ANP W13 The Sensory System
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What are the 3 classifications of Sensory Receptors based on its structure?
Free dendrite (pain/temp)_
End-organ/modified or encapsulated’ dendrite (touch/pressure)
Specialized (rods and cons of retina)
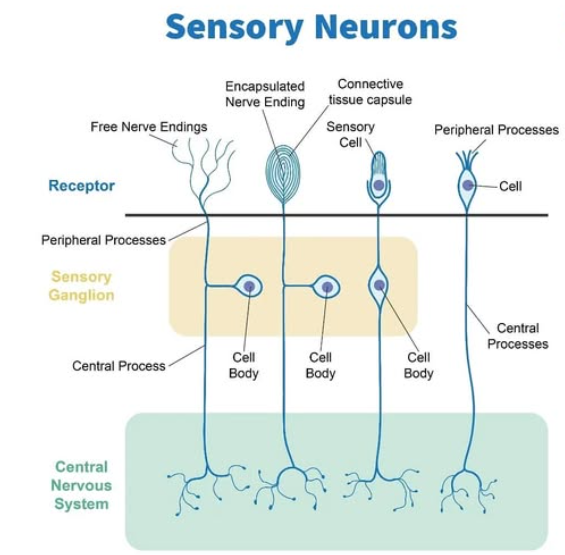
What are the 4 classifications of Sensory receptors based on function (type of stimulus they respond to)
Chemoreceptors → taste and smell
Photoreceptors → light
Thermoreceptors → temperature
Mechanoreceptors → movement
Sensory receptors can be classified based on the distribution. What receptors are considered Special Sense?
Special sense = localized special sense organ
Vision
Hearing
Equilibrium
Taste
Smell
Sensory receptors can be classified based on the distribution. What receptors are considered General sense?
General sense = widely distributed receptors throughout body
Pressure
Heat/cold
Pain/Touch from skin and internal organs
Proprioception (sense of position from muscles, tendons and joins)
What is a palpebra? What muscle is it attached to?
eyelid → protecting front of the eye.
upper eyelid attached to levator palpebra
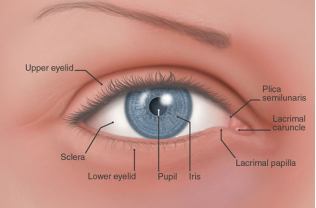
What is the conjunctiva?
Thin membrane lining the surface of the eyelid and covers the visible portion of the sclera (white part of eye)
How many extrinsic muscles does the eye have?
6 - originate on the bone of the orbit and insert on the surface of the sclera.
named after their location and direction of the muscle fibres.
responsible for “convergence” of the eyes = normal inward movement of both eyes to form 1 visual field.
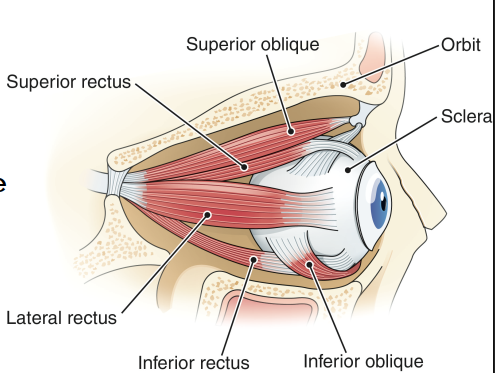
Which nerve supplies the eye for transmit visual information to the brain?
Optic Nerve (CN 2) and Ophthalmic branch of the Trigeminal Nerve
Which cranial nerves innervate the eye muscles?
Trochlear CN 4
Abducens CN 6
Oculomotor CN 3 (largest)
What are the 3 layers of the eyeball?
Sclera (white part of the eye)
Choroid → vascular layer; delicate network of connective tissue; pigmented dark brown to help prevent light scatter
Retina → neural layer; contains rods and cones; covers posterior surface only
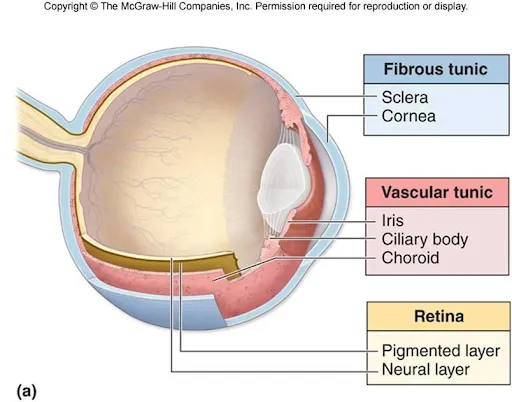
What are the 4 refractive parts of the eye?
