Econ practice set ch.1, 2, 3 & 5
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
constant unitary elasticity
when a given percent price change in price leads to an equal percentage change in quantity demanded or supplied
elastic demand
when the elasticity of demand is greater than one, indicating a high responsiveness of quantity demanded or supplied to changes in price
elastic supply
when the elasticity of either supply is greater than one, indicating a high responsiveness of quantity demanded or supplied to changes in price
elasticity
an economics concept that measures responsiveness of one variable to changes in another variable

inelastic demand
when the elasticity of demand is less than one, indicating that a 1 percent increase in price paid by the consumer leads to less than a 1 percent change in purchases (and vice versa); this
indicates a low responsiveness by consumers to price changes
inelastic supply
when the elasticity of supply is less than one, indicating that a 1 percent increase in price paid to the firm will result in a less than 1 percent increase in production by the firm; this indicates a low responsiveness of the firm to price increases (and vice versa if prices drop)
infinite elasticity
the extremely elastic situation of demand or supply where quantity changes by an infinite amount in response to any change in price; horizontal in appearance
AKA perfect elasticity
price elasticity
the relationship between the percent change in price resulting in a corresponding percentage
change in the quantity demanded or supplied
price elasticity of demand
percentage change in the quantity demanded of a good or service divided the percentage change in price
price elasticity of supply
percentage change in the quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price
zero inelasticity
the highly inelastic case of demand or supply in which a percentage change in price, no matter how large, results in zero change in the quantity; vertical in appearance
allocative effciency
