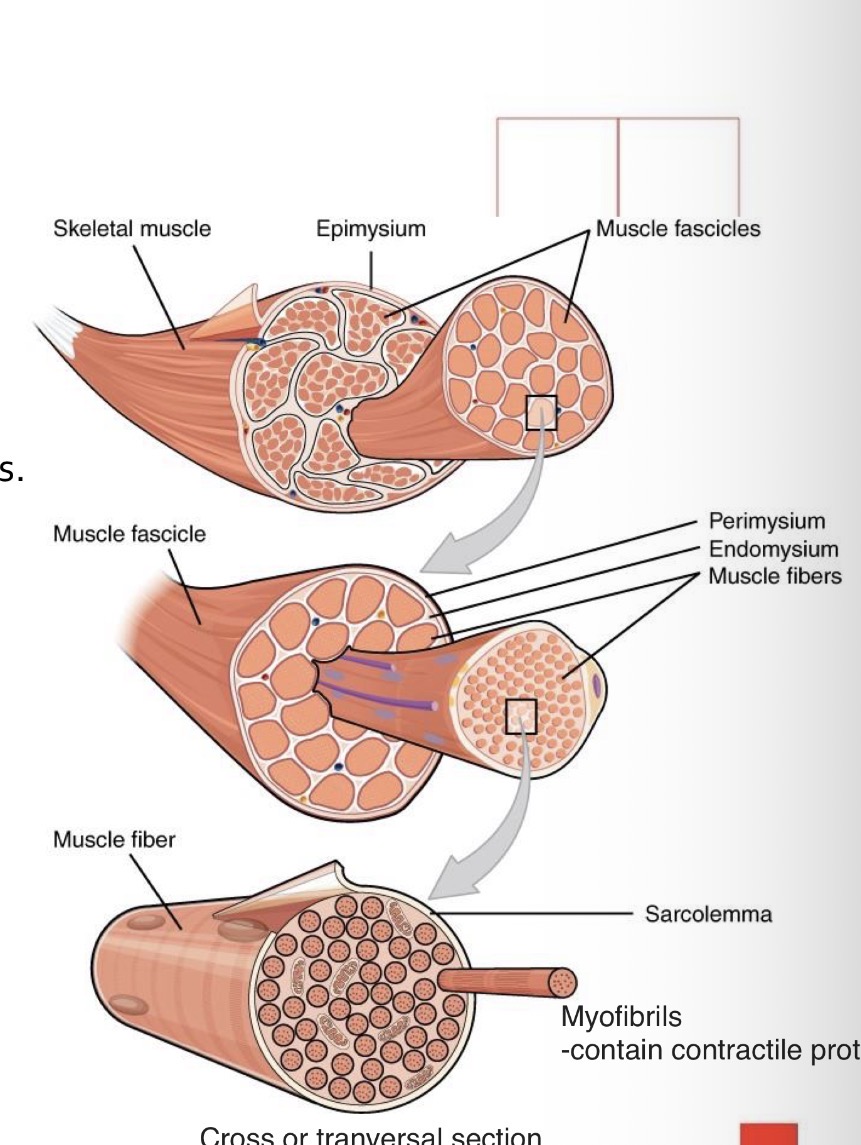
What is the endomysium?
Reticular connective tissue surrounding individual muscle fibers.
