Topic 2 A - cell division, growth and stem cells
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
2.1 What is mitosis?
Nuclear division that gives two genetically identical diploid daughter cells.
in humans, this diploid number is 23 pairs of chromosomes.
2.1 All body cells (and not games) are produced by mitosis of the ..?
mitosis of the zyote
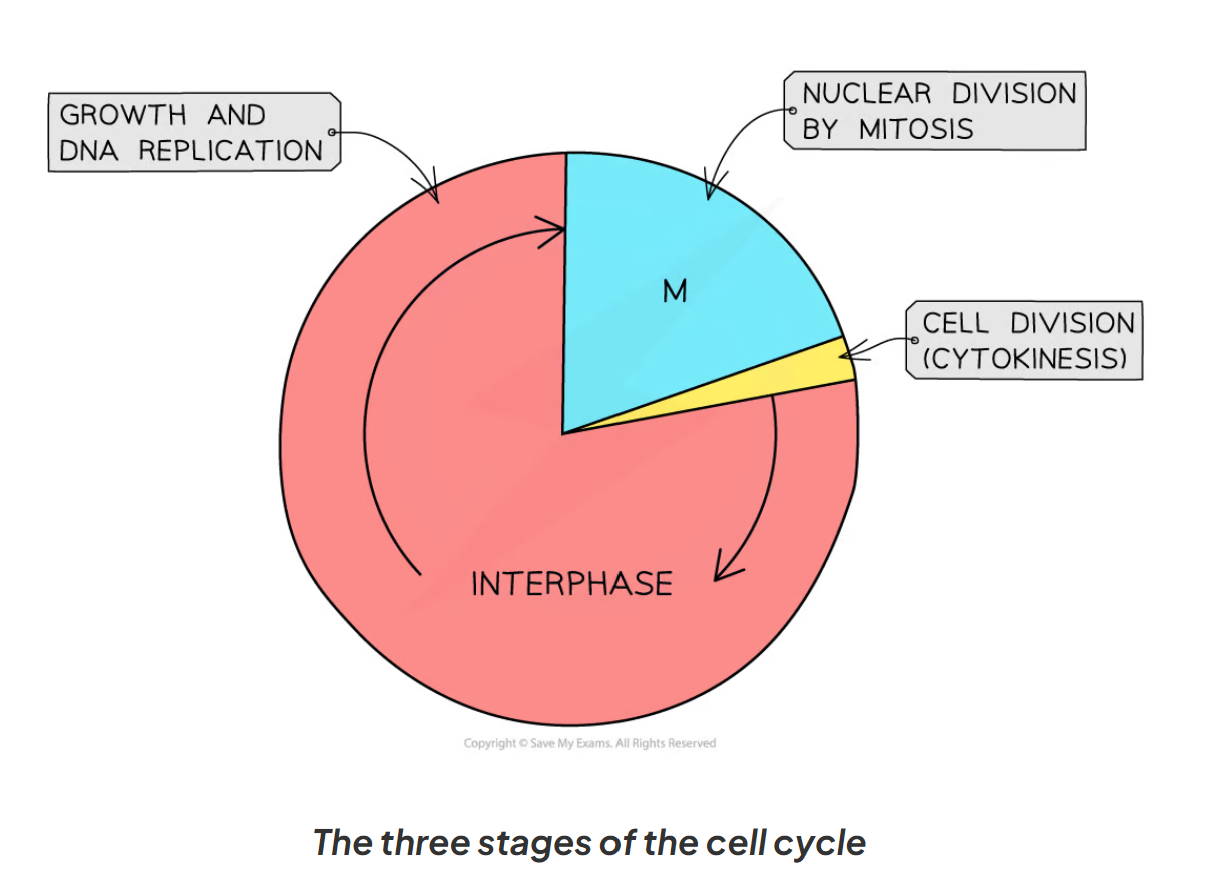
2.1 What are the 3 parts of the cell cycle?
Interphase - Just before mitosis, the DNA in the nucleus copies itself exactly (forms a-shaped chromosomes)
Mitosis - chromosomes line up along the centre of the cell where cell fibres pull them apart
Cytokinesis - The cell cytoplasm and membrane divides to produce new daughter cells: each new cell have a copy of each of the chromosomes
2.1 Here is a diagram of the cell cycle
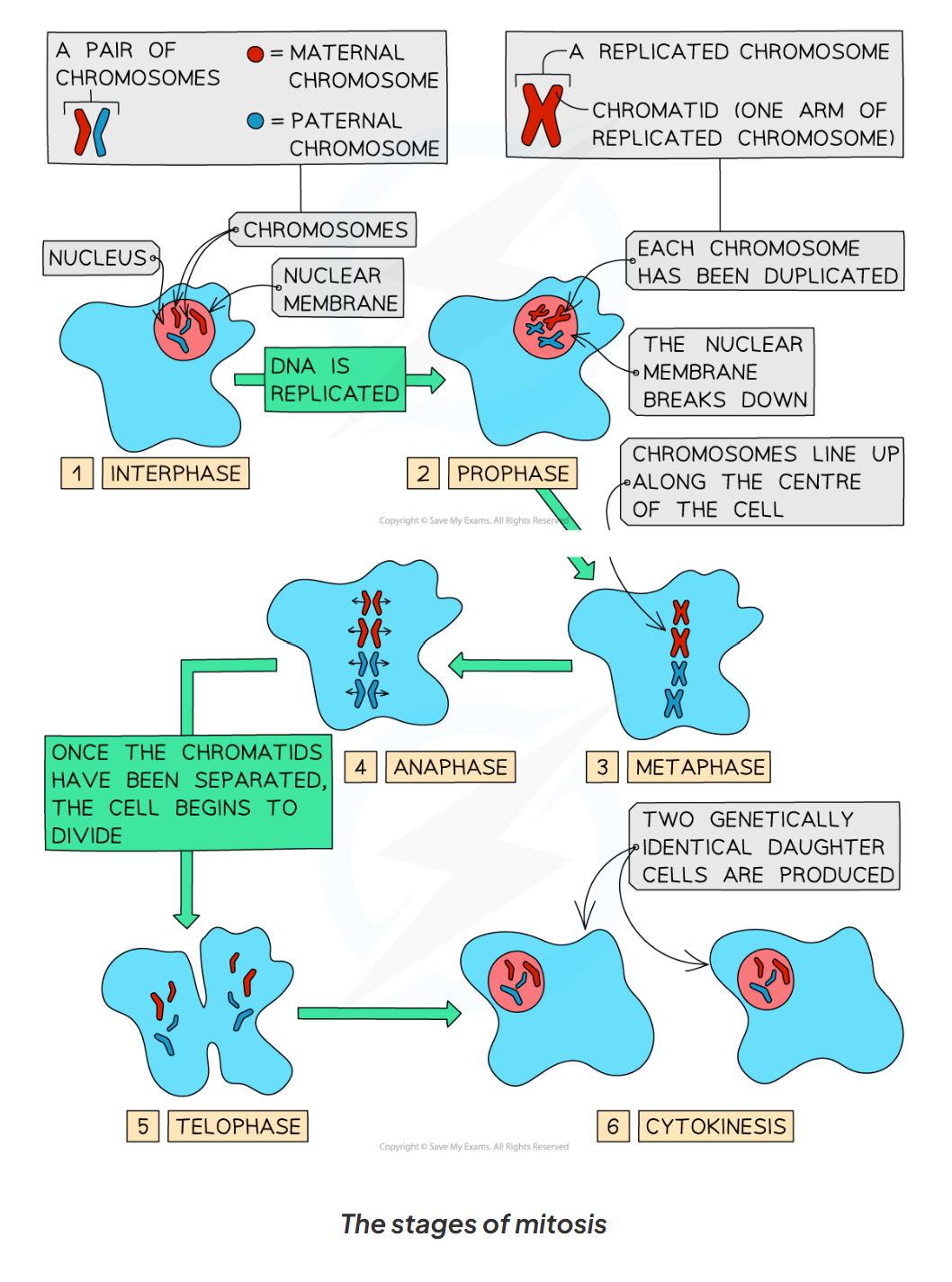
2.1 What are the stages of mitosis, and explain what happens in each phase
Prophase: DNA condenses, chromosomes become visible and nuclear membrane breaks down
Metaphase: Chromosomes line up at the equator of the cell
Anaphase: Fibres split the chromosomes down the centre and pull one chromatid to either side of the cell
Telophase: New membranes form around the chromosome sat either ends of the cell
2.1 Diagram of the process of mitosis
2.2 What is the purpose of mitosis?
Growth: mitosis produces new cells
Repair: to replace damages or dead cells
Asexual reproduction: mitosis produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent
2.4 What is mitosis regulated by?
By many different genes to ensure that cells divide only when they need to and stop when required
2.4 How is cancer caused?
By a mutation in the DNA of cells that leads to uncontrolled cell growth and division - this can result in the formation of a tumour (a mass of cells)
Usually, tumours form as a result of loss of control of the cell cycle.
