Macro - Dynamic AD/AS model
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
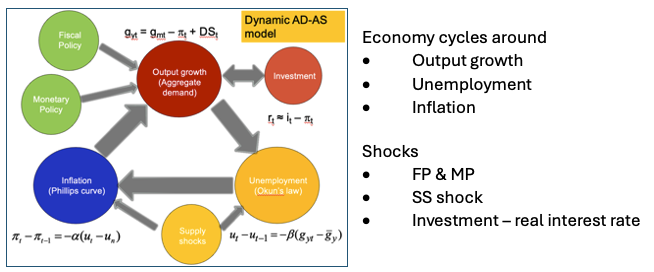
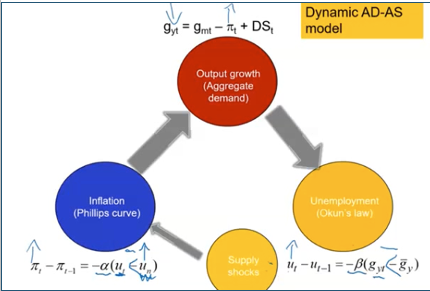
3 parts of Dynamic model
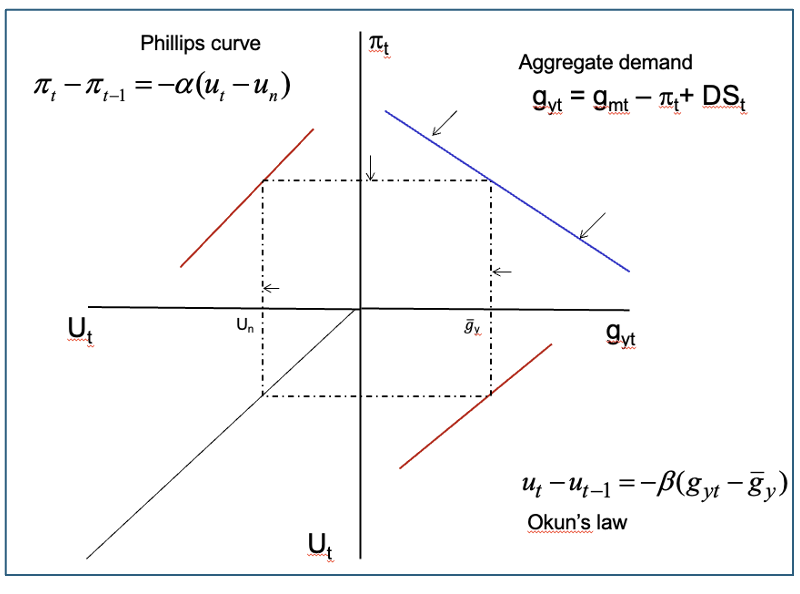
Okun’s law
Phillips curve
AD
How dynamic model works
Phillips curve
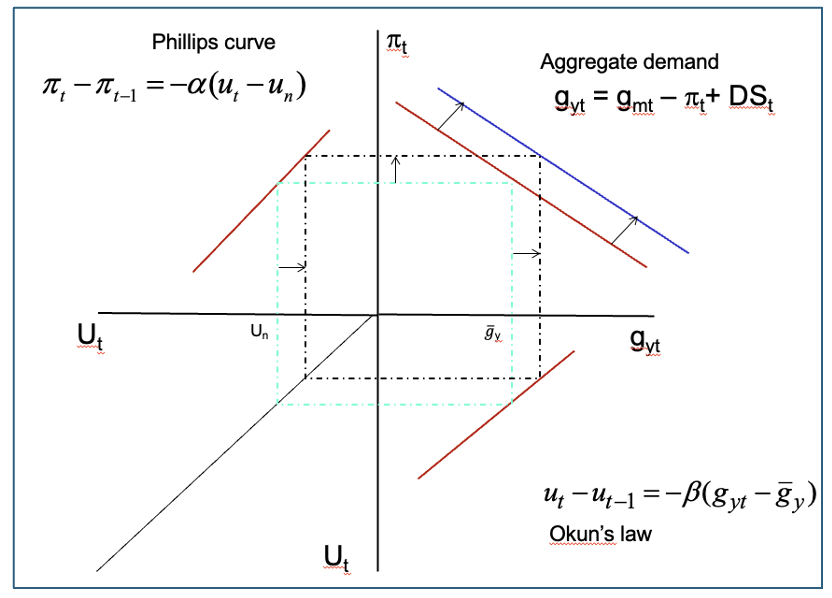
the aggregate supply relation written in terms of inflation, expected inflation and the unemployment rate
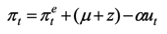

Phillips curve - Static expectations
Pet = Pt-1
When back to MR change in inflation = 0
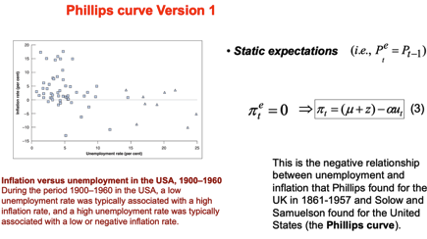
Fits data really well until 19
Wage price spiral