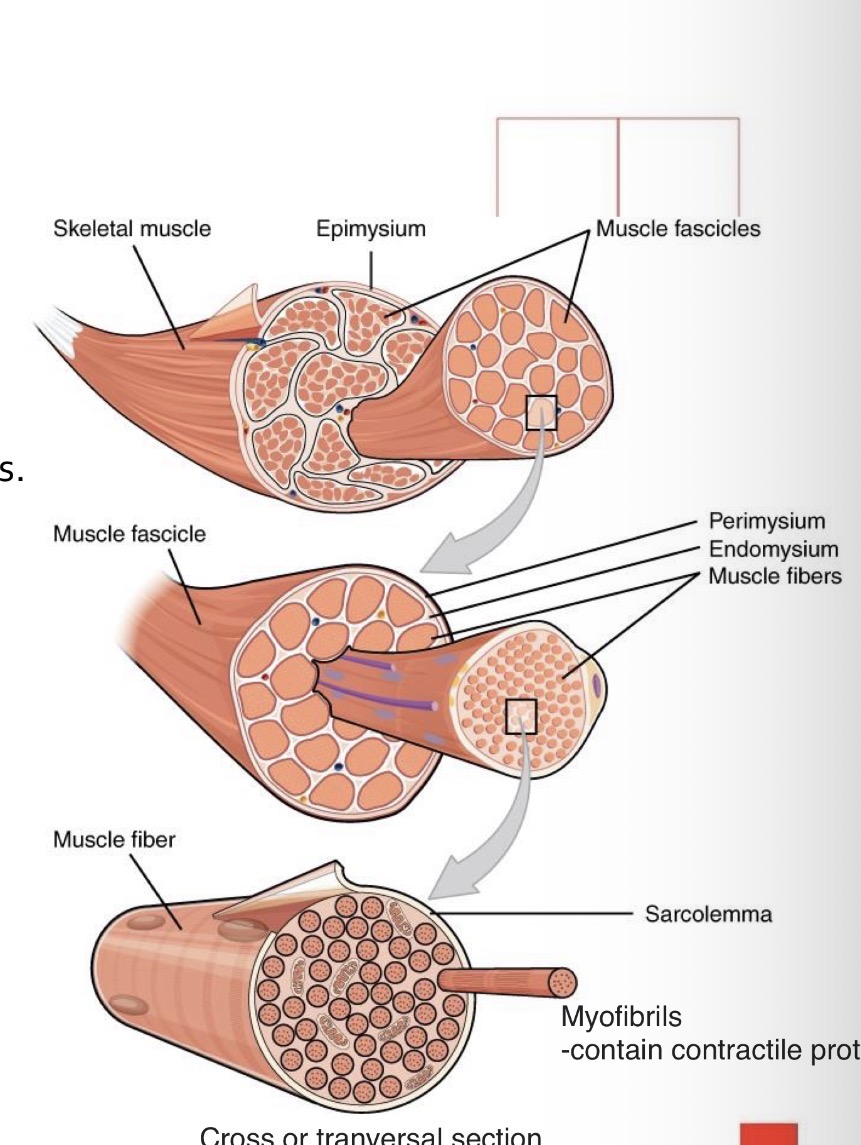
What is the sarcolemma?
The plasma membrane of a muscle fiber.
What are T-tubules?
Invaginations of the sarcolemma that conduct action potentials into the fiber.
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
A specialized smooth ER that stores and releases Ca²⁺ for muscle contraction.
What are myofibrils?
Parallel contractile structures composed of actin and myosin filaments.
What is a sarcomere?
The repeating functional unit of a myofibril.
Which filaments form myofibrils?
Thick myosin filaments
Thin actin filaments
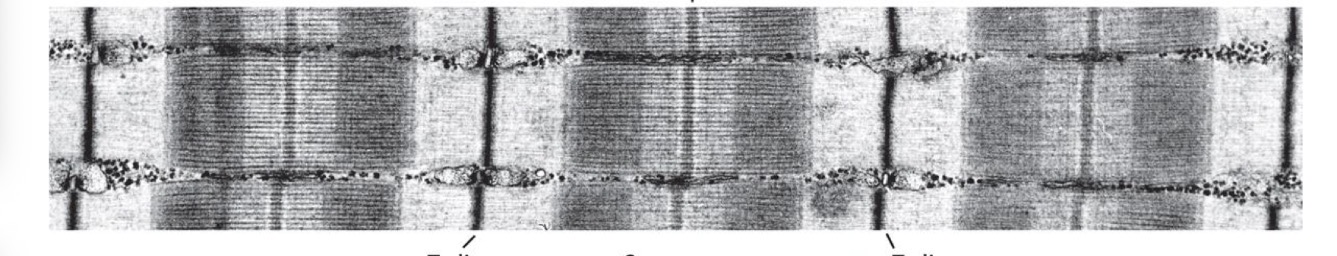
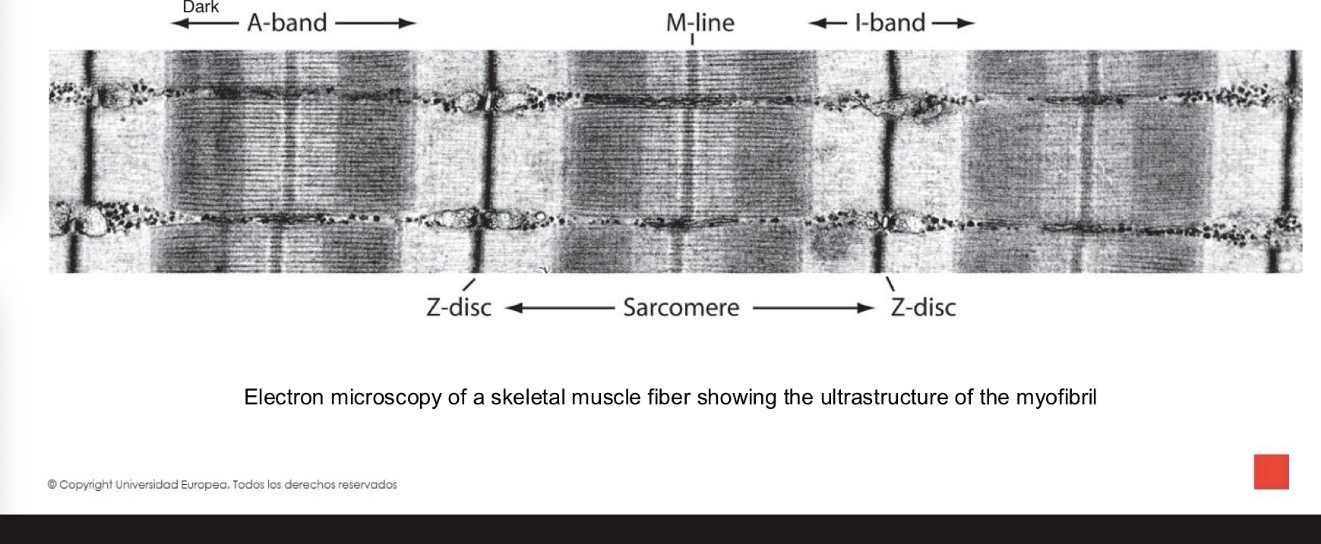
What structures define a sarcomere?
Z lines at each end.
What is the A band?