the channeling of resources to their most productive and desired uses
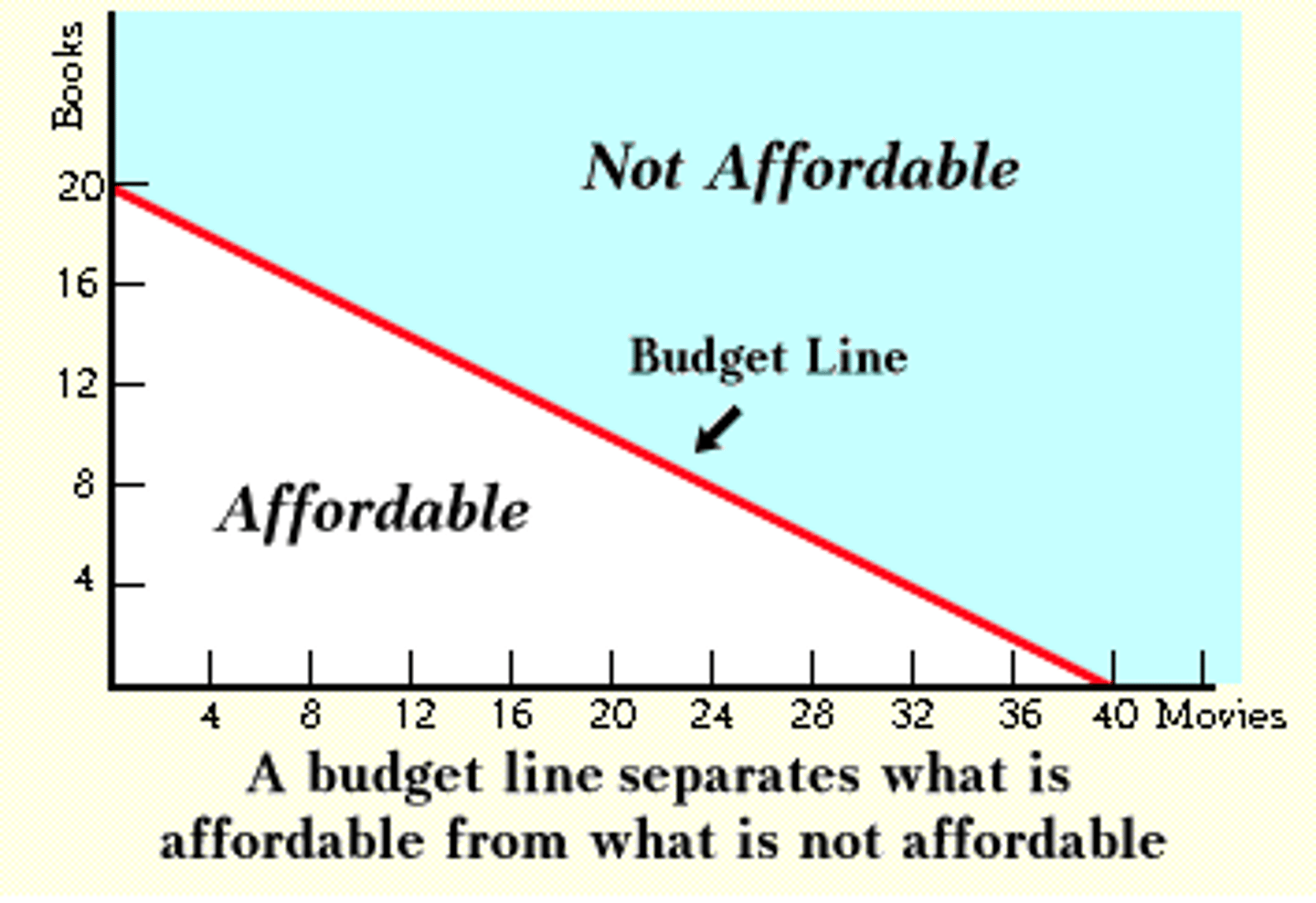
budget constraint
all possible consumption combinations of goods that someone can afford, given the prices of goods, when all income is spent; the boundary of the opportunity set

comparative advantage
when a country can produce a good with a lower opportunity cost than another country

invisible hand
Adam Smith's term for the natural self-regulation of a market economy driven by self-interest and efficiency

law of diminishing marginal utility
as we consume more of a good or service, the utility we get from additional units of the good or service tend to become smaller than what we received from earlier units
