Pregnancy Nutrition: Key Concepts and Outcomes
1/267
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
268 Terms
What is the most intense period of growth and development in humans?
Pregnancy, lasting nine months.
What factors influence pregnancy outcomes?
Many factors, most of which are modifiable, including nutrition.
What do natality statistics assess?
They assess reproductive outcomes through examination of vital statistics.
What does infant mortality reflect about a population?
It reflects the general health and socioeconomic status.
What improvements are related to decreases in infant mortality?
Improvements in social circumstances, infectious disease control, availability of safe food, technological advancements, and access to health care.
What was the maternal mortality rate per 100,000 live births in 2019-2021?
33 deaths per 100,000 live births.
What was the fetal death rate per 1,000 deliveries over 20 weeks gestation in 2019-2021?
5.7 deaths per 1,000 deliveries.
What is the neonatal mortality rate per 1,000 live births in 2019-2021?
1.96 deaths per 1,000 live births.
What percentage of births are classified as low birthweight (LBW)?
8.5% of births are LBW.
What percentage of infant deaths are comprised of low birthweight infants?
Low birthweight infants comprise 16% of infant deaths.
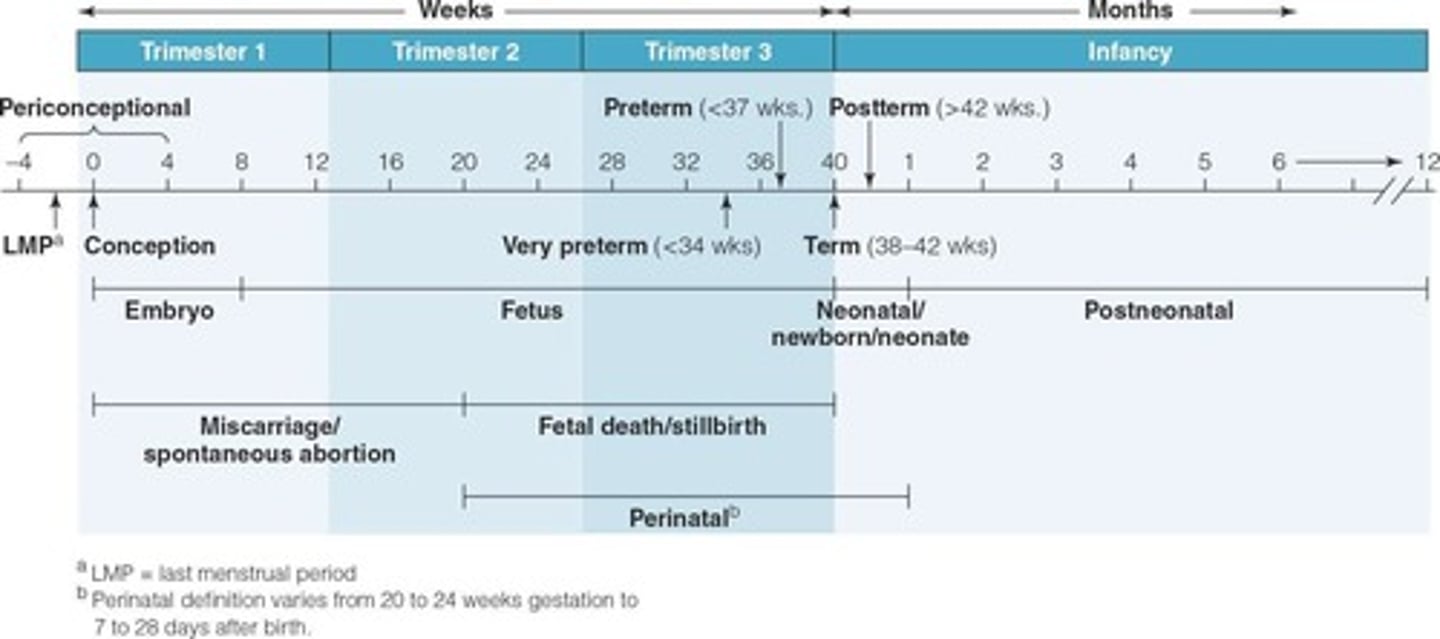
What percentage of newborns are born preterm?
10.5% of newborns are born preterm.
What is the relationship between pregnancy duration and birthweight?
Generally, the shorter the pregnancy, the lower the birthweight.
