biology lions/nature test review
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Was historic distribution of lions greater than the present distribution in India?
Yes
What is the difference between the red and the blue areas?
Historic range is much larger than present
Why is historic range or distribution of some species like lions greater than those in the present?
Human interference
Biodiversity loss
Overhunting
Why are there gaps in the historical range?
Different biomes
Lions live in grasslands + wooded areas (northern Africa + middle east are desert; central Africa is rainforest)
What causes different environments/ habitats?
Different combinations of temperature and moisture (precipitation, freshwater availability)
Why would lions like these areas?
Lions are camouflaged for grasslands
Need large amount of prey
Grasslands provide large grazing animals
What does that make a lion or an animal needing to feed on prey?
A predator
What do lions hunt in?
Prides
Population
An area where all of the same species/animal are (ex: lions)
Community
These populations of different species together
What else lives in the areas where lions live?
Grass, antelopes, zebras, etc.
Are there other predators where lions live?
Yes, but they typically don’t eat the same thing or in the same place
What would happen if lions were removed from the ecosystem?
Other predators would start eating their prey so the ecosystem would survive, but it would look a bit different
What is the dominant species?
Grass
What determines the dominant species in an ecosystem?
Generally, biomass and abundance
Most dominant species are plants that support the consumers
What determines the kinds of plants that grow to be dominant species?
Temperature/sunlight and moisture/precipitation
Biotic
Living
Abiotic
Nonliving
what is the most important species in the African grasslands besides grass?
Wildebeest
What are Wildbeest’s contributions that make them the most important species?
Keep grass managed, minimizing fire + maintaining plant health
Allowing for trees to grow providing habitat/ shade
Keystone species
Though they may not be the most numerous or dominant species in an ecosystem, their role is critical to maintaining the balance and health of that ecosystem.
Sub species
A species that differs from a certain species but not different enough to be recognized as a different species
Species
A group that breeds in the wild producing viable offspring
Similar biome in the US and Africa
Grassland biomes
What do biomes have?
Species that have adapted to similar conditions and fill similar niches
Biomes
A large, distinct ecological community of plants, animals, and other organisms that exist in a particular climate and geographical area.
Ecosystem
All the organisms in a given area as well as the abiotic factor with which they interact
What are bitotic factors?
Animals, plants, bacteria, algae, fungus, etc.
What are abiotic factors?
Rock, wind/air, water, temperature, sunlight, ptl, etc.
Are all organisms in an ecosystem the same?
No
How can organisms in an ecosystem be organized?
By the different ways they acquire food
Autotrophs
Producers in an organism that can make their own food using abiotic factors such as light, water, CO2, etc. (plant is an example of this producer)
Heterotroph
Consumers in organisms that get food by eating other organisms
Detritivores
Decomposers that break down + feed on dead and decaying material
Trophic levels
The group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain
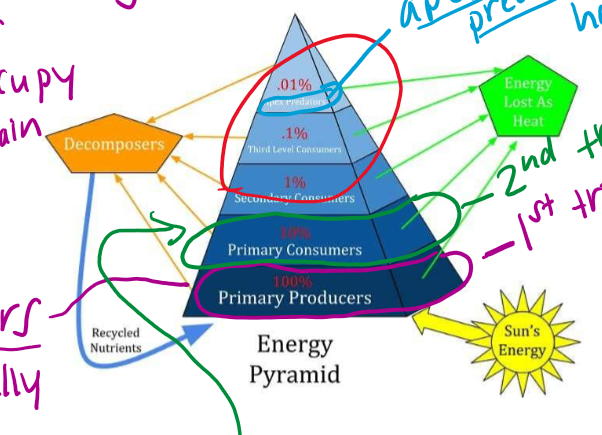
What does solar radiation do?
Provides the input of energy which is used by primary producers
Primary producers
Usually plants + algae
Primary consumers (second trophic level)
Herbivores (only eat plants) that gain energy by eating primary producers
Trophic levels 3, 4, and 5
Carnivores (eat only animals) and omnivores (eat animals + plants)
How are the components of an ecosystem tied together?
Biotic and abiotic factors linked together by nutrient and energy cycles
Plants pull nutrients from the soil
Primary consumers gain nutrients by eating the plants
The nutrients pass up to higher trophic levels as secondary, tertiary, and quaternary consumers eat lower levels
Those consumers and producers will die, and nutrients are released by decomposers as they break down the dead organism
Do all nutrients move through the ecosystem in the way?
No
Water
All organisms need this resource because it is the structure of body, temp. regulation, chemical reactions, etc.)
Nitrogen
This is the most abundant gas in atmosphere and is essential to the formation of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids
Carbon
This is the basic building block of all organic material and of all organisms on earth
Phosphorus
This element is essential for the formation of cell membranes, ATP, and nucleic acids
Where does the world’s water cycle through?
Lakes, rivers, oceans, the atmosphere, and the land in an ongoing cycle
What state is water when it cycles through?
It can be any state (solid, liquid, or gas)
What does nitrogen form?
