ANSC 3060 Quiz 1 Video 1
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lymphatic & Immune System
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
functions of the lymphatic system
drains excess interstitial fluid from body tissues and returns to circulatory system
transports lipids and fat soluble vitamins absorbed through intestines
immune response
components of the lymphatic system
lymph
lymphatic vessels
primary lymphatic organs & tissue (immunocompetence) - red bone marrow, thymus
secondary lymphatic organs & tissues (battle grounds) - lymph nodes, spleen, lymphatic nodules (including GALT)
lymph
clear, yellowish liquid derived from intestinal fluid
up to 3 L created daily
mainly water and proteins
interstitial fluid
formed when blood plasma filters out of capillaries; fills spaces between cells
lymphatic capillaries
fluid can come in but not go out
composed of overlapping endothelial cells anchored to tissues
how is lymph circulated?
1-way valves - animal movement squeezes vessels
skeletal muscle pump - muscles squeeze back towards heart
respiratory pump
lymphoid cells
lymphocytes
macrophages
dendritic cells (APCs)
reticular cells
lymphocytes
protect the body against specific infectious antigens; when activated, they differentiate into powerful immune cells; B cells and T cells
B cells
differentiate into plasma cells which eliminate antigens using protein antibodies (secrete antibodies); stay in bone marrow
T cells
attack and destroy infected cells directly; leave bone marrow and go to thymus for immunocompetence - cells that don’t make it undergo apoptosis
macrophages
generalist phagocytes that eat foreign substances and activate T cells
dendritic cells
capture antigens and present them to the lymphocytes in lymph nodes and elsewhere
lymph nodes
small bean-shaped organs; occur in dense clusters near mammary glands, axillaries, & groin; filter lymph; site of B cell proliferation

label lymph node locations (not in picture - ears)
& parotid - ears

lymph node anatomy
mainly solid - lots of reticular tissue; outer cortex has B cell follicles, inner cortex has T cells in transit
lymph node circulation
lymph enters through afferent lymph vessels
flows along subcapsular sinuses
flows along trabecular sinuses
collects in medullary sinuses
thymus
around the heart
pre-t cells - more mature than in cortex
dendritic cells
epithelial cells
thymic copuscle - contains regulatory T-cells which prevent autoimmune reactions
spleen