Phillips curve - Adaptive expectations
Expectation for inflation next year = inflation rate now * parameter
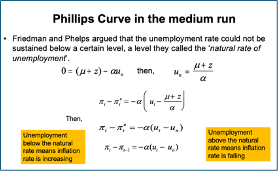
When Ut = Un then we’re in MR equilibrium and inflation change = 0 (inflation is the same very year)
Phillips curve - Rational expectations
Rational expectations - Using all the information available + perfect understanding of how macro economy works → perfectly forecast inflation (only unexpected events can mean your prediction was wrong)
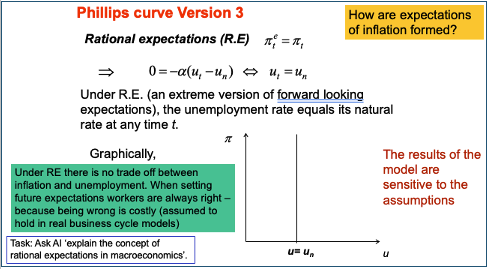
This makes the Phillips curve perfectly vertical – no trade-off between unemployment and inflation
No business cycle implied unless unexpected shocks
Pre election booms & expectations
Pre-election, political parties often artificially create a boom through expansionary FP
• With adaptive expectation (only using past data) this is unexpected and so there is a boom and inflation increases and U falls
• With rational expectations you understand there is an incentive to do this and so it is already factored into your expectations – You move up the Phillips Curve (higher inflation) but stay at un
Okuns law

Relax asssumption that L is constant
If GDP growth > 3% then the change in the unemployment rate is negative → If growth is strong, U will be falling
3% GDP growth is MR equilibrium (normal growth rate)
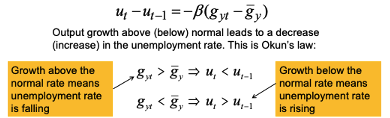
AD
Y = M/P as we ignore FP

We assume growth of MS is positive (if growth rate of MS UP (expansionary MP) then growth rate of Y UP
AD & MP or FP

AD and permanent MP

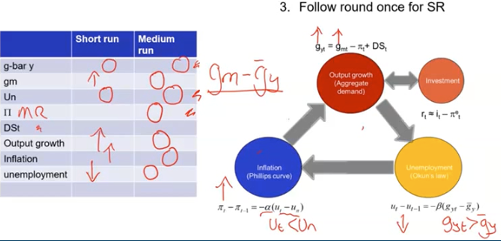
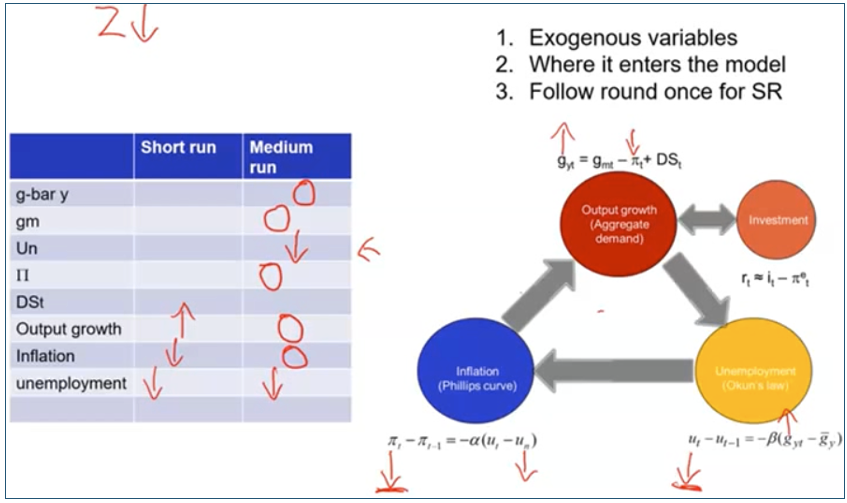
Dynamic model summary
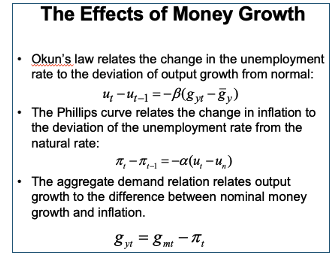
SR expansionary MP overview
Positice change in growth rate of MS
Causes SR boom
SR expansionary MP explained
Expansionary MP shifts MS out → Move along MR as i falls
MS shifting → LM to shift out
Move along IS as lower i leads to higher I & C → Y rises
GDP growth rate > natural growth rate
Y rises → L rises as firms offer higher W (L has bargaining power) → Firms cost rise so P rises
Okun’s law shows that u < un → inflation is above natural
Inflation expectations start to adjust and so economy cycles round again until MR equilibrium
What happens in MR
• Output must grow at its normal rate of growth
• Unemployment must return to the natural rate, un
• Expected Inflation must equal actual inflation, pit = piet Delta pi = 0
• Therefore the increase in money supply growth is exactly equal to the increase in inflation
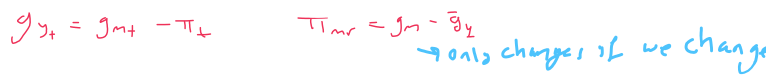
Permanent Expansionary MP
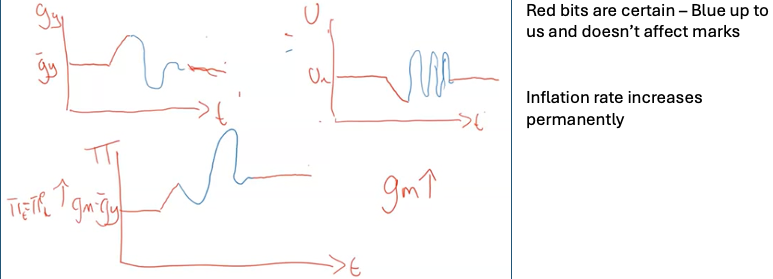
If an economy has a problem with inflation it can change it by changes in the growth rate of MS – only permanent fix
Problems with reducing inflation
reducing inflation will induce a recession for a time