The dark band containing thick (myosin) filaments.
What is the I band?
The light band containing thin (actin) filaments only.
What is the H zone?
The central region of the A band containing only thick filaments.
What is the M line?
The region containing proteins that bind thick filaments.
What theory explains muscle contraction?
The sliding filament theory.
Fine actin filaments slide over thick ones towards the center of the A band, shortening the sarcomere
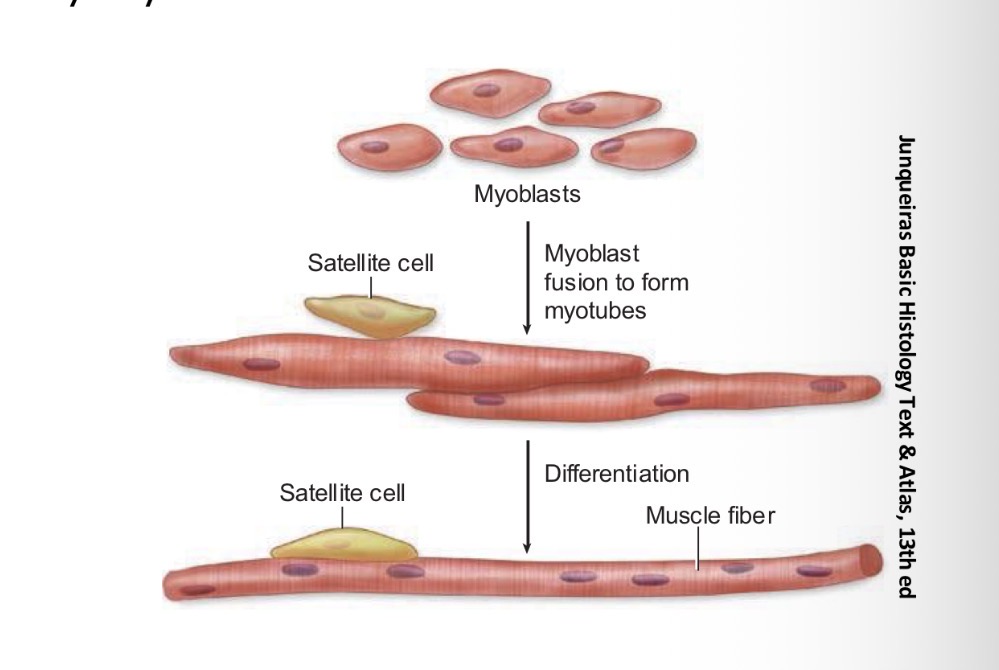
Characterize satelite cells
Small size, small nuclei,
Share basmemnt membrane with myocytes
What role do satellite cells play in skeletal muscle?
They enable regeneration by differentiating and fusing with muscle fibers.