Cornea
Aqueous Humor → watery fluid fills the eyeball anterior to the lens
Lens → biconvex shape
Vitreous body → soft jelly-like substance filling the space behind the lens and maintains eyeballs shape
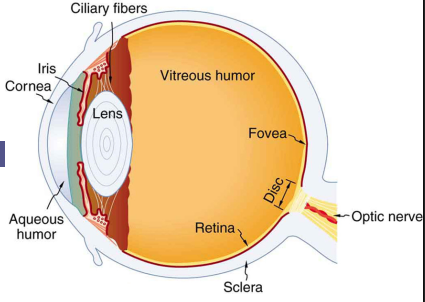
What is Accommodation of the eye?
process of adjusting the lens thickness to allow for vision at near and far distances.
Ciliary muscles contracts and removes the tension on suspensory ligaments.
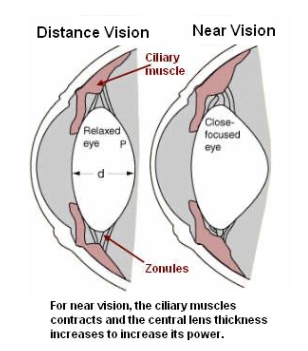
What is the function of the Iris?
Regulates amount of light entering the eye by contracting and relaxing circular muscle fibres and radial fibres of the iris to change the size of the pupil
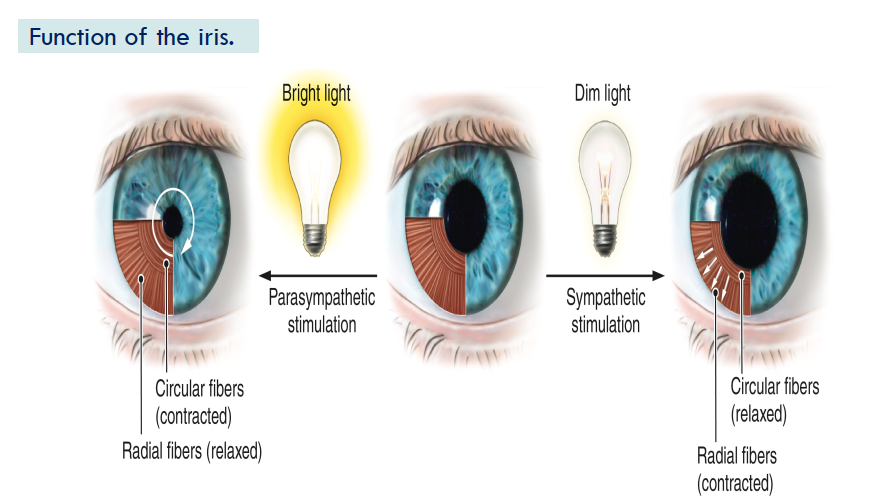
Photoreceptor Rods
work best in dim light
does not detect colour
greater number than cones
Rhodopsin pigment → Vit A required to produce pigment
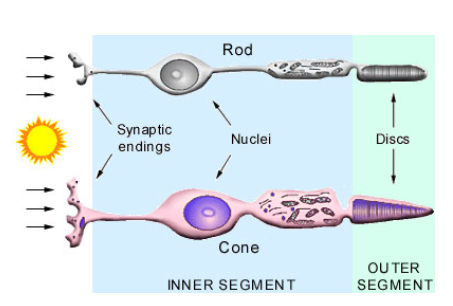
Photoreceptor Cones:
Sensitive to light
detects colour
gives sharp images
located in center of retina (fovea centralis)
3 types of cones. Red, green blue light (L,M,S)
What is Amblyopia?
loss of vision in a health eye because it cannot work properly with the other eye (from persistent strabismus)
also called lazy eye
What is Inclusion conjunctivitis?
An acute eye infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis.
Trachoma = chronic infection from chlamydia that can cause blindness
What is the name of the type of conjunctivitis that is introduced at birth?
Ophthalmia neonatorum aka neonatal conjunctivitis
How does diabetes affect the retina?
Diabetic Retinopathy = high blood sugar damages the retina's blood vessels. This damage leads to leaking, swelling, abnormal blood vessel growth, and can result in blurred or distorted vision, floaters, and even blindness.