largest lymphatic organ, located below stomach and kidneys
functions:
destruction of old RBCs
immune response to blood-borne pathogens
platelet & macrophage storage
blood supply
splenic artery
splenic vein
spleen anatomy
very fragile, composed of reticular CT
capsule
trabeculae (muscular)
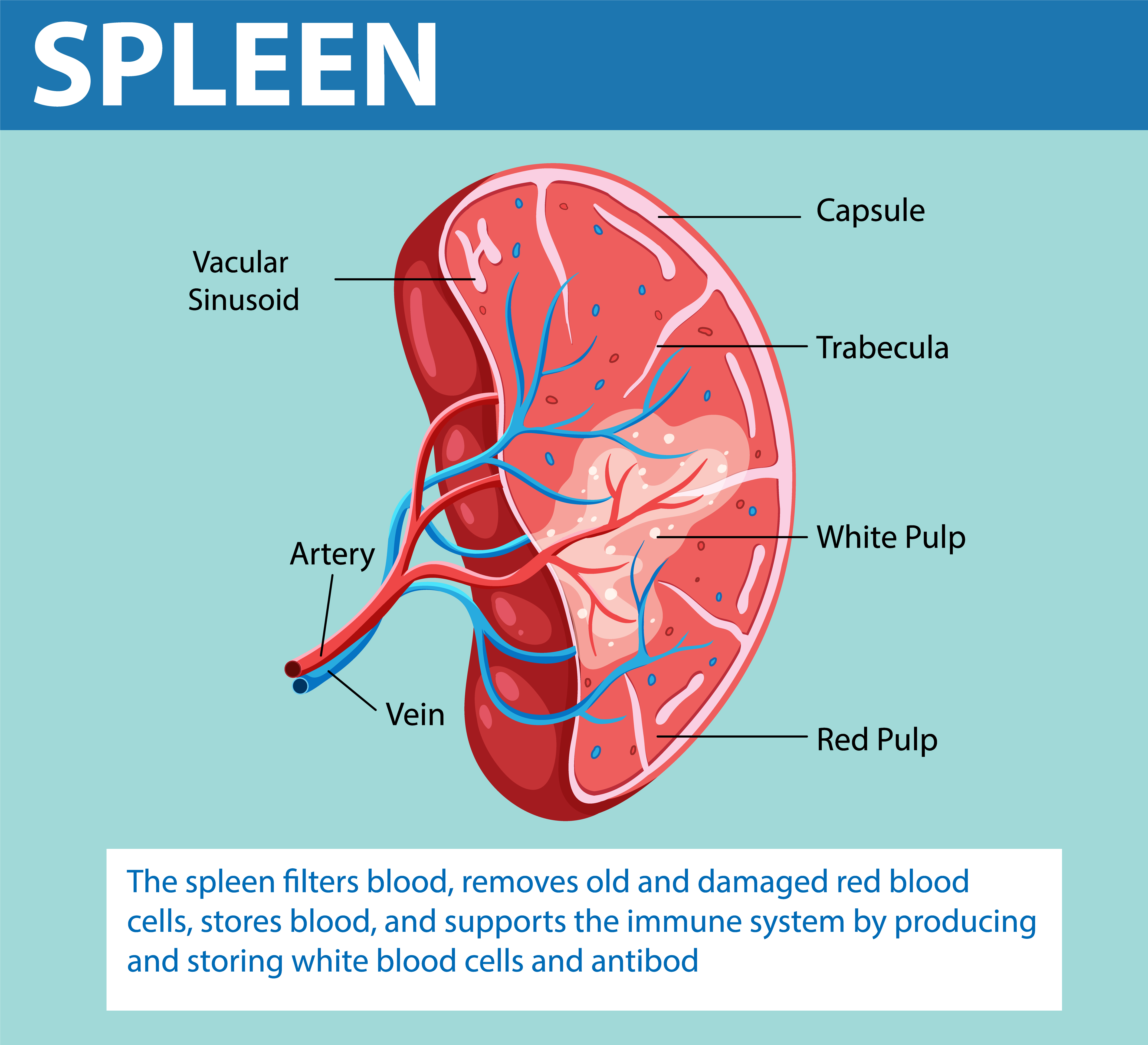
spleen white pulp
lymph & macrophages; B&T cells (WBCs) proliferate and perform immune functions
macrophages destroy blood-borne pathogens
spleen red pulp
venous sinuses; removal of old blood cells
platelet storage
production of
Gut Associated Lymphatic Tissues (GALT)
scattered throughout connective tissue lining mucus membranes
NOT surrounded by capsule
ex: tonsils, appendix, peyer’s patch (intestines)
lots of lymph in DI tract - food contamination
tonsils
body learns abt pathogens and begins to mount defense/create antibodies for future
peyer’s patches
clusters of lymphoid tissue located in wall of intestine
essential in the immune surveillance of pathogens entering digestive tract
antigen
any substance or organism that provokes an immune response (pollen, bacteria, virus); often proteins
pathogen
disease-producing microbes (bacteria viruses, protozoa, fungi)
resistance
ability to ward off diseases by recognizing the pathogen (looks at part = antigen; pathogen can be antigen)
nonspecific resistance
present at birth, provide immediate but general protection against many pathogens, internal or external
ex: inflammatory response, phagocytes, natural killer cells, antimicrobial proteins
natural killer cells (NK)
attack cells that display abnormal plasma proteins
kill pathogen by releasing perforins or inducing apoptosis
phagocytes
ingest microbes and cellular debris through phagocytosis, two types
neutrophils - granular leukocyte
macrophages - from monocytes (type of leukocyte); wandering/fixed
inflammation
non-specific defense responsive to tissue damage
symptoms - redness, heat, swelling
vasodilation (immediate) - release of substances from damaged tissue increases diameter of arterioles and permeability of capillaries
emigration of phagocytes (1 hr+) - diapedesis
diapedesis
process by which white blood cells move out of the capillaries into the surrounding tissue
specific resistance (adaptive immunity)
ability of body to defend itself against specific pathogens
specificity, memory, systemic
cell-mediated immune response, antibody-mediated immune response
cellular immunity
t-cells act against target cell