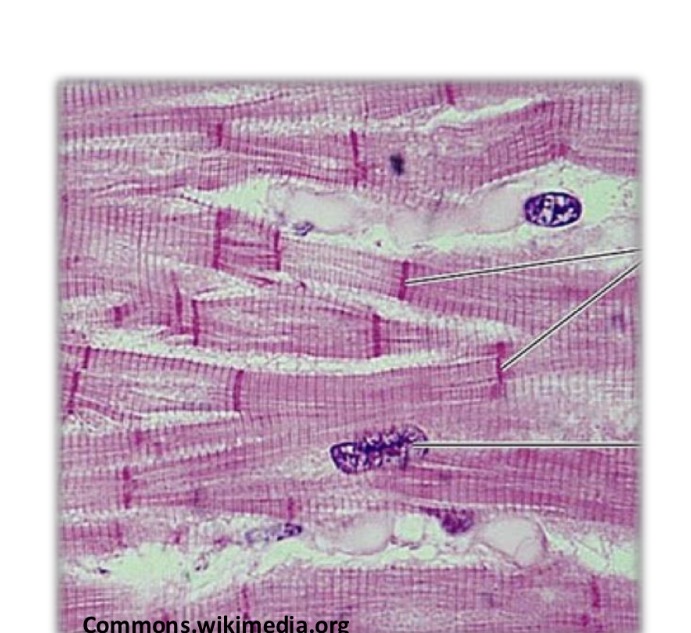
General characteristcs of Cardiac muscle
Long cells with 1-2 nuclei
Ends of the fibers divide into bracnhes, which communicate thorugh intercalary discs at Z disk
40% of cytosol is mitochondra
Wrapped in endomysium, no perimysium and epimysium
Control of cardiac muscle
Involuntary and regulated by ANS and hormones
Type of contraction of cardiac
Contionous and spontaniuos contraction high enerfy consuming
Components of cardiac muscle?
GAP junction for transmission of AP
Desmosomes and adherence junctions for anchoring myofibrils
How are the t tubules in cardiac muscle?
Big
How is the contraction control in cardiac muscles?
Involuntary