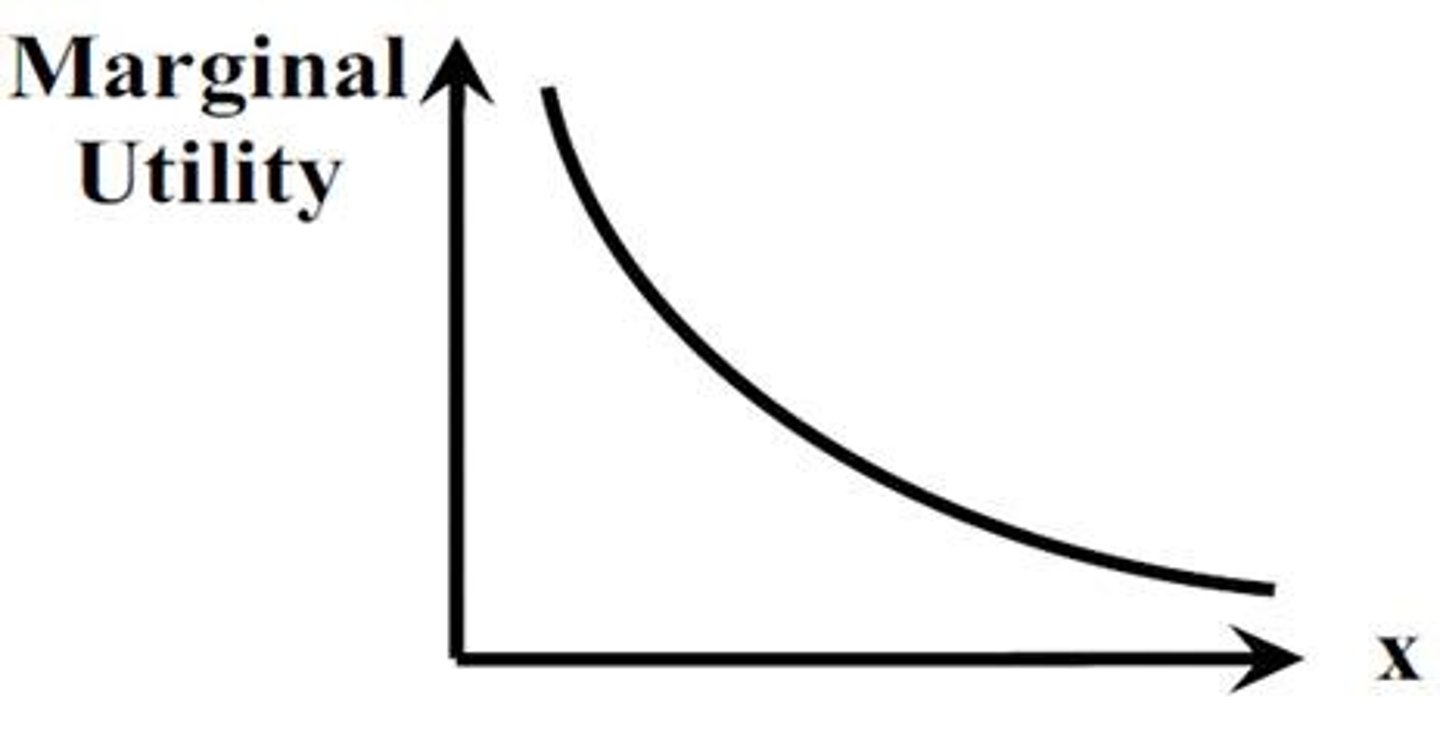
law of diminishing returns
as additional increments of resources are added to producing a good or service, the marginal benefit from those additional increments will decline
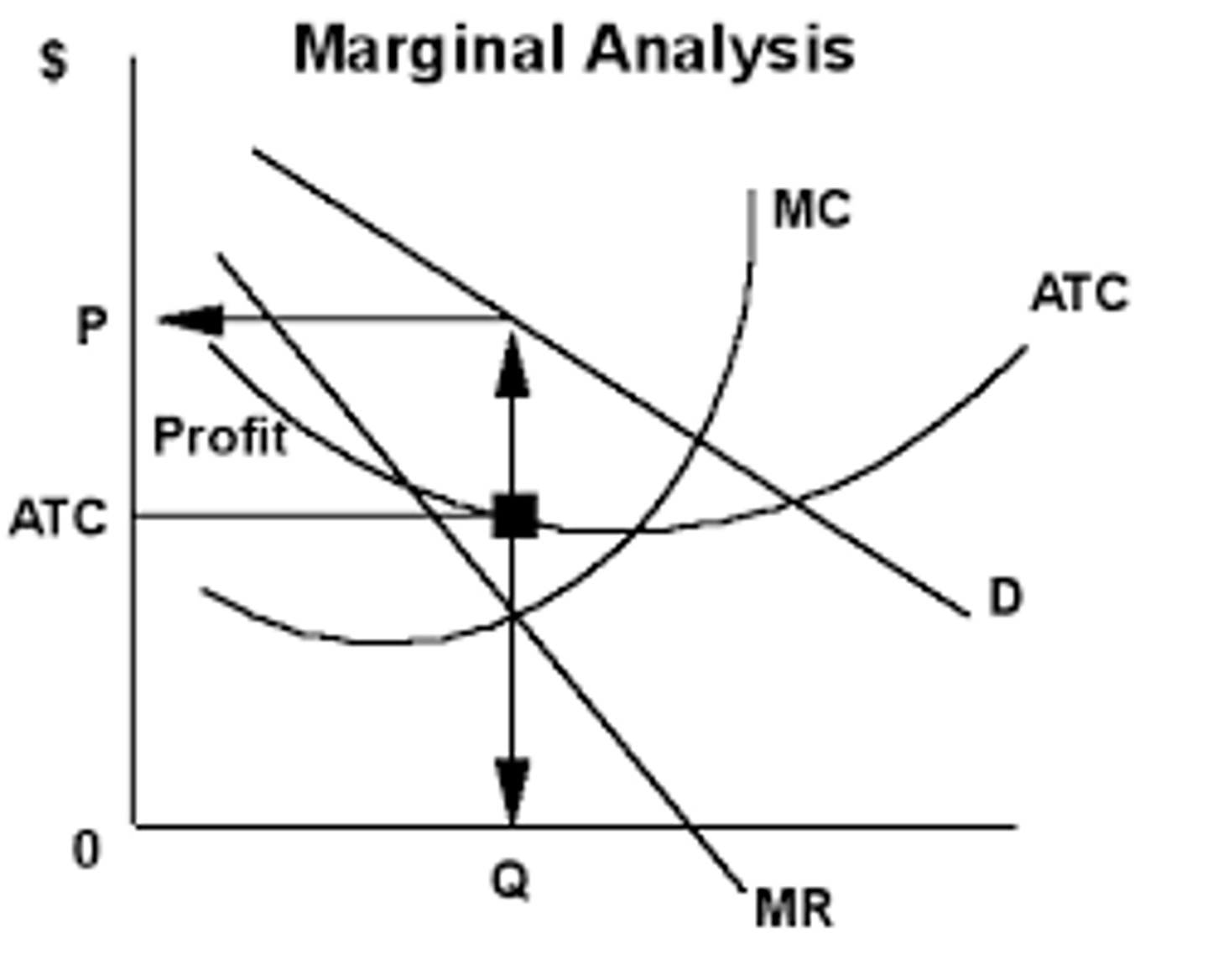
marginal analysis
examination of decisions on the margin, meaning a little more or a little less from the status quo
normative statement
statement which describes how the world should be

opportunity cost
Cost of the next best alternative use of money, time, or resources when one choice is made rather than another

opportunity set
all possible combinations of consumption that someone can afford given the prices of goods and the individual's income