What is the rate of very low birthweight newborns in 2019-2021?
1.4 per 100 live births.
What is the rate of very preterm births (less than 34 weeks gestation) in 2019-2021?
2.8 per 100 live births.
What is the rate of adolescent pregnancies per 1,000 females aged 15 to 19 years in 2019-2021?
20.3 per 1,000 females.
What is the rate of twin births per total live births in 2019-2021?
1 in 32 live births.
What is the rate of triplet plus higher-order multiple births per total live births in 2019-2021?
1 in 1,250 live births.
What are the consequences of low birthweight and preterm delivery?
They are associated with a high risk of dying in the first year of life.
What is the perinatal mortality rate in 2019-2021?
3.7 deaths per 1,000 live births.
What is the postneonatal mortality rate in 2019-2021?
5.6 deaths per 1,000 live births.
What is the significance of the year 1995 in the context of maternal mortality?
The maternal mortality rate was 7.0 deaths per 100,000 live births.
What was the rate of births less than 37 weeks gestation in 2014-2016?
9.9 per 100 live births.
What does a decrease in infant mortality indicate?
Improvements in health care and social conditions.
What is the desirable birth weight range for newborns?
3500-4500 grams (7lb 12oz to 10lb)
What are some health issues less likely to develop with a desirable birth weight?
Heart and lung diseases, diabetes, and hypertension
What are the 2030 health objectives related to pregnant women and infants?
Reduce fetal deaths, maternal deaths, preterm births, illicit opioid use, and severe maternal complications; increase early prenatal care, abstinence from alcohol and drugs, healthy weight before pregnancy, and postpartum depression screening.
What is the average duration of pregnancy?
38 weeks, though 40 weeks is commonly used based on the last menstrual period.
What physiological changes occur in maternal body composition during pregnancy?
Changes occur in a specific sequence, including plasma volume expansion and nutrient support.
At what gestational week does maternal plasma volume reach its maximal rate of change?
20 weeks
At what gestational week does placental weight reach its maximal rate of change?
31 weeks
What are some normal changes in maternal physiology during pregnancy?
Hemodilution, increased blood and plasma volumes, increased cholesterol and triglycerides, increased glucose and insulin levels, and increased appetite.
What is hemodilution in the context of pregnancy?
A decrease in vitamin and mineral blood concentrations due to increased blood volume.
How much does body water increase during pregnancy?
From 7 to 10 liters.
What causes edema during pregnancy?
Accumulation of extracellular fluid.
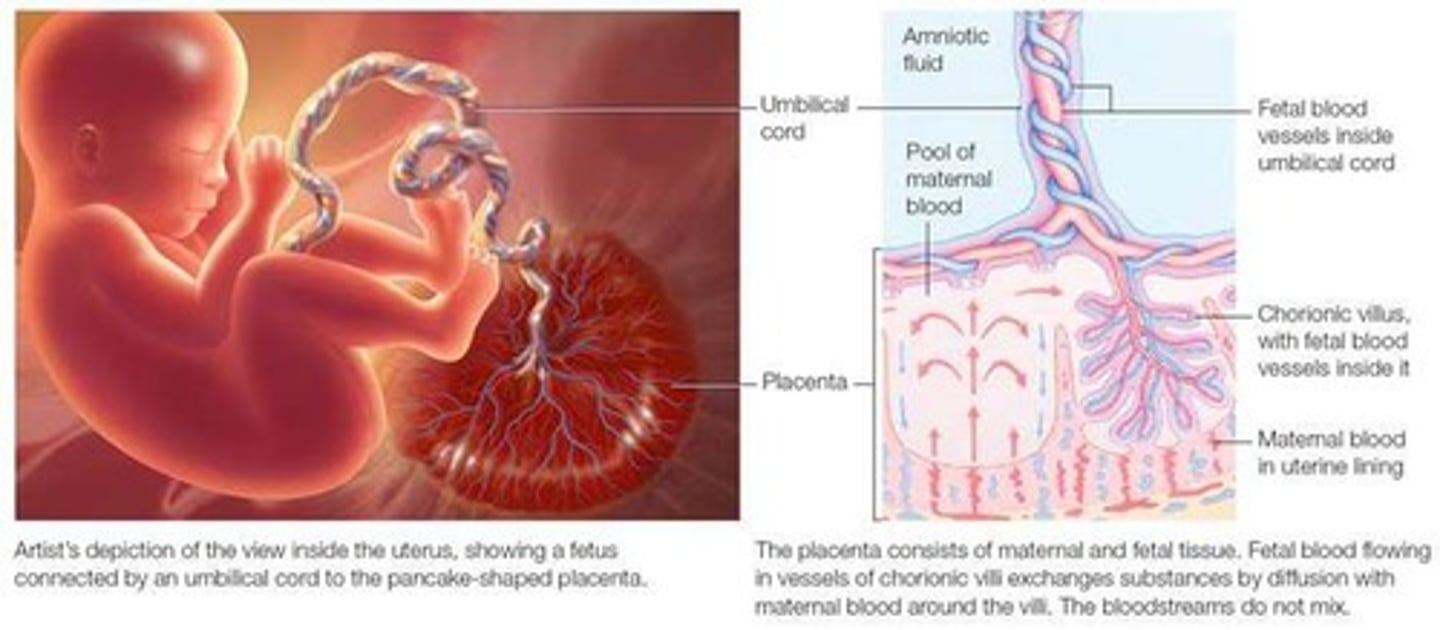
What is the role of the placenta during pregnancy?