kill infected cells, release chemicals that enhance inflammatory response or activate other lymphocytes /macrophages
cellular immunity has cellular targets
humoral immunity
antibodies produced by b-cells circulating freely in body fluids, bind temporarily to target cell
temporarily inactivate
mark for destruction or phagocytes or complement
humoral immunity has extracellular targets
epitope
reactive region of antigen
antigen receptors
molecules capable of recognizing certain kinds of antigens
antigen receptor diversity
genes determine which foreign substances the immune system will recognize
cell receptors result of acquired knowledge of microbes likely in environment
lymphocytes make up to a billion different types of antigen receptors
coded for ~25k genes
gene segments shuffled by recombination
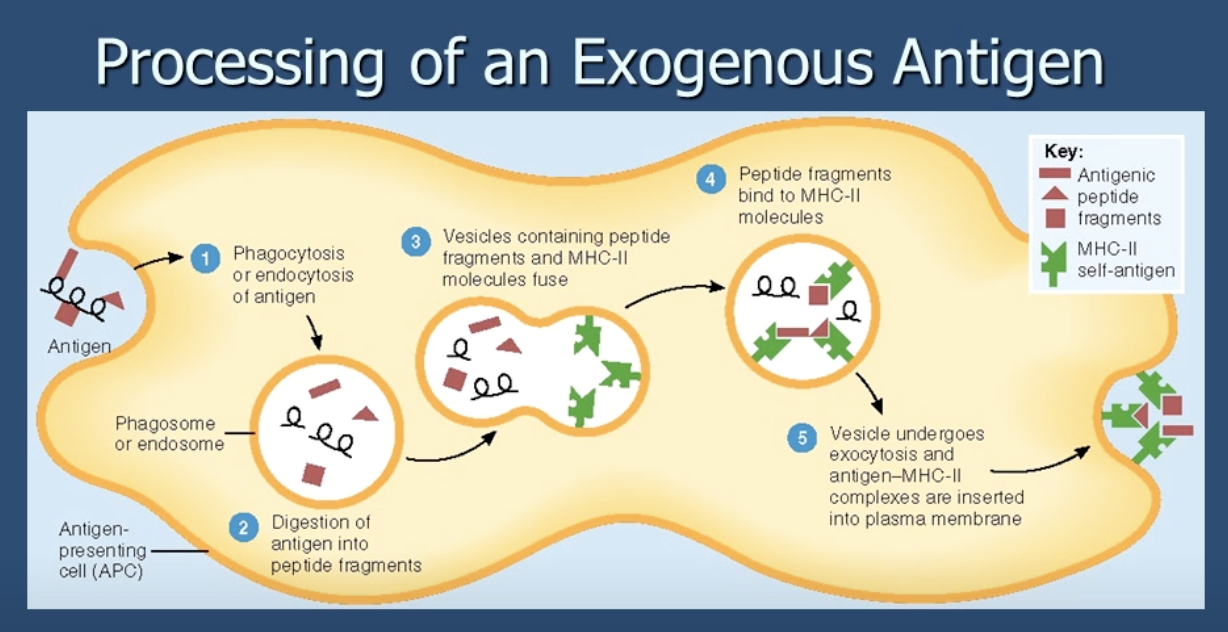
processing of an exogenous antigen
t-cell types
helper t-cells, cytotoxic t-cells, memory t-cells
helper t-cells
recognize foreign antigens associated with MCH II markers on Antigen-presenting cells (APC)
cytotoxic t-cells
recognizes foreign antigens associated with MHC I markers on infected body cells
kills target cells (with perforin or lymphotoxin)
memory t-cells
remain after cell-mediated immune response with specificity to antigen already encountered
antibody mediated immunity
b-cells bind to free region
come antigen taken into cell, combine with MHC II, incorporated into cell membrane
helper t-cells recognize antigen-MHC complex and costimulate b-cell
some activated b-cells divide and differentiate into plasma cells
plasma cells produce antibodies which attack antigen directly
antibodies (immunoglobulins)
glycoproteins that bind with and disable specific antigens; produced by plasma cells
antibody classes
IgG - most abundant in blood
IgA - protects mucus membranes from bacteria/viruses
IgM - found in blood lymph
IgD - found mainly on antigen receptors
IgE - located on cast basophils (least abundant)
ELISA
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; test that uses antibodies and color change to identify (ex: SNAP tests, pregnancy test, heart worm/panleuk/parvo tests)
active immunity
results from exposure to the antigen via infection/vax (artificial active imm.)
results in formation of memory B and T cells
effects are long-lasting
passive immunity
results from administration or transfer of antibodies but NOT generation of B or T cells
relatively short lived
ex. colostrum antibody transfer