positive statement
statement which describes the world as it is
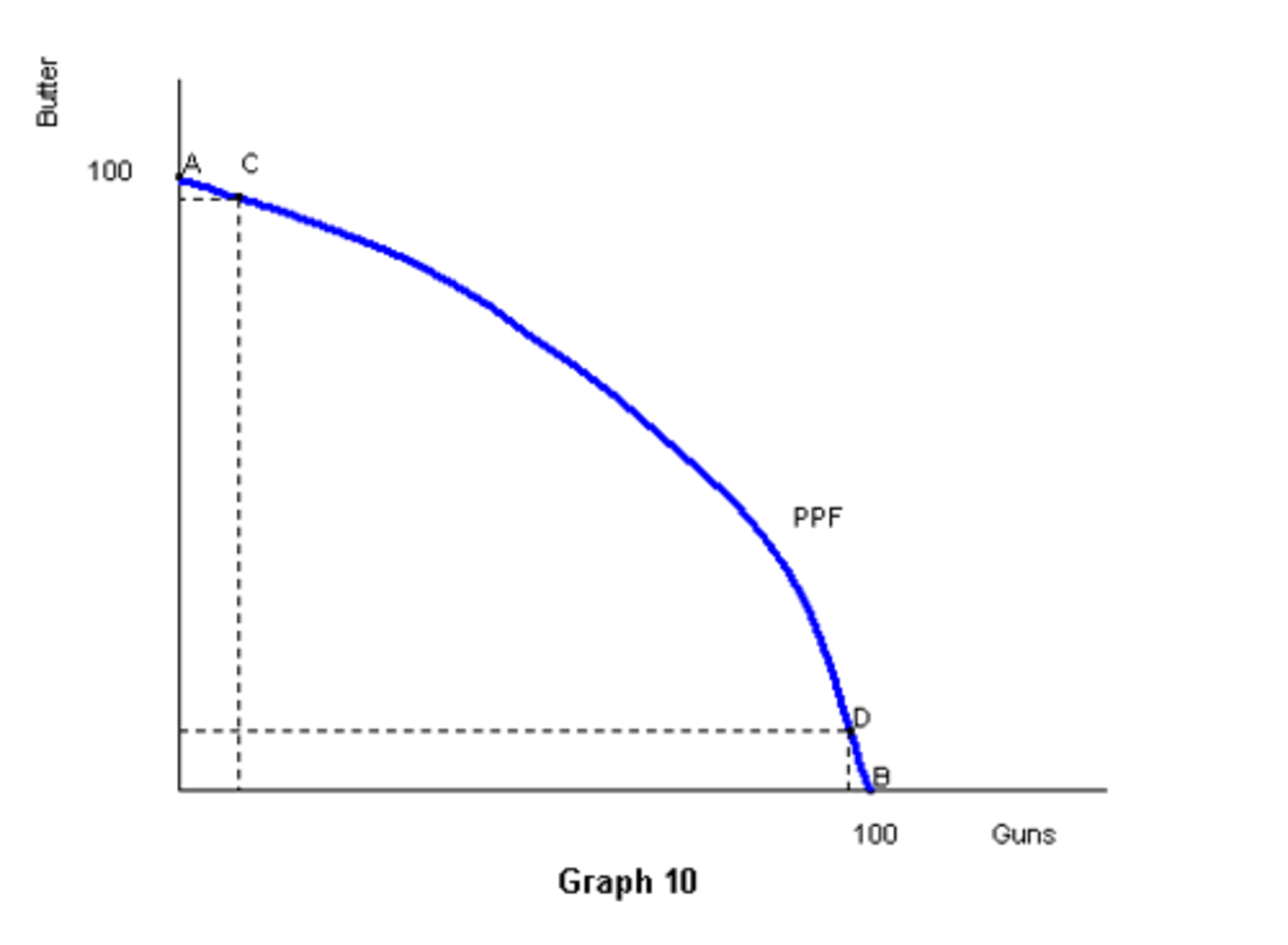
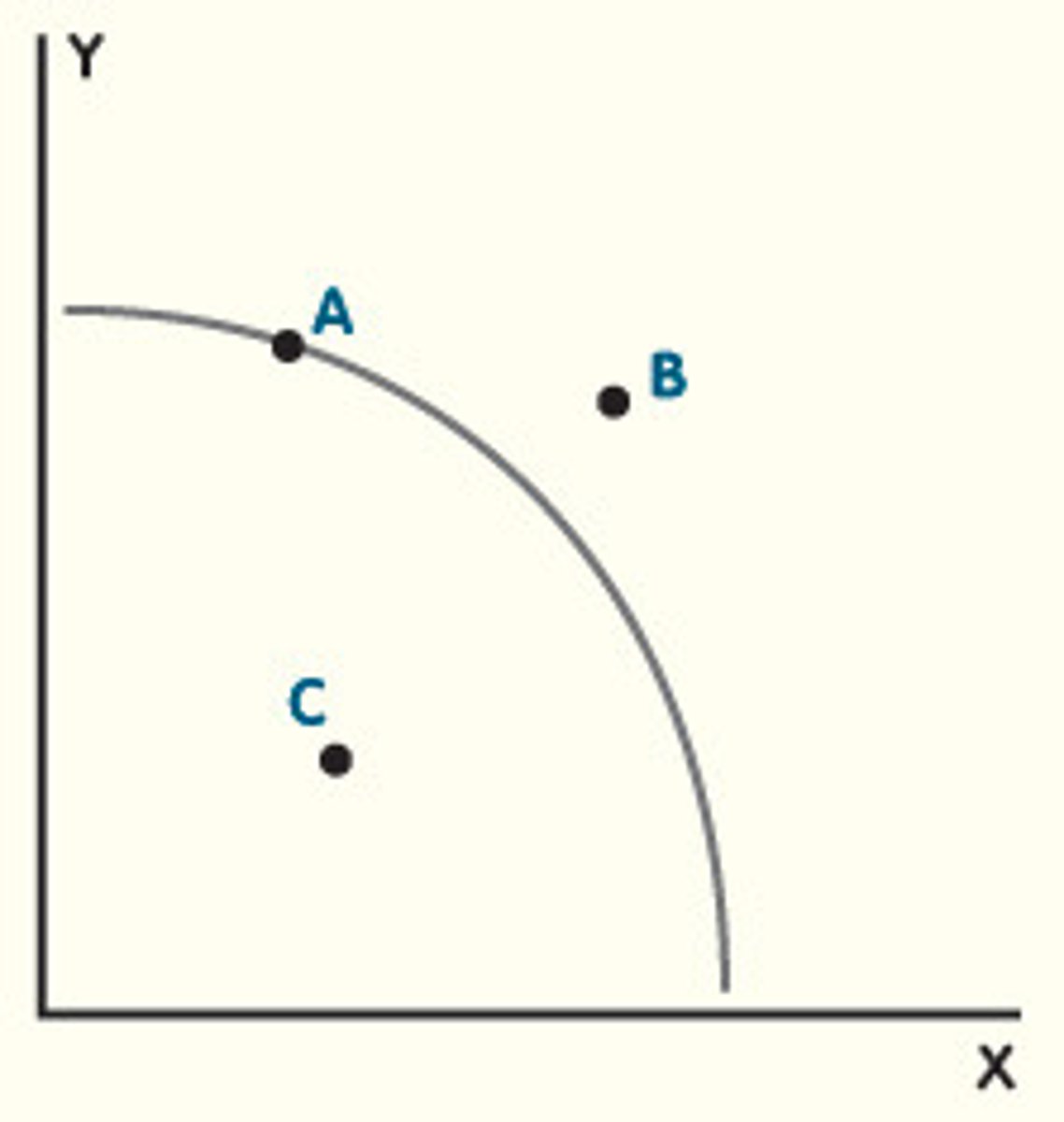
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)
a curve showing the maximum attainable combinations of two products that may be produced with available resources and current technology
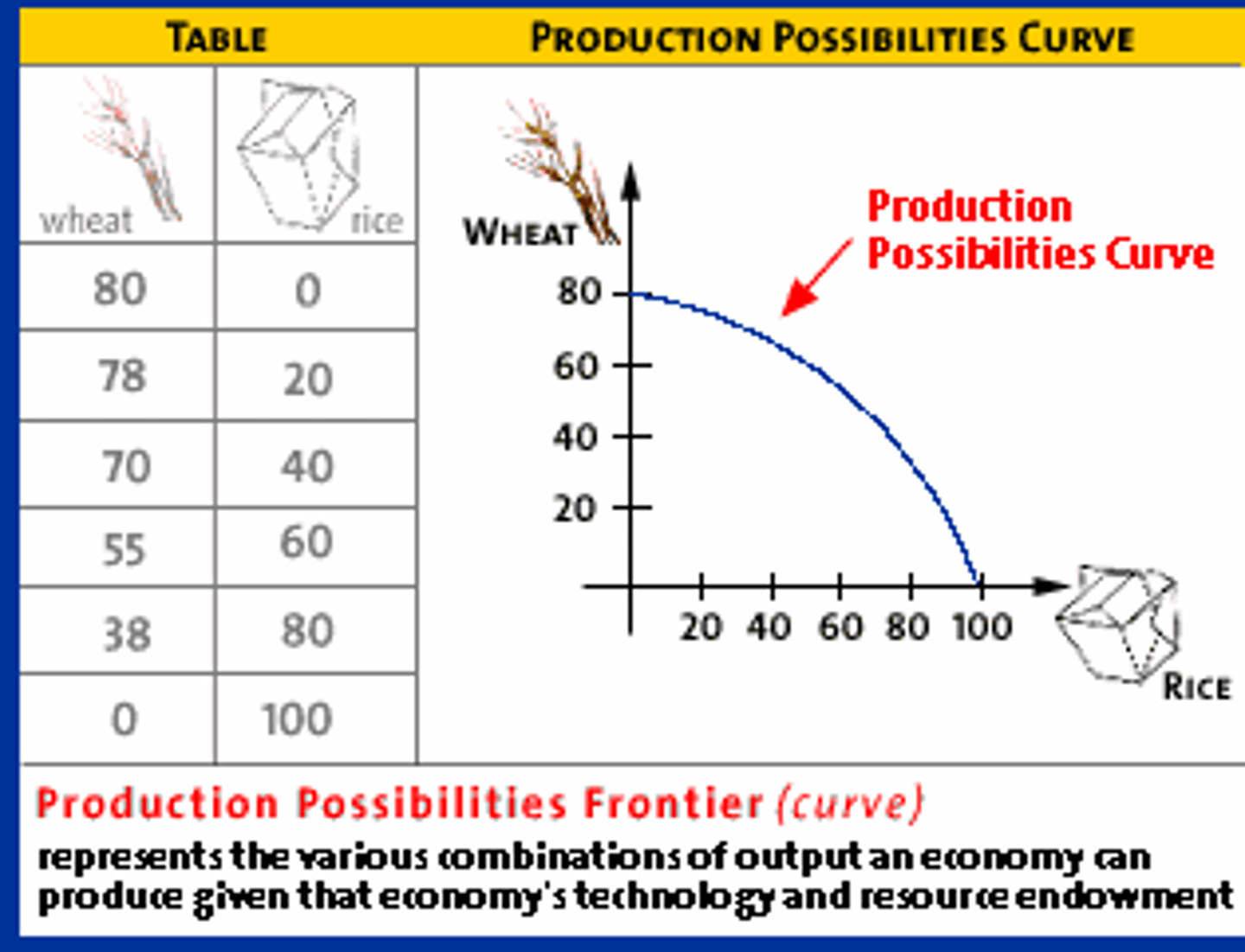
productive efficiency
a situation in which a good or service is produced at the lowest possible cost
sunk costs
costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered

Utility
Ability or capacity of a good or service to be useful and give satisfaction to someone.

