Chapter 3 - Depreciation and Depletion
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Depreciation
an allowable expenses in general accounting purposes and income tax accounting purposes
Depreciation
differ categorically from other conventional expenses because _____ charge does not occur in any outflow of business fund
Depreciation
allows for the companies to recover cost of an asset when it was purchased
Depreciation
allows the companies to cover the total cost of an asset over its lifespan
Depreciation
an important aspect in analyzing cost because it represents a significant portion of expenses
Depreciation
the decrease in the value of a physical property with the passage of time
Physical Depreciation
Functional Depreciation
What are the types of depreciation?
Physical Depreciation
TYPES OF DEPRECIATION
this is due to the reduction of the physical ability of an equipment or asset to produce results
Functional Depreciation
TYPES OF DEPRECIATION
this is due to the lessening in the demand for the function which the property was designed to render
To enable the cost of depreciation to be included as a cost in the production of goods and services
Annual costs of depreciation are being put up in a fund called depreciation reserve for replacement of the property
To recover capital invested in the property
Provide as an additional capital termed as depreciation reserve
Purpose of depreciation:
It must have a determinable life and the life must be greater than 1 year.
It must be something used in business or held to produce income.
It must be something that gets used up, wears out, decays, become obsolete, or loses its value due to natural causes.
It must not be an inventory stock in trade or investment property.
Properties of depreciable assets:
Initial Investment/First Cost (FC)
the cost of acquiring an asset, including transportation expenses and other normal costs of making the asset serviceable for its intended use
Book Value (BV)
worth of a property or an asset as shown on the accounting records of the company
Book Value (BV)
the original cost of the property less allowable depreciation deductions
Salvage Value (SV)
the amount that will be paid by a willing buyer to a willing seller for a property after depreciation is completed
Useful Life (L)
the expected period that a property will be used in trade or business to produce income
Physical Life
the length of time during which the property is capable of performing the function
Economic Life
length of time during which the property may be operated at a profit
Recovery Period (n)
the number of years over which the basis of property is recovered through the accounting process
Recovery Rate (i)
a percentage for each year of the recovery period that utilized to compute an annual depreciation deduction
d = annual cost of depreciation
L = useful life
n = any year during the life of the property
dn = depreciation cost during year n
Dn = total cost of depreciation after n years
FC = initial investment, original cost, first cost
SV = salvage value/scrap value
BV = book value at the end of n years
Methods of depreciation symbols:
Straight Line Method (SLM)
Sinking Fund Method (SFM)
Declining Balance Method
Double Declining Balance Method (DDBM)
Sum of the Year Digit Method (SOYDM)
Service-Output Method (SOM)
Methods of depreciation:
Straight Line Method (SLM)
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
the simplest depreciation method
Straight Line Method (SLM)
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
assumes that the loss in the value is directly proportional to the age of the equipment or asset
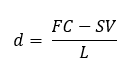
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
For the straight line method (SLM), what is the formula for finding the annual cost of depreciation?
Dn = nd
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
For the straight line method (SLM), what is the formula for finding the total depreciation after n years?
BVn = FC - Dn
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
For the straight line method (SLM), what is the formula for finding the book value at the end of n years?
Sinking Fund Method (SFM)
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
assumes that a sinking fund is established in which funds will accumulate for replacement
Sinking Fund Method (SFM)
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
the total depreciation that has taken place up to any given times is assumed to be equal to the accumulated amount in the sinking fund at that time
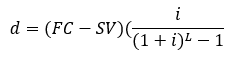
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
For the sinking fund method (SFM), what is the formula for finding the annual cost of depreciation?
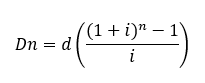
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
For the sinking fund method (SFM), what is the formula for finding the total depreciation after n years?
BVn = FC - Dn
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
For the sinking fund method (SFM), what is the formula for finding the book value at the end of n years?
Constant Percentage Method/Matheson Formula
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the declining balance method sometimes called?
