6.4- Cloning and Biotechnology
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
vegetative propagation
form of asexual reproduction
genetically identical individuals develop from non-reproductive tissues of parent plant such roots, stems, leaves
methods of natural vegetative propagation
rhizomes
stolons (runners)
Suckers
Tubers
Bulbs
rhizomes
specialised horizontal underground stems
store food and can produce new vertical shoots and roots from nodes along rhizome
e.g. marram grass
stolons
horizontal stems that grow along soil surface away from parent plant
nodes or stem tips that can root to form new plant upon contact with ground
e.g. strawberries
suckers
shoots that emerge from shallow root bud of parent plant
e.g. elm trees
tubers
form when tip of stem becomes swollen with food
buds on tuber surface can develop into new shoots
e.g. potatoes
bulbs
form when leaf base becomes swollen with stored food
bud inside bulb can form new shoots
e.g. daffodil
what is a cutting
a section of stem, root or leaf taken from parent plant and planted in soil→ grows into clone of parent
taking stem cuttings
cut 5-10 cm piece of parent’s plant stem using sharp, sterile tool
remove lower leaves, leaving only one leaf at the top
dip cut end in rooting powder- contains plant hormones to encourage root growth
plant cutting in a suitable growth medium e.g. compost
place in warm, moist conditions to promote root development
transplant new clone once rooted
cuttings from roots or leaves
root cuttings → take section of root and make angled cut on one end before treating it as you would a stem cutting
leaf cuttings→ remove entire leaf, score veins and place in growing medium with scored veins facing down
advantages of vegetative propagation
fast
high yield ensured
cost effective
maintains quality of crop
allows plant to survive adverse conditions and regenerate each season
disadvantages of vegetative propagation
results in lack of genetic variation in offspring
plants more susceptible to diseases, pests and climate change
what is micropropagation
technique for producing many identical plant clones from a single parent plant through tissue culture
type of asexual reproduction
steps in making a tissue culture for micropropagation
explant collection:
small tissue samples taken from parent plant to start micropropagation
typically taken from stem and root tips→ meristem cell which are totipotent
sterilisation
explant’s cells sterilised to remove and inhibit growth of contaminants e.g. bacteria
reduces risk of widespread infection
culture
sterilised explant cells cultured on nutrient rich medium→ supplies minerals, sugar, growth hormones etc
development
cells in each explant divide to form undifferentiated mass of cells→ callus
callus cells transferred to new medium with specific conditions to encourage shoot and root formation
