Cell: The Unit of Life
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Two types of organisms?
(i) Unicellular
(ii) Multicellular
Define Cell.
Cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
Who discovered the first dead cell?
Robert Hooke
Who discovered the first living cell?
Anton Van Leewenhooke.
Who discovered the cell nucleus?
Robert Brown
Matthias Schleidan
German Botanist ;
observed all plants are composed of different kinds of cells which form tissue of the plant.
Theodore Schwann
German Zoologist ;
discovered the plasma membrane in animals ;
concluded cell wall is unique in plants
Ruldolf Virchow
Ommnis cellula - e - cellula (all cells arise form pre existing cells)
Cell Theory
All living organism are composed of cell and cell products.
all celss arise form pre - existing cells.
activities of an organism are the outcome of the sum total of activities and interactions of its constituent cells.
Two types of cells
Prokaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic Cells
differnece in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells?
P( non membrane bound nucleus and organnelles, 70S ribosomes)
E( membrane bound nucleus and organelles, 80S ribosome[e xcept mitcbhondira and chloroplast])
main areana of cellular activities
cytoplasm
size of Mycoplasma
0.3 micro meter
longest cell
nerve cell
largest cell
egg of ostrich
size of bacteria
3 to 5 micro meter
RBC size
7 micrometer
eg. prokaryotic cells?
bacteria,
blue green algae,
mycoplasma,
PPLO (pleuro pnemonia like organisms)
in which type of cell the gentic material is basically naked?
Prokaryotic Cells
Which cells multiply faster?
Prokaryotic Cells
what is additional circular DNA outside genomic DNA called?
Plasmid
Advantages/Uses/Characteristics of Plamid?
it confers to unique charteristics( resistance to antibodies)
used for bacterial transformation with foreign DNA.
3 layered strcture of Cell Envelope
Glycocalyx
Cell Wall
Plasma Membrane
Cintents of Mesosome?
Tubules
Vesicles
Lamellae
covering of Glycocalyx
coating of mucus or polysaccharides macromolecules.
Slime Layer and Capsule
SL- Loose Sheath[ protects from water loss and dehydration]
Capsule- gummy, sticky charcter [ allows bacteria to hide from immune system]
Function of Cell Wall
provides strong structural support to prevent bursting or collapsing of bacteria
2.determines the sape of the cell
Study of Cell
Cytology
why is cell walll rigid?
due to presence of ‘peptidoglycan’(murein or mucopeptide)
Selectively permeable
plasma mebrane
where is mesosome presnt
plasma membrane
how is mesosome formed?
invagination of plasma membrane into the cell
functions of mesosme?
1. Help in cell wall formation
DNA replication
distribution of daughter cells
respiration and secretion
increase surface area of plasma membrane and enzymatic content
Who introduced Gram Staining?
Christian Gram
Gram types?
Gram positive and gram negative
3 main componets of motile bacteria ( flagellum)
hook
filament
basal body
no. of rings in basal body
4[ L, P, S, M] proteinacious disc like structure connected by central rod
two sets of basal body
Distal [ cell wall] and proximal { plasma membrane] sets
flagellum?
thin filamentous extentions from their cell wall in motil cells
filament
longets
hollow
rigid
cyclindrical
made of flagellin protein
hook?
in P Cells { Flagellin Protein}
in E Cells { Tubulin Protein}
two more non motile bodies in bacteria?
pili and fimbriae
pili?
elongated
pilin protein
help in congugation( transfer of plsmid from one bacterium to another)
true only in gram negative
fimbriae
small
bristle like
slender tubes of helically arranged protein subunits
function: attachment
two subunits of ribosomes?
70 S and 80 S
ribosome size
15 - 20 nano meter
ribosome function?
site of protein synthesis
cytoplasmic ribosomes?
remain with the cell
ribosomes on the plasma membrane
transported out cell
polysome/ polyribosome?
chain or ribosomes on a single strand of mRNA
Inclusion Bodies
material is tored in cytoplasm in form of inclusion bodies
nucleiod?
nucleus like structure
contain genetic material of prokaryotic cells- genophore
Charcteristics / Properties of an Eukaryotic Cell
cytoskeltetal structure
membane bound organelle
organisation of gentic material into chromosomes
eg of uekrayotic cells
protista, fungi,plants and animals
2 layers of lipids in Plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells
hydrophobic (inwards,water fearing and non polar)
hydrophillic ( outwards, water loving and polar)
what is plasma membrane of eurkaryotic cells composed of?