Declining Balance Method
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
in this method, it is assumed that the annual cost of depreciation is a fixed percentage of the salvage value at the beginning of the year
Declining Balance Method
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
the ratio of the depreciation in any year to the book value at the beginning of that year is constant throughout the life of the property and is designated by k, the rate of depreciation
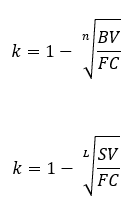
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the formula to find k for the declining balance method?
dn = Fc(k)(1 - k)n - 1
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the formula to find the annual depreciation d for the declining balance method?
SV = Fc(1 - k)L
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the formula to find the salvage value for the declining balance method?
Dn = Fc(1 - (1 - k)n)
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the formula to find the total depreciation Dn for the declining balance method?
BVn = FC - Dn
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the formula to find the book value at the end of n years for the declining balance method?
Sum of the Year Digit Method (SOYDM)
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
a method of evaluating depreciation where the depreciation changes from year to year
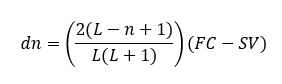
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the formula to find the annual depreciation for the sum of the year digit method (SOYDM)?
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the formula to find the total depreciation for the sum of the year digit method (SOYDM)?
BVn = FC - Dn
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the formula to find the book value of the sum of the year digit method (SOYDM)?
Service-Output Method (SOM)
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
this method assumes that the total depreciation that has taken place is directly proportional to the quantity of output of the property up to that time
Service-Output Method
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
this method has the advantage of making the unit cost of depreciation constant and giving low depreciation expense during periods of low production
Service Method (number of hours used)
Output Method (number of units produced)
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What are two methods under service-output method (SOM)?
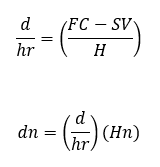
H = total units of hours used and within the useful life
Hn = total number of hours used at nth year
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the formula for the service method in the service-output method (SOM)?
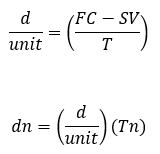
T = total number of units produced within the useful life
Tn = number of units produced at the nth year
METHODS OF DEPRECIATION
What is the formula for the output method in the service-output method (SOM)?
Depletion
this method is generally applied in case of wasting assets (e.g., mines, quarries, natural resources)
Depletion
here, the rate of production is measured by the rate of exhaustion of the asset
Depletion
under this method, the total reserve of asset is measured by an expert value, which after, the cost per unit of reserve asset is ascertained by dividing the cost of acquisition of the asset by the total reserve of that asset
Periodic Depreciation
calculated by multiplying the reserve of assets exhausted during the period by the cost per unit of reserve asset
Depletion Method
in this method, the asset is reduced to zero at ends of the total exhaustion
cost depletion
The capitalized costs that generally go into the _____ basis for petroleum and mining projects are for mineral rights acquisition and/or lease bonuses or their equivalent ascertained costs.
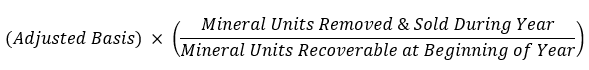
where,
Adjusted Basis - Cost Basis ± Adjustments - Cumulative Depletion
What is the formula for cost depletion?
Step 1: Determination of the depletion base.
Step 2: Computation of depletion rate per unit.
Step 3: Computation of depletion/depreciation charge.
Three steps involved in computation of depreciation under depletion method:
Depletion Base
comprises of cost incurred to acquire or lease the asset, exploration cost, development cost, and any cost incurred to restore the property to its original condition after the assets or resources have been fully depleted
Depletion Rate Per Unit of a Natural Resource or Asset
depends upon the total number of units expected to be extracted
Depletion Rate Per Unit of a Natural Resource or Asset
calculated by dividing the depletion base less salvage value (if any) by the number of units expected to be extracted

What is the formula for the depletion rate per unit of a natural resource or asset?
Depletion Charge for the Period = Units Extracted During the Period × Depletion Rate
The units extracted during the period are multiplied by the depletion rate per unit to compute the depletion/depreciation charge for the period.
What is the formula for the depletion/depreciation charge for the period?
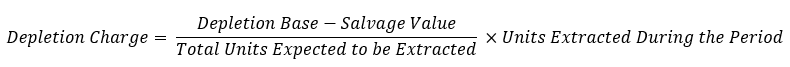
What is the combined formula of the three steps to find the depletion/depreciation charge?