2.4 what are the 2 main types of tumours?
Benign and Malignant
2.4 what is Benign and it’s features?
Benign tumours are growths of abnormal cells which are contained in one area.
-they are slow growing
-don’t often spread to other parts of the body
-can press on other body organs and look unsightly
-often have capsules around them so can be removed easily
-these tumours are not cancerous
2.4 what are Malignant tumours and their features?
-They are cancerous
-faster growing
-the cells of these tumours invade neighbouring tissues and spread to different parts of the body vi the blood and lymphatic system where they form secondary tumours
- as the tumours grow, cancer cells detach and can form secondary tumours on other parts of the body
2.5 What is growth?
permanent increase in size or mass.
2.5 what are the 2 key processes both plants and animals growth via?
Cell division - mitosis
Cells differentiation - specialised features creating a specialised cell
2.5 what is the unique way plants grow?
Through elongation: they is where hormones such as auxin cause cells to grow longer in response to certain stimuli e.g the sun
2.6 What are specialised cells?
Cells that have structural adaptations that enable them to perform specific functions within the organism
2.6 what happens to the genes when cells differentiate?
When cells differentiate these active genes cause the development of subcellular structures which enables it to carry out a certain function.
2.6 How is a nerve cell formed?
To form a nerve cell the cytoplasm and cell membrane of an undifferentiated cell must elongate to form connection over large distances.