lipids in a bilayer, carbohydrates, and proteins
protein:lipid in humans
52:40
who introduced the fluid mosaic modal of Plasma Membrane
singer and nolsan
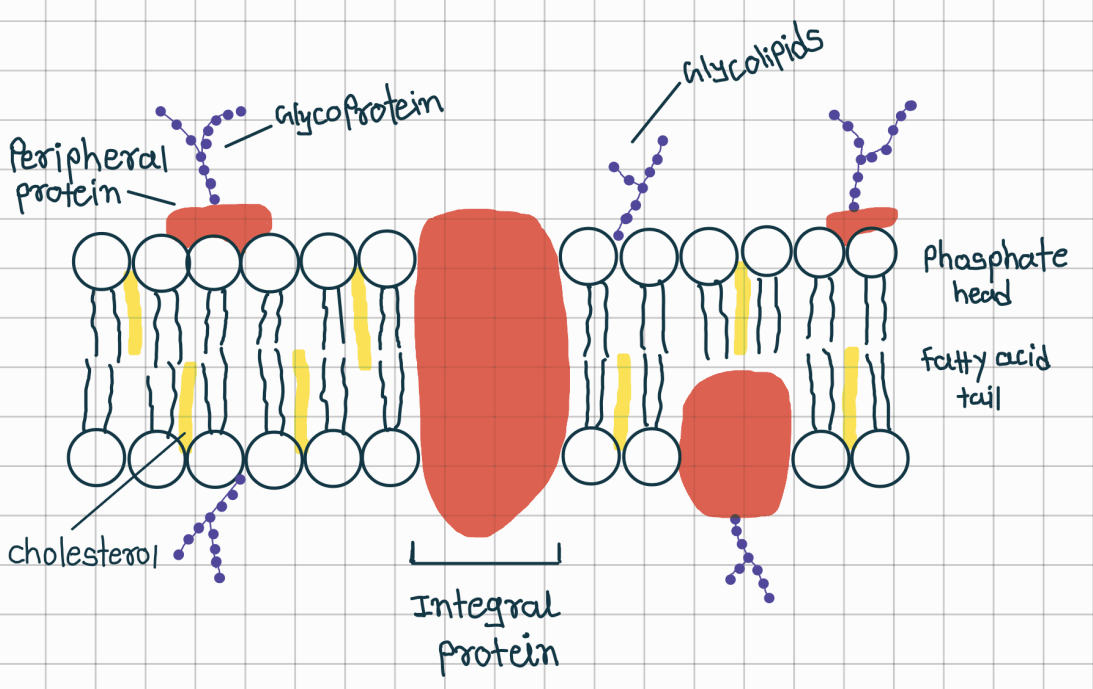
Two plasma membrane proteins of eukaryotic cells
integral/tunnel/ransmembrane/intrisic proteins( harder to extract,buried in the membrane)
Peripheral/ Extrinsic proteins( lie on surface, easy to extract)
movement of phospho lipid?
lateral and flipflop
movement of protein
lateral due to large size
what is fluidity?
the ability to move iwthin the membrane is measured as its fluidity
Functions of Plasma membrane of uerkaryotic cells
The fluid nature is important for functiosn like - cell growth, formation of intercellular junctions, secretions,endocytocis,cell dvision etc.
transport of molecules through it by Active and Passive Trandport
Passive Transport
movement of molecules across the memebrane without the requirment of energy along the concentration graddent is called passive transport.
Active Transport
The uphill movement of materials across the membrane wher ethe solute particles move against their concentration gardient is called Active Transport.(requires energy/ATP)
what is plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells also knows as
Amphipathic( smth with both polar and non polar ends)
Endocytosis?
intake of materials in the form of carrier vesicles formed by invagination of plasma membrane
two types of Endocytosis
Pinoctosis [cell drinking]
Phagocytosis [cell eating]
Exocytosis
It is the process of discharge of undigested waste products to the outside of the cell through plasma membrane [Cell Vommiting/ Ephagy]
composition of cell wall of plants
insoluble polysaccharides(cellulose)
hemicellulose
pectin
proteins
composition of fungi cell wall
chitin
componets of bacteria cell wall
peptidoglycan
Chracteristics of Cell Wall
rigid
non living
surround plasma membrane
functions of cell wall
maintains shape of cell
protects cell form mechanical injury
wards off attacks of pathogens like virus, bacteria, fungi etc.