What is the disorder caused by retinal degeneration or lack of vitamin A that leads to inability to see in dim light ?
Nyctalopia (night blindness)
Where is the blind spot located in the eye?
Optic disk where optic nerve exits the eye.
What are the difference between Wet and Dry Age-related Macular degeneration?
Wet = abnormal bloos vessel growth under the retina causing detatchment
less common
Dry = material accumulates on th retina causing gradual vision loss.
more common
dry progresses to wet typically (not the other way around)
What are the 3 main components of the ear?
Outer ear = pinna (entire ear structure outside the skull) and canal
Middle ear = air space containing 3 small bones
Inner ear = contains the sensory receptors for hearing and equilibrium
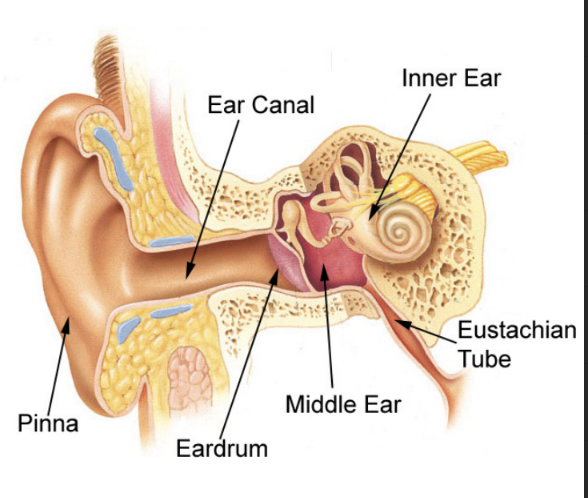
What structure of the outer ear has a thin lining and contains ceruminous glands (producing ear wax)?
External auditory canal/Meatus
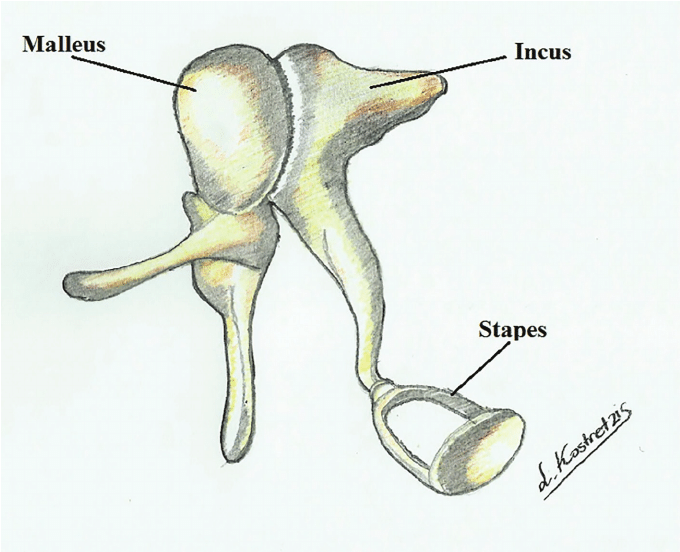
3 ossicles of the middle ear.
Malleus → incus → stapes (in contact with inner ear)
fx: amplifies sound waves and transmits to the inner ear
What are the 3 divisions of the inner ear. Describe each.