2.6 here is a diagram showing the differentiation of a human cell
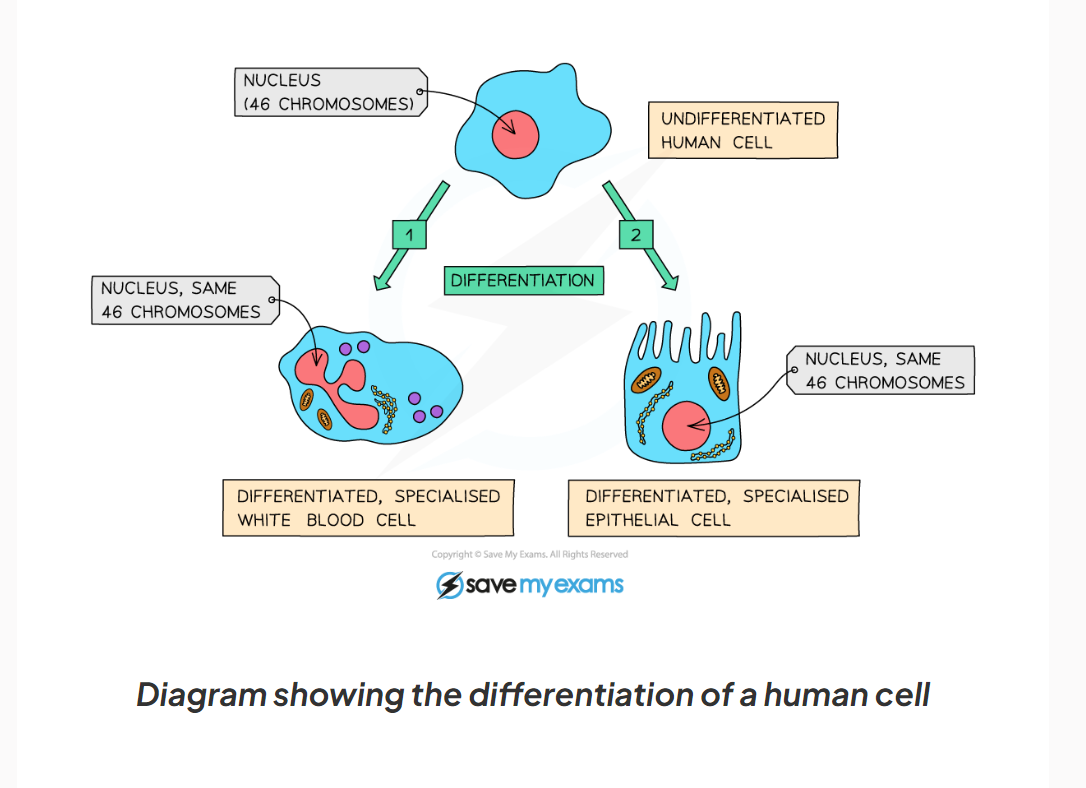
2.6 Why is differentiation important?
Because it is how a multicellular organism develops, its cells differentiate to form specialised cells
2.7 In animals when do most cells differentiate?
In an early stage of its development . cell division is mainly needed for repair and replacement in mature animals
2.7 Do animals cells ever lose their ability to differentiate?
Yes, after they have become specialised early in the life of the animal
-however some cells in parts of the body retain the ability to differentiate through the life of the animal. These cells are called adult stem cells and are mainly involved in replacing and repairing cells (such as d blood or skin)
2.6 Do plant cells ever lose the ability to fully differentiate ?
-Many types of plants cells retain the ability to differentiate throughout the life of the plant, not just the early stages of development
2.7 how is growth monitored?
By using growths charts
2.7 how are growth charts used to monitor growth? Give an example
By comparing its growth to usual trends for that particular organism.
E.g In humans, the growth of a baby is monitored using indicator measurements such as mass, length and head circumference.
These measurements are then compared with historical data collected from other children of the same age
Any potential issues can then be highlighted and assessed if necessary
2.7 what are some potential issue that a growth chart could highlight?
Malnutrition
Obesity
Inconsistencies across different measurements e.g. a large baby with a small head
Sudden changes in trend (which may indicate expression of a new health problem)
2.7 How would you compare the growth of a child using a growth chart?
-find the child’s age on the X-axis
-find the child’s weight on the y-axis
-read across and up to the growth chart lines and find where they intersect (the correct percentile is the line closest to the intersection)
2.7 Give some extra info about growth charts?
Children can fluctuate around a growth trend, this is more obvious in younger children
Girls follow a different growth chart to boys
Specialised growth charts have been produced for children who suffer from specific health issues, such as Down syndrome
2.8 What is a stem cell?
-An undifferentiated cell that is capable of dividing to produce many more cells of the same type.
-stem cells can give rise to other types of cells through the process of differentiation