Responsible for nutrient and gas interchange between mother and fetus.
What happens to the glomerular filtration rate during pregnancy?
It increases, leading to a higher risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs).
What hormonal changes occur during pregnancy?
Hormones produced by the placenta increase significantly.
What are common gastrointestinal symptoms experienced during pregnancy?
Nausea, vomiting, heartburn, and constipation.
How does pregnancy affect oxygen consumption?
Oxygen consumption increases during pregnancy.
What happens to the immune system during pregnancy?
Immunity is suppressed.
What is the relationship between birth weight and plasma volume?
Birth weight is strongly related to plasma volume.
What physiological changes occur in heart rate during pregnancy?
Heart rate and stroke volume increase.
What is the significance of prenatal care during pregnancy?
Early and adequate prenatal care can improve pregnancy outcomes and reduce complications.
What is the impact of maternal weight before pregnancy on pregnancy outcomes?
A healthy weight before pregnancy is associated with better outcomes.
What is the importance of screening for postpartum depression?
It helps identify and address mental health issues that may arise after childbirth.
What are some objectives to reduce maternal deaths during pregnancy?
Implementing measures to prevent pregnancy complications and ensuring access to healthcare.
What is the significance of reducing the use of illicit opioids during pregnancy?
It helps prevent adverse effects on fetal development and maternal health.
What is the role of human chorionic somatomammotropin (hCS) during pregnancy?
It plays a role in maternal nutrient metabolism and affects carbohydrate metabolism.
How does carbohydrate metabolism change during early pregnancy?
High estrogen and progesterone stimulate insulin, increasing glucose conversion to glycogen and fat.
What hormonal changes occur in late pregnancy regarding glucose metabolism?
hCS and prolactin inhibit the conversion of glucose to glycogen and fat.
What is the diabetogenic effect of pregnancy?
It results from maternal insulin resistance.
How much protein accumulates during pregnancy?
About 925 grams of protein.
What is the primary source of protein for the fetus during pregnancy?
The mother's intake of protein, as the body does not store protein early in pregnancy.
What happens to fat metabolism during pregnancy?
Fat stores accumulate in the first half and there is enhanced fat mobilization in the last half.
What is the significance of increased cholesterol during pregnancy?
It is used by the placenta for steroid hormone synthesis and by the fetus for nerve and cell membrane formation.
What role does calcium play in pregnancy?
It is needed for bone formation and there is increased maternal absorption and calcium mobilization.
What happens to sodium levels during pregnancy?
Sodium accumulates in the mother, placenta, and fetus, and restriction can be harmful.
What are the main functions of the placenta?
Hormone and enzyme production, nutrient and gas exchange, and waste removal from the fetus.
What is the structure of the placenta?
It has a double lining of cells separating maternal and fetal blood and acts as a barrier for harmful compounds.
What factors affect nutrient transfer through the placenta?
Size and charge of molecules, lipid solubility, concentration of nutrients, and transport mechanisms such as passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, active transport, and endocytosis.
What types of molecules pass easily through the placenta?
Small molecules like water, cholesterol, and ketones.
What types of molecules are not transferred through the placenta?
Large molecules such as insulin and enzymes.
How does maternal nutrition impact the fetus?