allows materials to pass in and out of cell
helps in cell interaction and provides barrier to undesirable macromolecules
2 cell walls
1 primary cell wall
secondary cell wall
Chracteristics of Primary Cell wall
single layer
thin; elastic; capable of expansion in growing cell
grows by addition of more wall material within existing one
Charecteristics of Secondary Cell Wall
formed after maturtaion
causes thicining of Cell wall
thicker; more rigid; may contain lignin and suberin
What are Pits?
the secondary cell wlal isnt uniform and he unithickened areas are called pits
Types of pits
Simple Pit: uniform diameter of pit cavity
Bordered pit: flask shaped pit cavity
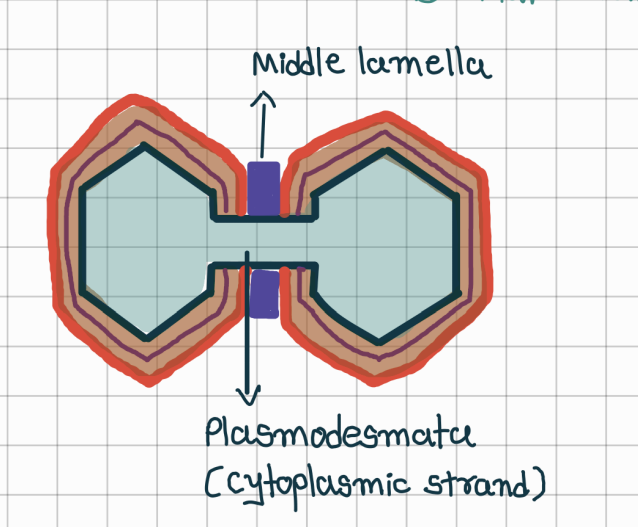
What is middle lamella
connects two adjaent cels
thin; sticky; amorphous(no clear shape)
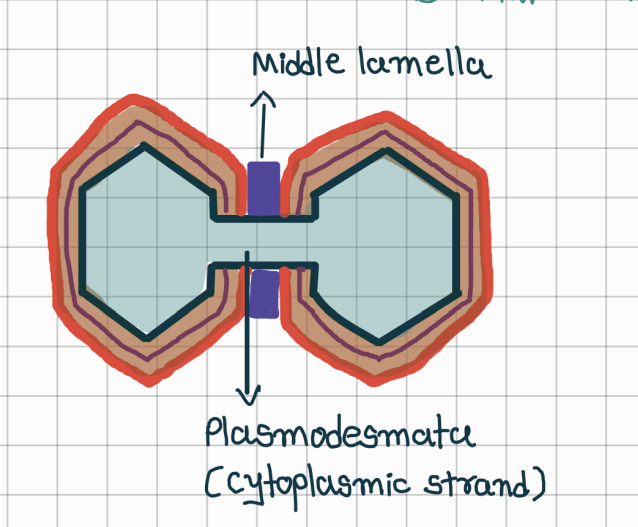
Plamodemata?
cytoplasmic starnds are present in pit through which cytoplasm of one cell is in contact with another.
what makes up the endndomembrane system?
E.R
Goldi complex
Lysosome'
Vaculoles
why aren’t mitochondira, chloroplast,and plastids included in endo.. system
their functions arent cordinated
two compartments of E.R
Luminal Compartment (inside E.R)
Extra Lumina Compartment (outside E.R)
Location of E.R
nucear membrane to plasma membrane
3 structures of E.R
cisternae
vesicles
tubules
What is Cisternae of E.R?
long; flattened; parallel; sac like structures
fount in active protein synthesis cellls
tubules of e.r
branvhed or unbranched
free from ribsome
found in cells involved in lipid or sterol synthesis
Vesicles of E.R.
oval
membane bound
vascular
free of ribosomes
types of E.R
RER
SER
SER
Free of ribosomes
smooth tubular structure
found in muscle cell- sarcoplasmic reticulum(muscle contraction)
desmotubule(inplasmodemata) is derived from SER
specialised in synthesised of lipids and sterols
detocificaion of drugs
associated with uscle contraction and uptake of Ca2+ ions
synthetic products of RER pass through SER onto GC
RER?
bear ribosomes
granular apperance
extensive and continious with other membrane of the nucleus
contains two glycoproteins- ribophorin I nad ribophorin II
protein sysnthessi and secretion
gives rise to SER
forms hydrolytic enzymes for lysome
who observed golgi appartus first?
camillo golgi
what is golgi appartus
desly stained reticular structures present neart the nucleus of the cell
a network of interconnected membrane systems and vesicles.