Science
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:48 AM on 5/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
1
New cards
microbe
An organism invisible to the naked eye, especially one that causes disease
2
New cards
pathogen
An organism that causes disease
3
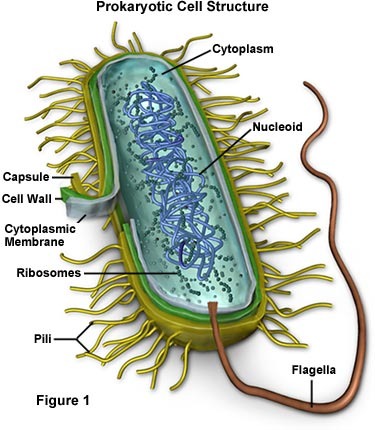
New cards
Bacteria
single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus, cause disease by releasing toxins. example: strep throat.
4
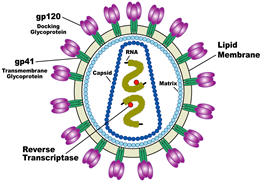
New cards
Virus
A tiny, nonliving particle that invades and then reproduces inside a living cell. covid.
5
New cards
prion
made of misshapen proteins, attack other proteins like the nervous system. Mad cow disease.

6
New cards
fungi
Can colonise the skin or other surfaces like the mouth and genital tract. Usually results from an imbalance of the body’s normal, healthy bacteria. Thrush, ringworm.
7
New cards
protozoan
Have complex life cycles (more than one host organism). Malaria, Dengue fever.
8
New cards
infectious disease
any condition that is transmitted from one person to another
9
New cards
non-infectious disease
a disease not capable of being spread from one person to another, caused by lifestyle or environment e.g. asthma, diabetes
10
New cards
Phagocytes
A type of white blood cell that ingests invading microbes
11
New cards
Lymphocytes
Types of white blood cells that are part of the body's immune system: B and T cells
12
New cards
B cells
lymphocyte that produce antibodies

13
New cards
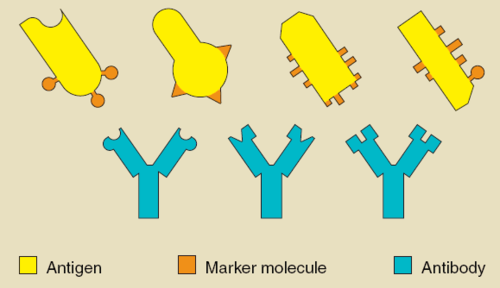
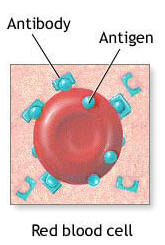
Antibodies
Protein that is produced by B cell that attaches to a specific antigen.
14
New cards
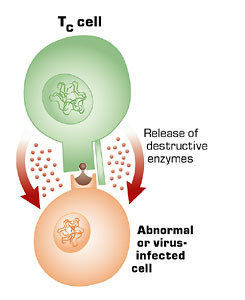
T cells
Cells that attack infected cells
15
New cards
Antigen
A part of a pathogen; triggers the immune response
16
New cards
Antibiotic
A medicine used to kill bacteria
17
New cards
vaccine
weakened or dead pathogenic cells injected in order to stimulate the production of antibodies
18
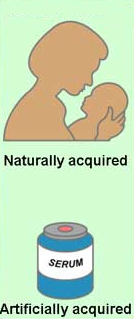
New cards
immunity
the condition in which an organism can resist disease
19
New cards
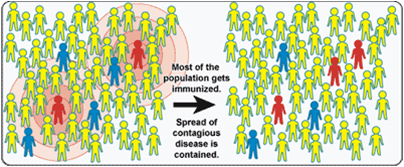
herd immunity
The resistance of a group to an attack by a disease to which a large proportion of the members of the group are immune
20
New cards
Difference between Pathogens and microbes
A microbe is only considered a pathogen if it causes a disease.
21
New cards
direct transmission
When a pathogen is passed directly from person to person through shared bodily fluids, sexual contact, touching skin, pregnancy, biting.