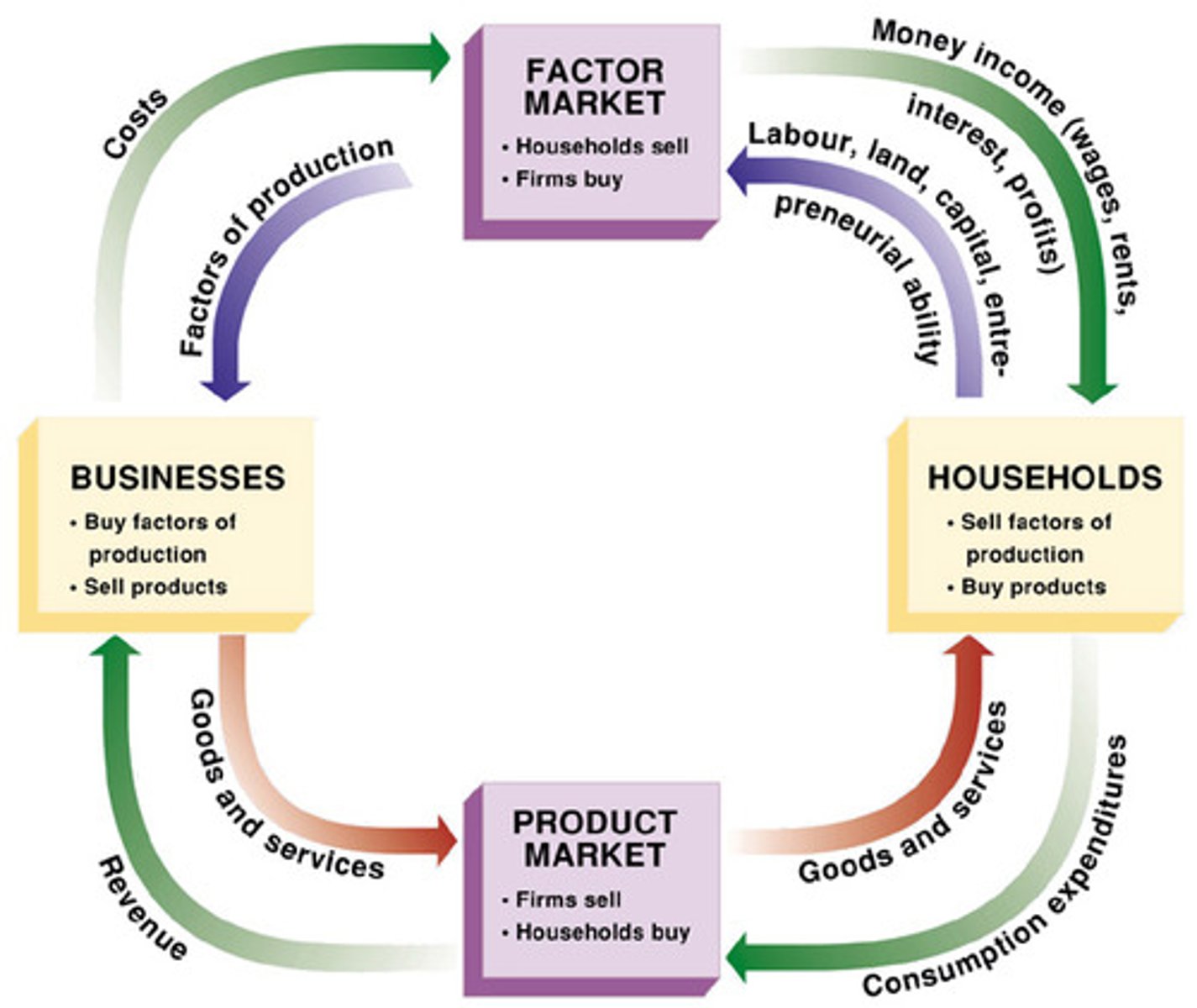
Circular Flow Diagram
a diagram that views the economy as consisting of households and firms interacting in a goods and services market and a labor market
Command Economy
an economy where economic decisions are passed down from government authority and where the government owns the resources
Division of Labor
the way in which different workers divide required tasks to produce a good or service
Economics
the study of how humans make choices under conditions of scarcity
Economies of Scale
when the average cost of producing each individual unit declines as total output increases
Exports
products (goods and services) made domestically and sold abroad
Fiscal Policy
economic policies that involve government spending and taxes
Globalization
the trend in which buying and selling in markets have increasingly crossed national borders
Goods and Service Market
a market in which firms are sellers of what they produce and households are buyers
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
measure of the size of total production in an economy
Imports
products (goods and services) made abroad and then sold domestically
Labor Market
the market in which households sell their labor as workers to business firms or other employers
Macroeconomics
the branch of economics that focuses on broad issues such as growth, unemployment, inflation, and trade balance
Market
interaction between potential buyers and sellers; a combination of demand and supply
Market Economy
an economy where economic decisions are decentralized, private individuals own resources, and businesses supply goods and services based on demand
Mircroeconomics
the branch of economics that focuses on actions of particular agents within the economy, like households, workers, and business firms
Monetary Policy
policy that involves altering the level of interest rates, the availability of credit in the economy, and the extent of borrowing
Private Enterprise
system where private individuals or groups of private individuals own and operate the means of production (resources and businesses)
Scarcity
when human wants for goods and services exceed the available supply
Specialization
when workers or firms focus on particular tasks for which they are well-suited within the overall production process
Theory
a representation of an object or situation that is simplified while including enough of the key features to help us understand the object or situation
Traditional Economy
typically an agricultural economy where things are done the same as they have always been done
Underground Economy
a market where the buyers and sellers make transactions in violation of one or more government regulations
Model
A more applied or empirical representation and used to test theories
Ceteris Paribus
Other things being equal. "Any given demand or supply curve is based on the ceteris paribus assumption that all else is held equal".
Demand Curve
A graphic representation of the relationship between price and quantity demanded of a certain good or service, with quantity on the horizontal axis and the price on the vertical axis.
Demand Schedule