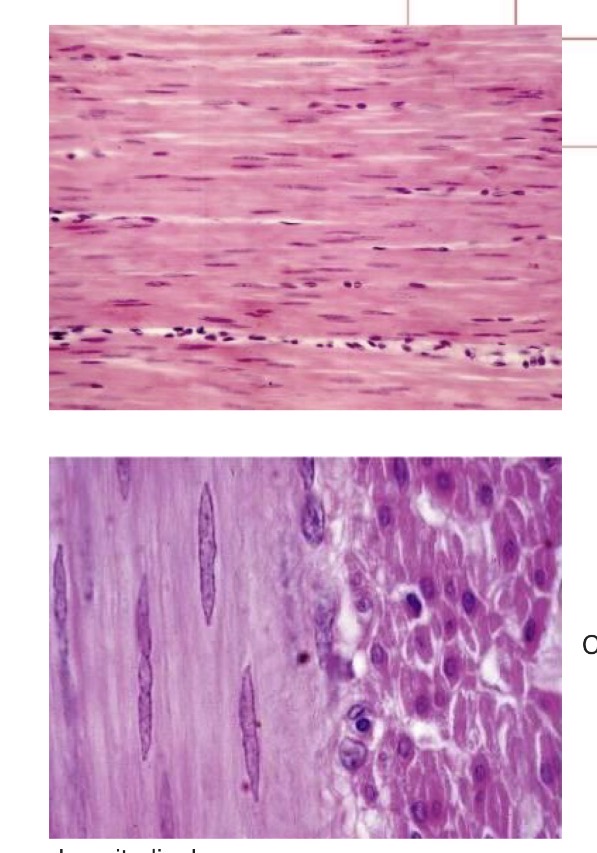
General charcteristics of smooth muscle
Spindle shaped with an elongated nucleus
Endomysium between musce cells
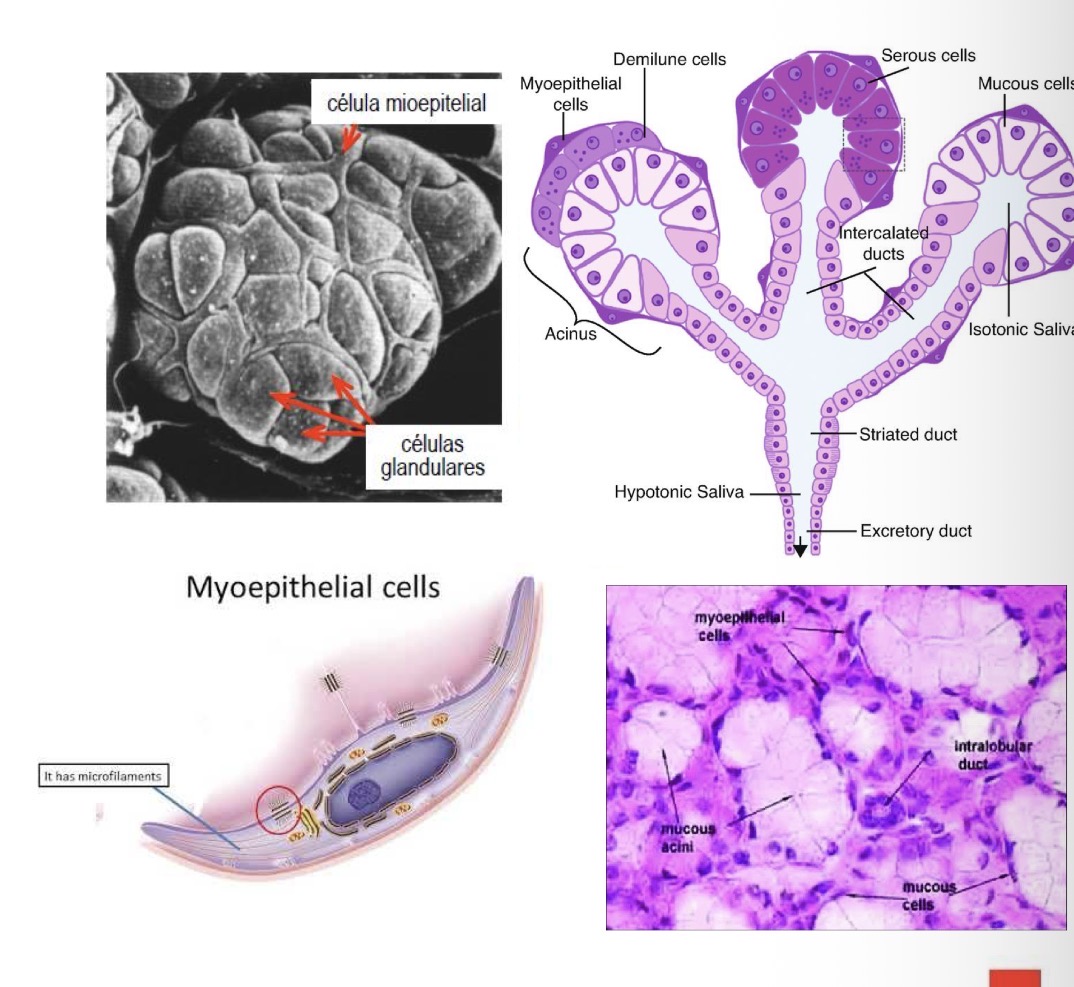
Myoepithelial cells
Surrounding glands
Increase secretion of ducts
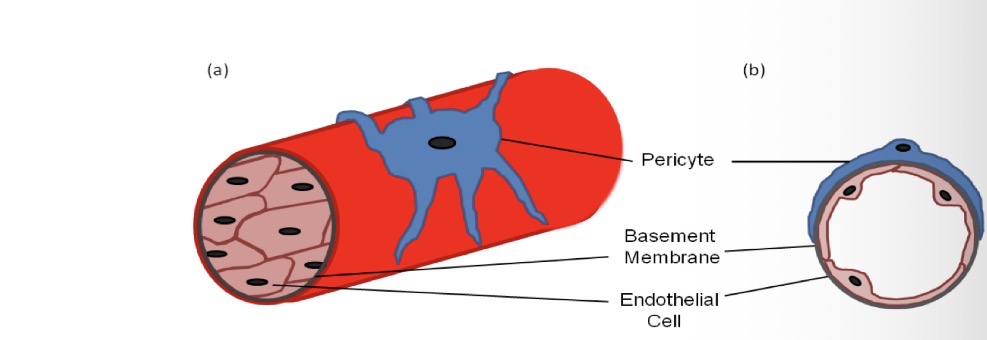
Pericytes
Regulate blood flow
Myofibroblasts
Attracted to damage border and regenerate connective tissue
T tubules in Smooth muscles
Not existing
Regenartion of skeletal muscle
Through satelite sells
Why does smooth muscle regenerate well?
Because it retains the ability to divide.
Mitotic division
Why is cardiac muscle regeneration minimal?
Because it lacks satellite cells.