Nutrients are first used for maternal needs, then for the placenta, and lastly for the fetus, meaning poor maternal nutrition harms the fetus more.
When does the highest level of growth and development occur during pregnancy?
During gestation.
What hypothetical weight would an infant reach by one year if growth rates continued at gestation levels?
160 lbs.
What would be the height of a person by 20 years old if growth rates continued at gestation levels?
20 feet tall.
What is the highest level of growth and development during gestation?
The highest level occurs during gestation, where if the rate of weight and height gains continued, an infant would weigh 160 lbs at one year and be 20 feet tall by age 20.
What are the estimated body weight changes of a fetus at 10, 20, 30, and 40 weeks of pregnancy?
10 Weeks: 10g, 20 Weeks: 300g, 30 Weeks: 1667g, 40 Weeks: 3450g.
What is the significance of critical periods in embryonic and fetal development?
Critical periods are preprogrammed times during development when specific cells, organs, and tissues are formed, most intense during the first 2 months after conception, and errors cannot be corrected once passed.
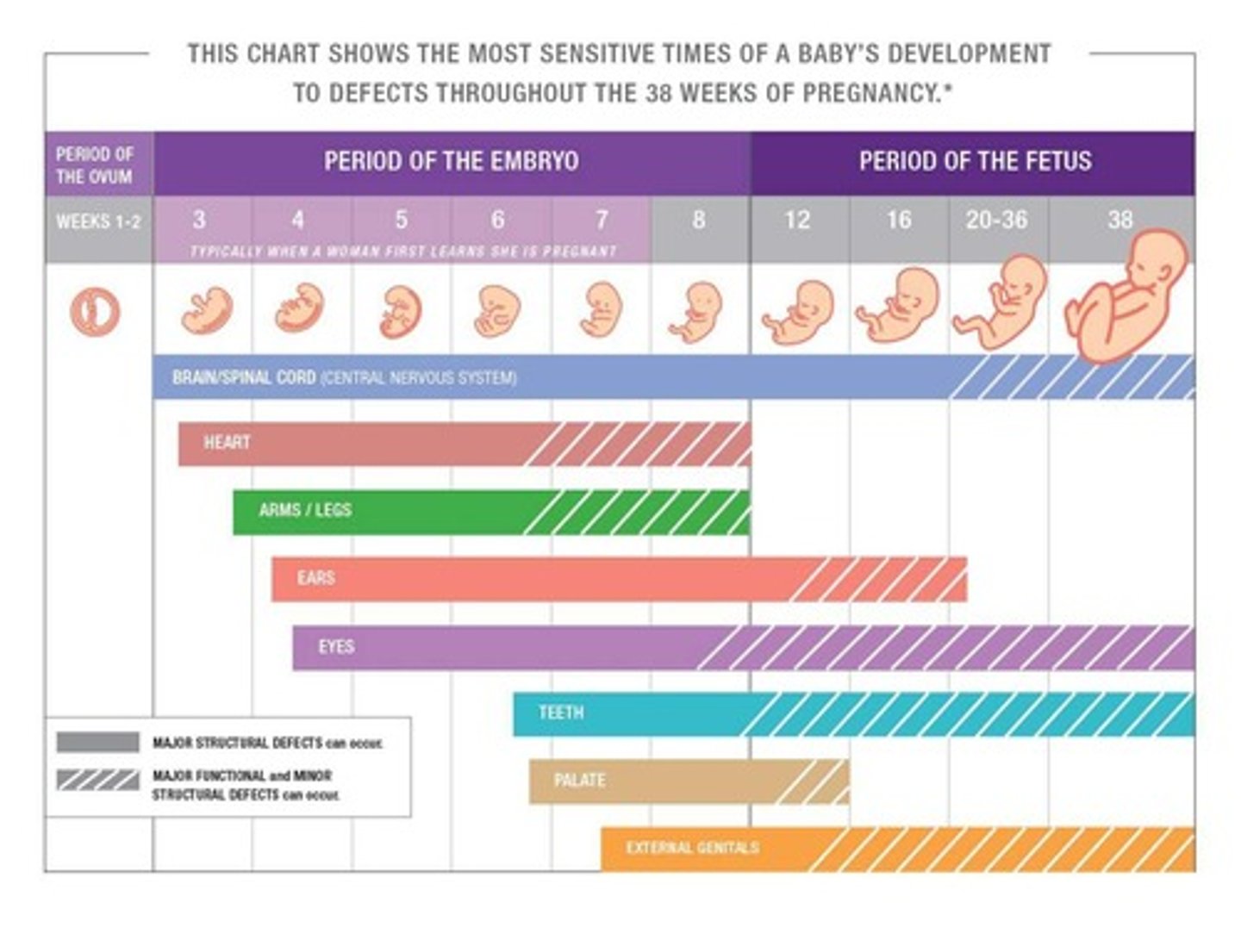
What are the four periods of growth and development in fetal development?