A table that shows a range of prices for a certain good or service and the quantity demanded at each price.
Demand
Refers to the amount of some good or service consumers are willing and able to
purchase at each price.
Quantity Demanded
The total number of units of a good or service consumers are willing to purchase at a given price.
Shift in Demand
When a change in some economic factor (other than price) causes a different quantity to be demanded at every price (ex: drought is predicted and people stock up on water).
Law of Demand
The common relationship that a higher price leads to a lower quantity demanded of a certain good or service and a lower price leads to a higher quantity demanded, while all other variables are held constant. It's an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Normal Good
A good in which the quantity demanded rises as income rises, and in which quantity demanded falls as income falls.
Complements
Goods that are often used together so that consumption of one good tends to enhance consumption of the other.
Substitutes
A good that can replace another to some extent, so that greater consumption of one good can mean less of the other.
Supply
The relationship between price and the quantity supplied of a certain good or service
Supply Curve
A line that shows the relationship between price and quantity supplied on a graph, with quantity supplied on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis.
Supply Schedule
A table that shows a range of prices for a good or service and the quantity supplied at each price.
Quantity Supplied
The total number of units of a good or service producers are willing to sell at a given price.
Shift in Supply
When a change in some economic factor (other than price) causes a different quantity to be supplied at every price.
Law of Supply
The common relationship that a higher price leads to a greater quantity supplied and a lower price leads to a lower quantity supplied, while all other variables are held constant.
Inputs/factors of production
The combination of labor, materials, and machinery that is used to produce goods and services; also called "factors of production".
Equilibrium
The situation where quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied; the point where the supply curve (S) and the demand curve (D) cross.
Equilibrium Price
The price where quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied.
Equilibrium Quantity
The quantity at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal for a certain price level.
Excess Demand/Shortage
At the existing price, the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied; also called a "shortage".
Excess Supply/Surplus
At the existing price, quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded; also called a surplus.
Price Ceiling
A legal maximum price. Keeps a price from rising above a certain level (the "ceiling").
Price Control
Government laws to regulate prices instead of letting market forces determine prices.
Price Floor
A legal minimum price. Keeps a price from falling below a certain level (the "floor").
Minimum Wage
A price floor that makes it illegal for an employer to pay employees less than a certain hourly rate