22
New cards
indirect transmission
When a pathogen is passed from person to person with no direct contact between them, airborne transmission, surface contact, contaminated food or water, “droplet” infection, vector transmission (through another organism e.g. mosquitoes).
23
New cards
First line of defence
Prevention, can be physical or chemical. examples: sweat which contains antimicrobial properties, that attack bacteria, Mucus lining of the stomach is another physical barrier, Intact skin forms a physical barrier, Acidic environment and digestive enzymes disrupt microbes.
24
New cards
Second line of defence purpose
Non specific responses that try to destory invader, triggered by non-self antigens, the purpose of the second line of defense is to stop a full-on invasion by a pathogen. In the case of bacteria, it is aiming to stop out-of-control reproduction which can overwhelm the infected tissue. In the case of virus, it is aiming to stop the infection of host cells.
25
New cards
Second line of defence examples
For example, blood flows to the affected area and it becomes red, warm and swollen.
White blood cells are being sent to the area to fight the pathogen, e.g. phagocytes.
When phagocytes hunt down and destroy the pathogen it is called phagocytosis.
White blood cells are being sent to the area to fight the pathogen, e.g. phagocytes.
When phagocytes hunt down and destroy the pathogen it is called phagocytosis.
26
New cards
Third line of defence
Specific to the pathogen that is attacking the body.
B cells produced proteins called antibodies which bind onto markers on pathogens to identify them
Each type of pathogen has unique markers
Once an antibody binds to a pathogen, the B cell releases millions of matching antibodies into the blood to fight the pathogen.
The B cell then clones itself into plasma cells to form an army which continues to release antibodies to fight and neutralize the pathogen.
After the infection is defeated, some B cells remain in the blood as memory cells, along with leftover antibodies.
B cells produced proteins called antibodies which bind onto markers on pathogens to identify them
Each type of pathogen has unique markers
Once an antibody binds to a pathogen, the B cell releases millions of matching antibodies into the blood to fight the pathogen.
The B cell then clones itself into plasma cells to form an army which continues to release antibodies to fight and neutralize the pathogen.
After the infection is defeated, some B cells remain in the blood as memory cells, along with leftover antibodies.
27
New cards
Water
H2O
28
New cards
carbon dioxide
CO2
29
New cards
Hydrogen gas
H2
30
New cards
Oxygen gas
O2
31
New cards
Ammonia
NH3
32
New cards
sodium chloride
NaCl
33
New cards
Hydrochloric Acid
HCl
34
New cards
Nitric Acid
HNO3
35
New cards
Sulfuric acid
H2SO4
36
New cards
Acetic Acid
CH3OOOH
37
New cards
Sodium Hydroxide
NaOH
38
New cards
Sodium Carbonate
Na2CO3
39
New cards
calcium hydroxide
Ca(OH)2
40
New cards
Acid+Base
Acid+Base→Salt+Water
41
New cards
Acid and Metal:
Acid + Metal → Salt + Hydrogen
42
New cards
Acid and Metal Carbonate
Acid + Metal Carbonate → Metal Salt + Carbon Dioxide + Water
43
New cards
photosynthesis
The energy of the sun is used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
44
New cards
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
45
New cards
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration is the process by which food, in the form of sugar (glucose), is transformed into energy within cells.
46
New cards
Biomass
the total quantity or mass of organisms in a given area or volume.
47
New cards
wave
Anything that moves energy from one place to another.
48
New cards
medium
The substance that the wave moves through e.g. water, air.
49
New cards
Transverse
Vibrate at right angles to the direction of travel. e.g. light, EM scale
50
New cards
Longitudinal
Vibrate parallel to the direction of travel. e.g. sound.
51
New cards
Wavelength (λ)
The distance in metres from any point on a wave to the exact same point on the next wave.
52
New cards
Frequency
The number of waves that pass a point in one second. (Hz)
53
New cards
amplitude
the maximum displacement of a periodic wave
54
New cards
wave equation
v=fλ
55
New cards
sound waves
are longitudinal, and require a medium to travel in.
56
New cards
How sound waves move in terms of particles:
sound is produced by a vibrating object which causes particles near to vibrate which causes a chain reaction and the sound moves.
57
New cards
Volume is indicated by
Amplitude of a sound wave, the greater the amplitude, the louder it is.
58
New cards
Pitch is indicated by
Frequency of a sound wave, the higher the frequency, the higher the pitch.
59
New cards
Light waves
are transverse, do not require a medium.
60
New cards
reflection
Light waves reflect from reflective surfaces e.g. mirror.
61
New cards
the law of reflection
The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
62
New cards
Absorption
The light is absorbed into the surface. e.g. brick, wood.
63
New cards
concave
curving inward, image is upside down, in car headlights.
64
New cards
convex
curving or bulging outward, image is enlarged, in makeup mirrors.
65
New cards
refraction
When light passes from one medium to another and it changes speed, causing the light wave to change direction.
66
New cards
electromagnetic spectrum
the name given to a group of energy waves that can travel through empty space.
67
New cards
order of the electromagnetic spectrum
Radio Waves → Microwaves → Infrared →Visible light → UV → x-rays → gamma rays
68
New cards
Wegener proposed what?
Pangaea and the idea the continents were joined together.
69
New cards
Fossil correlation
fossils from some species can be found on opposite sides of major oceans (e.g Mesosaurus fossils in South America and Africa)
70
New cards
Rock and mountain correlation
identical rock composition and mountain structures found on opposite sides of oceans.
71
New cards
Paleoclimate data
Coal deposits (which suggest tropical climates) have been found in cold areas, glacial erosion has been found in warm areas.
72
New cards
Plate tectonic theory
The theory that the Earth’s lithosphere (crust and outer mantle) is a number of tectonic plates that fit together like a jigsaw puzzle.
73
New cards
Continental crust features
Thicker, less dense.
74
New cards
Oceanic Crust features
thinner, more dense.
75
New cards
What causes tectonic plates to move
Convection currents in the earth's mantle.
Hot rock rises upwards and toward the crust.
The crust forces the hot rock to move outwards.
Rock cools and moves down towards the core.
Hot rock rises upwards and toward the crust.
The crust forces the hot rock to move outwards.
Rock cools and moves down towards the core.
76
New cards
Seafloor spreading
New oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity at mid-ocean ridges and slowly moves from where it is formed.
77
New cards
Magnetic striping
When the earth’s magnetic field reverses, a new stripe, with different polarity, begins.
This led to the recognition of seafloor spreading.
This led to the recognition of seafloor spreading.
78
New cards
Plate boundaries
Convergent, divergent, transform
79
New cards
Convergent boundary
where two tectonic plates push together, can form volcanoes, ocean trenches, mountain ranges.
80
New cards
Divergent boundary
where two tectonic plates spread apart, can form mid ocean ridges, rift valleys, volcanoes, seafloor spreading.
81
New cards
Transform boundary
where two tectonic plates slide against one another, can cause earthquakes.
82
New cards
Subduction zone
Oceanic crust goes under continental crust