1. Hyperplasia 2. Hyperplasia and hypertrophy 3. Hypertrophy 4. Maturation.
What factors are linked to variations in fetal growth?
Energy, nutrient, and oxygen availability, and conditions that interfere with genetically programmed growth, usually environmental.
What is the role of Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) in fetal growth?
IGF-1 is the main fetal growth stimulator, and its levels are decreased by maternal undernutrition.
What does SGA stand for in newborn weight classifications?
SGA stands for small for gestational age, defined as weight below the 10th percentile for gestational age.
What is the difference between dSGA and pSGA?
dSGA (disproportionately small for gestational age) has normal head circumference and length but weight <10th percentile; pSGA (proportionately small for gestational age) has weight, length, and head circumference all <10th percentile.
What does AGA stand for and what does it indicate?
AGA stands for appropriate for gestational age, indicating weight, length, and head circumference are between the 10th and 90th percentiles for gestational age.
What does LGA indicate in newborn weight classifications?
LGA stands for large for gestational age, indicating weight is above the 90th percentile for gestational age.
What are some causes of miscarriages?
Genetic abnormalities, immunological disorders, thyroid disorders, hormone imbalances, reproductive tract infections, and drug or alcohol abuse.
How does maternal underweight and oxidative stress affect miscarriage risk?
Underweight and high levels of oxidative stress increase the risk of miscarriage.
How does BMI relate to the risk of miscarriage?
The risk of miscarriage appears to increase proportionately with increases in BMI.
What are the risks associated with preterm delivery?
Infants born preterm are at risk for death, neurological problems, congenital malformations, and chronic health problems.
How can multivitamin supplements or folate intake affect pregnancy?
They decrease the risk of preterm delivery.
What dietary recommendation is protective against preterm delivery?
Consuming one to three fish meals per week.
What factors increase the risk of preterm delivery?
Being underweight or obese and having previously delivered preterm.
What is meant by 'developmental origins of health and disease'?
It refers to the relationships between maternal and fetal exposures during pregnancy and later disease risk in offspring.
What chronic health conditions are associated with developmental origins of health and disease?
Increased risk of obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and lung diseases.
What factors influence developmental programming?
Genes and environmental exposure in utero.
What is developmental plasticity?
The ability of the developing fetus to adapt to changes in the environment.
What role do epigenetic mechanisms play in fetal development?
They influence gene expression without altering the DNA sequence, affecting development and health outcomes.
What are some key recommendations for improving health outcomes in infants?
Entering pregnancy in good health, maintaining a healthy dietary pattern, gaining appropriate weight, and reducing exposure to harmful substances.
How does pregnancy weight gain relate to newborn health?
It is related to the weight and health status of the newborn infant.
What is the recommended weight gain for underweight women during pregnancy?
28-40 lb (12.7-18.2 kg).
What is the recommended weight gain for normal-weight women during pregnancy?
25-35 lb (11.4-15.9 kg).
What is the recommended weight gain for overweight women during pregnancy?
15-25 lb (6.8-11.4 kg).
What is the recommended weight gain for obese women during pregnancy?
11-20 lb (5.0-9.1 kg).
What is the recommended weight gain for twin pregnancies?
25-54 lb (11.4-24.5 kg).
What is the typical weight gain during the first trimester of pregnancy?
~3-5 pounds.
Why are rates of weight gain important during pregnancy?
They appear to be as important to newborn outcomes as total weight gain.
What is the fetal contribution to total weight gain during pregnancy?
The fetus compromises one-third of the total weight gained.
What components contribute to weight gain during pregnancy?
Fetus, placenta, uterus, amniotic fluid, breasts, blood supply, extracellular fluid, and maternal fat stores.
What is the total weight gain at term for healthy, normal-weight women?
14.7 kg or 32 lb.