Vestibule - 2 bony structures involved in maintaining equilibrium
Semicircular canal - 3 bony tubes in 3 planes involved in equilibrium
Cochlea - snail-shell shaped struture used for hearing
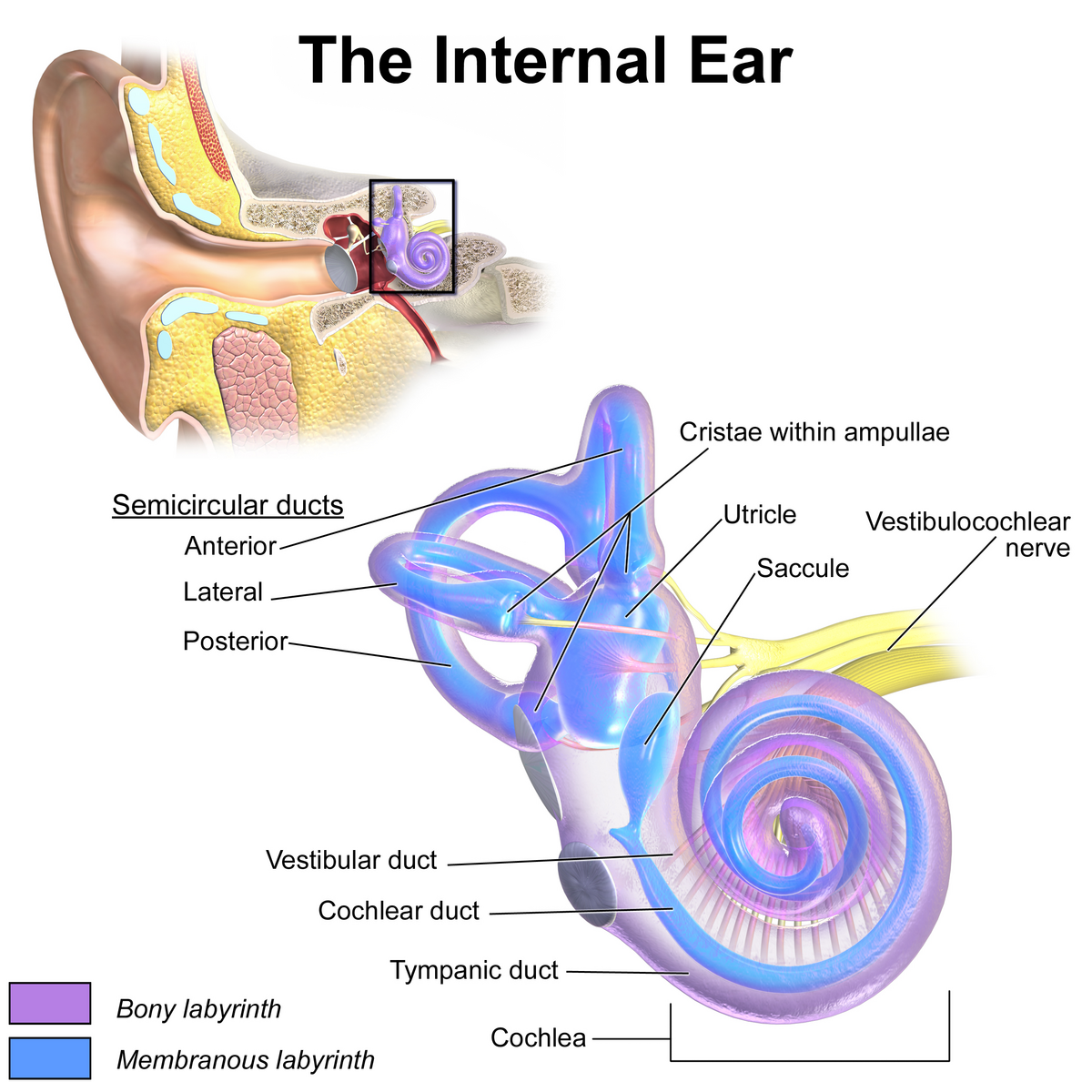
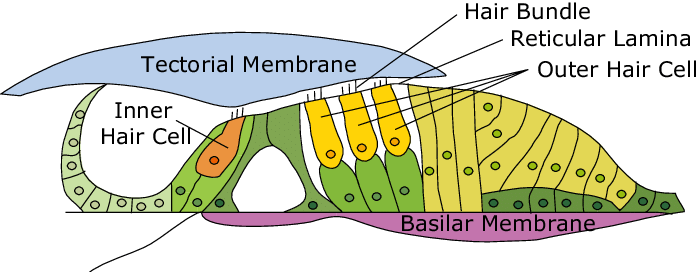
What is the name of the spiral organ, composed of hair cells that lies within the cochlea ?