Froms a triple bond with another nitrogen to make N2 (a very nonreactive compound)
What must occur for nitrogen to be used?
Nitrogen fixation
What can microorganisms taking atmospheric nitrogen make?
Can be converted to ammonia and ammonium which is then converted to nitrates and nitrites
Nitrates and nitrites
Can be used by the plants
How do carbon dioxide and carbon connect?
Through photosynthesis, carbon dioxide can be pulled from the air to produce food made from carbon for plant growth
How is carbon moved up the food chain?
Carbon in plants moves to the animals that eat them
What happens each time you exhale?
You are releasing CO2 into the atmosphere
What happens when animals and plants die?
Their bodies decay, bringing the carbon into the ground
Some is buried and will become fossil fuels
What happens when humans burn fossil fuels to power factories, cars, etc.?
Most of the carbon quickly enters the atmosphere as CO2
Why is it bad when carbon quickly enters the atmosphere as CO2?
CO2 is a greenhouse gas and traps heat in the atmosphere (the recent increase in greenhouse gases is significantly warming the planet) - GLobal Warming
Why is it also bad when too much CO2 gets into the ocean?
Too much can have negative impact like ocean acidification where it disintegrates shells because of the acid
What do humans need to survive?
Resources (food, water, shelter, etc.)
How do humans use resources?
Share, collect, store, fight for resources, etc.
Do animals interact with resources in the same way as humans?
Different animals need various resources and most (if not all) resources are limited
What resources do lions need?
Food, water, shelter, territory, etc.
Are there any other animals that need the same resources?
Yes, other predators need the same shelter and water
If an animals takes a resource…
It takes that resource away from another animal
Competition
Interactions between organisms where both require a resource that is in limited supply
Is all competition the same?
No, there can be direction competition or indirect competition
Do lions only compete with other species?
No (Intraspecific competition and Interspecific competition)
Intraspecific Competition
Different individuals and groups of the same species will compete with each other for the same resources
Interspecific competition
Individuals + groups of different species compete for resources
Interference Competition
A direct form of competition where organisms enter into direct conflict for resources
Is all competition direct?
No, there can be indirect competition where they do not interact with each other
Exploitation Competition
Indirect competition between individuals for a common limiting resource
Apparent Competition
Indirect competition where prey species compete for survival against a shared predator
Do all animals mature the same way?
No
Type 1
Most individuals will survive until old age & tends to be k-selected
Type 2
Constant loss (individuals die @ all ages) & can exhibit both k-selected and r-selected
Type 3
We see a massive portion die off @ a young age & tends to be r-selected
K-Selected reproduction strategy on curve
The animals produce fewer offspring and provide more long term care for said offspring → usually defined by a more stable environment (ex: humans)
R-Selected reproductive strategy on curve
The animals produce large numbers of offspring and provide little to no long term care after birth *usually by unstable/fluctuating environment (ex: trees)
Are all species still alive?
No, species become extinct for many reasons
Have any species gone extinct in the recent past?
Yes (ex: passenger pigeons from hunting and habit loss, Levana moth from pesticides, mexican grizzly bear from nuisance species, and more
When are animals considered extinct?
When there are no more individuals
“Extinct in the wild”
There are no more individuals in the wild, but some in captivity for example
Do species go extinct all at once?
No, their population decreases
Endangered species
An organism that is threatened by extinction
What do endangered and extinct species have in common?
Could have trouble finding mates
Slow reproduction and growth
Low ability to adopt to changing enivronnments
Specialists who have a narrow niche
Specialists
Have a narrow niche with incredibly specific needs to survive
Niche
The specific set of environmental conditions required by an organism or the function it performs in nature
What external factors cause species to become endangered or extinct?
HIPPO - (Habit Loss, Invasive Species, Pollution, Human Population, and Overexploitation)
Are there characteristics that would help a species thrive?
Yes
Being highly adaptable (wide range of tolerance)
Generalist
Generalist
A species with a broad niche that is easily adaptable to many environmental conditions
What happens when a nonnative species moves into a new ecosystem?
Competition
What 3 options do poor comepititors have?
Shift strategies (exploit different resources/same resources but at different times, or a smaller subset of resources but better at getting them than their competitor
Move
Go extinct
What factor is most responsible for threatened and endangered species?
Habitat loss but also invasive species too
Red important fire ants
Infest 2/3rds of eastern texas counties
Impact: damage crops, displace native ants, eliminate food sources, kill newborn livestock, etc.
Feral hogs
Destruct species, damage crops, transmit disease, etc.
Nutria
Economic impact: destroy nice crops and sugarcane
Ecological impact: Destroy habitats by rooting and digging
Which of the following is not a reason why invasive species are successful in an ecosystem?
Specialized niche
Why are invasive species successful in an ecosystem?
Not natural predators, high biotic potential, ability to live ina variety of habitats
What happens when people release pets into the wild?
If enough are released, self-sustaining, breading populations can take over
Can have negative impacts