allows callus cells to differentiate and develop into plantlets
transfer
fully formed plantlets moved to growth medium e.g. soil
can develop into mature plants- identical to parent plant
applications of micropropagation
enables rapid, large scale propagation of plants that naturally reproduce slowly or are rare or endangered
used for producing disease-free clones of crops and preserving valuable genetic resources
allows mass production of GM plants
can be used to produce seedless plants
advantages of micropropagation
produces genetically identical plants→ reliable inheritance of traits
can be carried out at all times of the year
more space-efficient compared to conventional propagation methods
rapidly produces large number of mature plants
disadvantages of micropropagation
All plants genetically identical (monoculture)→ vulnerable
may unintentionally propagate undesirable traits
expensive and requires skilled technicians- less feasible on small scale
explants and plantlets vulnerable to infection
natural animal cloning in invertebrates
some invertebrates undergo regeneration or fragmentation
forms new, genetically identical offspring from parts of bodies that have broken off
natural cloning in vertebrates
can occur naturally when early embryo splits into 2 genetically identical embryos
each embryo grows independently, resulting in genetically identical offspring i.e. identical twins
what is artificial embryo twinning
single embryo manually split
produces multiple identical offspring from single embryo
process of artificial twinning
female organism treated with hormones to produces multiple ova
ova extracted and fertilised in petri dish to produce embryo
embryo divides into several cells and embryo is split while cells are still totipotent
each cell placed into its own petri dish to develop into individual embryos
embryos implanted into uteruses of surrogate mothers
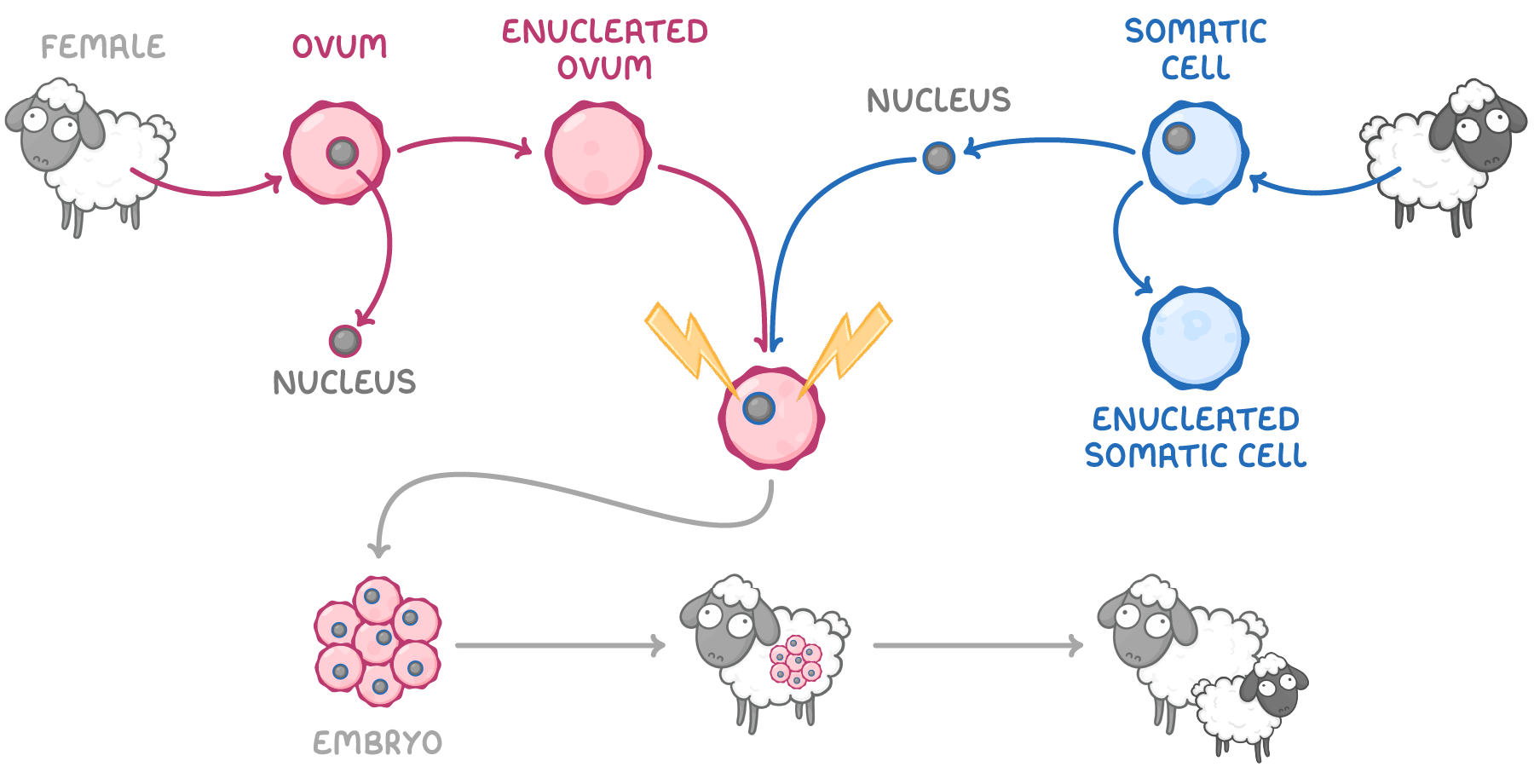
what is somatic cell nuclear transfer
nucleus transferred from somatic (body) cell of one animal into ovum of another to form embryo
steps in somatic cell nuclear transfer
somatic cell nucleus removed from adult animal
ovum of different female animal of same species is enucleated
nucleus from somatic cell transferred into enucleated ovum
somatic nucleus fused with enucleated ovum→ stimulated by electric shock
fused cell begins dividing→ forming embryo
embryo implanted into uterus of surrogate mother
surrogate eventually gives birth to clone of somatic cell donor
applications of animal cloning
medical research→ drug testing and disease modelling
Conservation→ can boost numbers of endangered species from limited gene pool
Agriculture→ can replicate animals with desirable characteristics
Pharming→ can produce therapeutic proteins
Stem cells→ provide source of immunocompatible stem cells for tissue repair
arguments for animal cloning