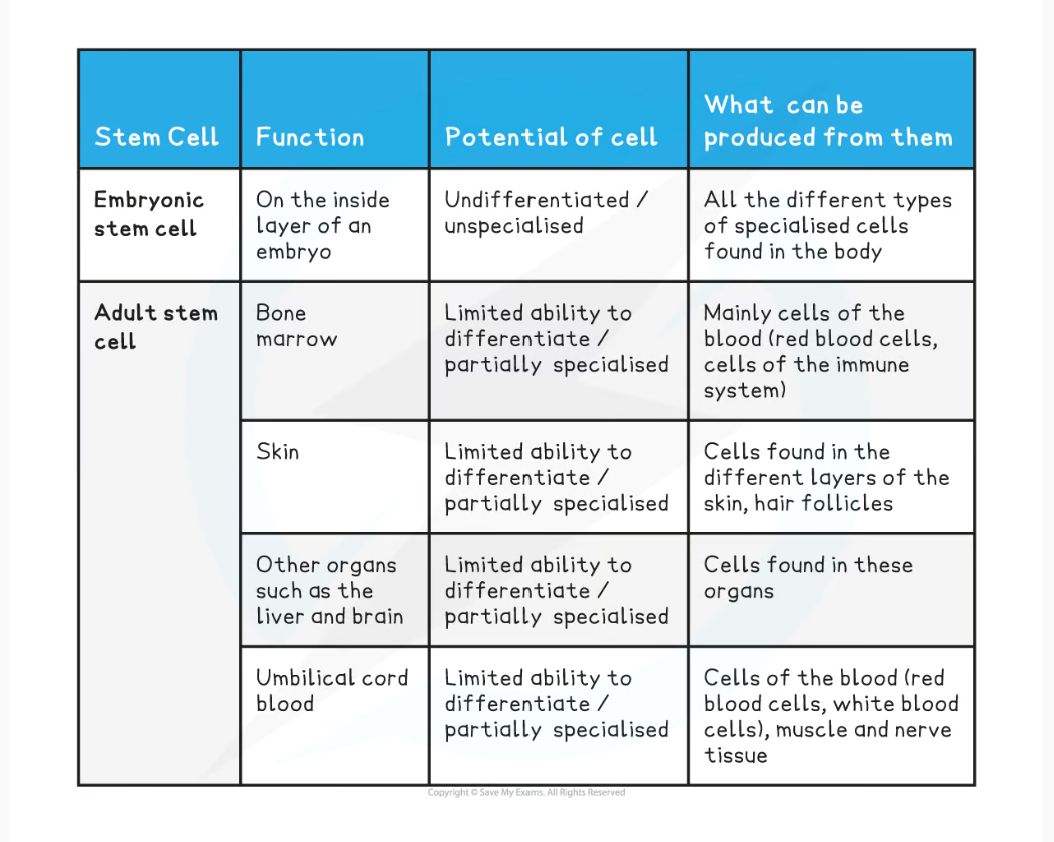
2.8 What are the features of embryonic stem cells?
-they can form a whole new individual.
-cells in very early embryos can differentiate to become any other type of cell
2.8 What are the features of adult stem cells?
-adult stem cells are much more limited
-can only differentiate to produce a few different cell types.
-they are predominantly used for replacing damaged cells or to produce new cells for growth. Although the bone marrow has to continually make new blood cells throughout life.
2.8 Here is an overview of animal stem cells and information about them
2.8 Where are plant stem cells found?
In the root and tip of the plant, in the meristem tissue
2.8 what are meristems? Give an example
-they are unspecialised cells that can differentiate into the cells needed the plant in region where growth occurs.
-for example, meristem cells in the root can differentiate into root hair cells as well as other cells required in this part of the plant.
2.8 How are plant stem cells different to animal stem cells?
Plant stem cells retain the ability to differentiate into any type of cell through their whole life however adult stem cells can only differentiate to some types of cells and embryonic stem cells only differentiate in the early stages of its life.
2.8 Can stem cells be used to clone other plants?
yes, plant stem cells can be used to clone plants with desired characteristics. e.g resistance to certain diseases
2.9 How can adult stem cells be used in medicine?
-adults stem cells can be cultured in the lab and can be made to differentiate into specialised cells (predominantly cells of the blood) but into fewer cell types than is possible with embryonic cells
2.9 have stem cells be used to treat any diseases?
yes, they have such as leukaemia (blood cancer), but there is huge potential for stem cells to be used to cure more disease in the future (e.g diabetes and paralysis)
2.9 Is it possible to grow human stem cells in the lab? if so what can be extracted from them?
-Yes, and embryonic stem cells can be extracted form them
-These embryonic stem cells can then be stimulated to differentiate into most types of specialised cells
-As a result they are very effective in treatment of certain disease or to repair damages organs by growing new tissue for the stem cells
2.9 How can stem cells be used to treat Diabetes (types 2)?
Type 2 diabetes occurs due to the pancreas not being able to produce insulin to control blood sugar levels.
-Stem cells could be differentiated into insulin- producing pancreatic cells which are transplanted into the patients body.
2.9 How can stem cells be used to treat paralysis?
Paralysis is the damage to nerve cells in the brain or spinal cord, preventing signals from the brain reaching muscles in parts of the body (such as arms or legs), resulting in loss of movement.
-stem cells could be differentiated into nerve cells (neurones) which are transplanted into the damaged region of the nervous sytem.
2.9 What are the source of stem cells for these treatments?
stem cell donors or therapeutic cloning
2.9 What are the benefits of using stem cells?
-great potential to treat a wide range of diseases from diabetes to paralysis
-organs developed from a patients own stem cells reducing the risk of organ rejection and the need to wait for an organ donation.
-adult stem cells are already used successfully in a variety of treatments acting as proof of benefits
2.9 What are some risks/ issues associated with the use of stem cells?
-stem cells cultured in a lab could could become infected with a virus which could be transmitted to the patient
-there is a risk of cultured stem cells accumulating mutations tat can lead them to developing into cancer cells.
-low numbers of stem cell donors.
2.9 what are some social issues to the use of stem cells?
-it is possible for embryonic stem cells to be collected before birth (from amniotic fluid) or after birth (umbilical cord blood) and stored by a clinic - (this can be ex[pensive)
-a lack of peer-reviewed clinical evidence of success of stem cell treatments
-educating the public about what stem cells can and cannot be used for.
2.9 what are some ethical issues to the use of stem cells?
-stem cells can be sourced from unused embryos produced in IVF treatment - is this right? Who gives permission?
-is it right to create embryos through therapeutic cloning and then destroy them? Who owns the embryo?
-should an embryo be treated as a person with human right? or an a commodity (a raw material)?