Organ of Corti - located inside cochlear duct
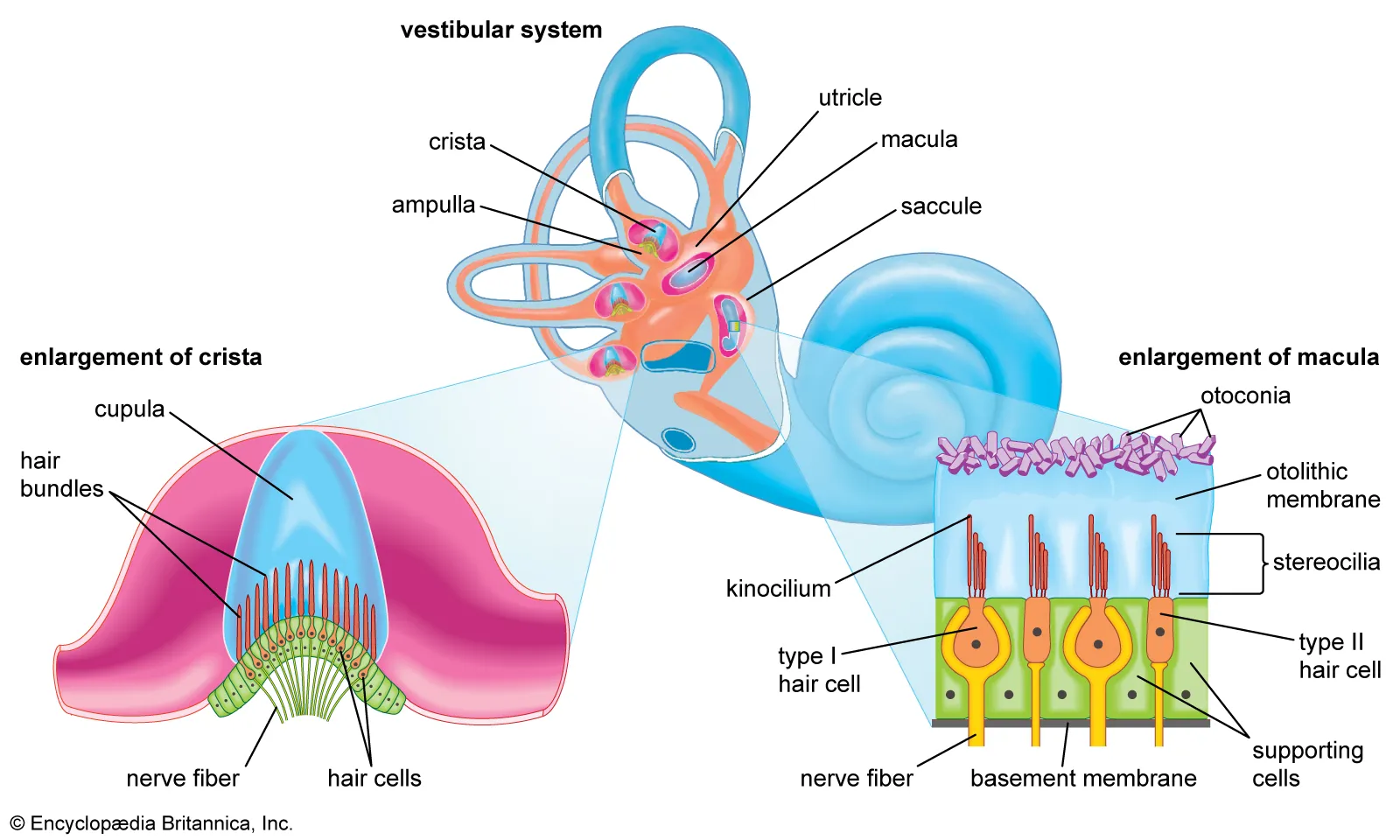
The sensory receptors within the vestibule and semicircular canals are _____. What are the 2 types?
Ciliated
Maculae → in the vestibule; senses position of the head relative to gravity and acceleration
Cristae → in the semicircular canals; detects rotational acceleration
*supplied by the vestibular nerve (CN8)
What is the difference between sensorineural hearing loss and Conductive hearing loss?
Sensorineural = damage to auditory nerves or cochlea
ex. age related hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss = problems with the structures that conduct sound waves to the inner ear
ex. wax accumulation, otosclerosis, damage to tympanic membrane/ossicles
What are the 2 cranial nerves involved with taste receptors?
Facial (CN7) and Glosspharyngeal (CN9)
most taste receptors are located on the vallate papillae
Which lobe of the brain receives impulses from olfactory receptors?
Temporal lobe
Which receptors detect light touch?
Mesinners corpuscle (tactile corpuscles)
fingertips, toes, lips, tip of the tongue
Which receptors detect pressure ?
Pacinian corpuscle - located in subcuntaneous tissue in skin and near the joints
Sense of positioning is detected by which receptors?
Proprioceptors - located in muscles, tendons, joints
What do Nociceptors detect?
Pain - widely distributed
2 pathways of pain to the CNS.
sharp acute pain pathway
slow chronic pain pathway
What are 5 methods of pain relief?
Analgesics → non-narcotic drugs, narcotics → acts on CNS
Anaesthetics → prevent pain, relieve chronic pain
Endorphins → released naturally by the body
Applications of heat or cold
Relaxation or distraction techniques