ensures transmission of desirable characteristics to multiple offspring
enables reproduction of infertile animals
helps preserve biodiversity
can rapidly increase population size of species
facilitates medical advancements that could alleviate suffering
arguments against animal cloning
high costs and technically complex
reduced genetic diversity increases disease risk
potential for shorter lifespans in clones
ethical concerns regarding destruction of embryos
cloned animals have health issues
inefficient→ high failure rates so many ova used to produce 1 cloned offspring
what is biotechnology
use of living organisms or their components e.g. enzymes to synthesise, break down or transform materials for human use
often uses microorganisms
applications of microbes in biotechnology
brewing
baking
Cheese Making
Yoghurt
medicines→ bioengineered fungi + bacteria produce drugs
bioremediation→ microbes speed up degradation of pollutants like oil spills
bioremediation
uses microbes to decompose pollutants and contaminants in soil or water
two main approaches:
use natural organisms→ uses microbes’ natural ability to digest organic materials
develop GM organisms for specific contaminants→ uses bacteria to break down/ accumulate specific pollutants
advantages of using microorganisms in biotechnology (7)
cost-effective mass production= lower consumer prices
no ethical issues related to animal welfare
rapid reproduction rates= large-scale production
simple nutrient requirements
high protein, low fat= efficient food source as meat alternative
genetic modification= enhanced nutrient profiles
independent of weather or breeding cycles
Disadvantages of using microorganisms in biotechnology (6)
sterile conditions necessary- can increase costs
risk of contamination by unwanted microbes
potential toxin production
separation of microorganisms from nutrient broth required for food production
differences in taste and texture from traditional food sources
social concerns about GM foods or microbes on waste products
why are microorganisms cultured in biotechnology
to generate biomass of microorganisms→ use in producing single cell protein as animal feedstock
to manufacture compounds the microbes synthesise e.g. antibiotics, vitamins, enzymes
primary metabolites
substances that are produced in processes essential for microbial functioning
e.g. ethanol from respiration of yeast
secondary metabolites
substances produced in non-essential processes
e.g. antibiotics or plant defence chemicals
components of bioreactors (6)
metal/ plastic tank with inputs and outputs for liquids and gases
paddles for mixing culture to ensure even distribution of food, oxygen and temperature throughout
probes to monitor pH, temperature and dissolved oxygen
ports for adding ingredients and removing products
sterilisation system e.g. steam injection
nutrient medium
how are conditions optimised inside bioreactors (5)
fresh medium circulated by bioreactors→ constant supply of nutrients for microbes
heating/cooling water jacket surrounds vessel→ ensures optimal temp. for microbes
pH monitored by pH probe and adjusted automatically by adding acids and bases→ allows optimal pH for enzyme activity
sterile air pumped in→ allows sufficient oxygen for aerobic respiration
steam sterilisation between batches and removal of waste products→ prevents contamination which could kill the culture
batch fermentation
microbes grown in a fixed volume in individual batches until nutrients deplete and waste accumulates
each batch followed by emptying and cleaning of the vessel before starting next batch
continuous fermentation
continuously supplying fresh nutrients and removing culture broth
maintains growth of culture indefinitely
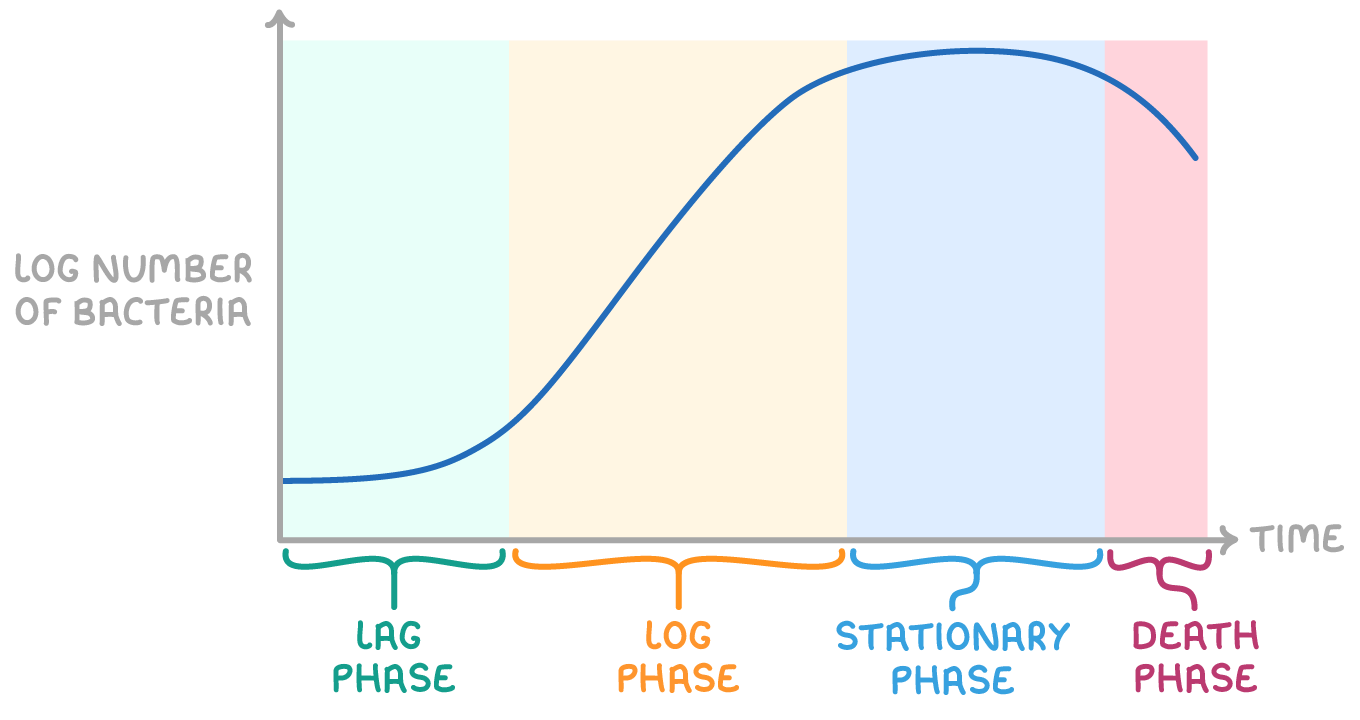
microbial growth curves in batch cultures
lag phase→ initial cell growth as they adapt to environment and produce essential enzymes
log phase→ rapid doubling of cell numbers occurs under ideal conditions and growth rate is at its maximum
stationary phase→ growth rate plateaus as nutrients diminish and waste accumulates- cell growth= cell death
death phase→ cell death exceeds cell growth rate due to resource limitation and build up of toxins
factors affecting microbial growth
temperature
pH
nutrient availability
antimicrobial substances
what is enzyme immobilisation
a way of reusing enzymes
attaching or enclosing an enzyme onto a solid support or matrix
allow the reuse of the enzyme and increases its stability
main methods of immobilising enzymes
binding→ enzymes bound to insoluble support materials e.g. cellulose/ collagen fibres by covalent or ionic bonds
adsorption→ enzymes adsorbed onto the surface of insoluble support materials
entrapment→ enzymes trapped in a matrix or microcapsule
encapsulation→ enzymes isolated by partially permeable membrane
advantages of using immobilised enzymes
cost effective→ allows reuse of enzymes= reduced need to purchase new enzymes
product purity→ avoids contamination of products with the enzyme
improved stability→ immobilised enzymes more tolerant of temp. and pH changes- less likely to denature
disadvantages of enzyme immobilisation
higher initial costs
reduced enzyme activity- may change shape of active or allosteric sites
technical problems→ complex reactor systems more prone to technical problems
immobilising lactase to produce lactose-free milk
lactase enzyme attached to alginate beads to immobilise it
lactase- containing beads packed into a column
milk allowed to flow through the column
lactase hydrolyses lactose in milk into glucose and galactose→ produces lactose- free milk
lactase remains in column, allowing continual processing of milk
lactose-free milk can be used to make dairy products