SS shock - Negative shock to x or z
SR: U rises + Pi rises + Y falls Enters via PC
MR: U permanent rise + Y → Yn + Pi = Pin
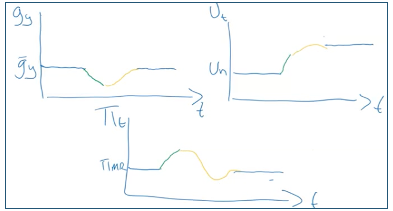
Problem with policy response to negative SS shock
In SR: High inflation + low growth
However they cant fix both problems at once – policy is either inflationary and U decreasing or U increasing but deflationary
Positive SS shock to ̅gy
E.g. AI making everyone more productive

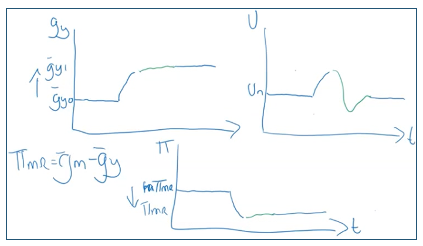
Positive SS shock - fall in z
Nominal i
Interest rates expressed in terms of currency
Real i
Interest rates expressed in terms of a basket of goods
Real i in dynamic model
In MR, r determined by balance of S & I. We assume it varies only if changes to FP
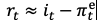
r & i behave similarly in SR but different in MR
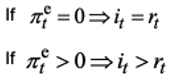
In ISLM + static , we assumed in MR pi = 0 → pie = 0 → i = real i
Which interest rate is directly affected by MP
nominal i
Which interest rate affects spending and Y
real i
its the i affected by costs → impacts I as raises OC + reduces present value of I
What do the effects of MP and FP on Y growth depend on
SR - how movements in the nominal interest rate translate into movements in the real interest rate.
MR - If real i changes in MR then composition of GDP changes. If not then composition doesn’t change even if nominal i changes in MR
How does permanent chnages in Ms affect i
If MS increase → SR - lower i MR - higher i
→ SR - lower r MR - original r
How MP affects i in SR (IS-LM)
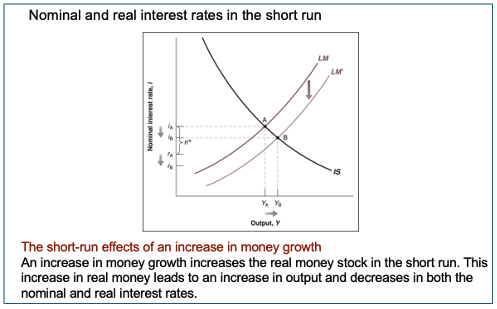
Expansionary MP shifts LM out → More cash in Money market →
Return on alternative financial asset falls (nominal i falls) → translates to an equal change in real i → I rises so move along IS
Fisher Hypothesis
In MR, a change in the growth rate of the money supply will lead to a one-for-one increase in the nominal interest rate and inflation
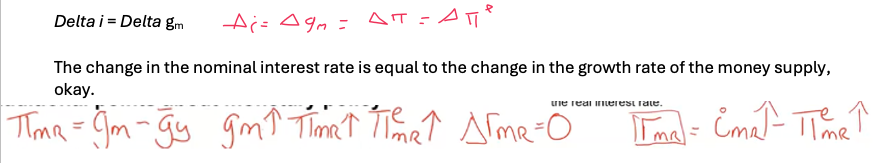
How Expansionary MP affects economy + i in SR (Dynamic AD/AS)
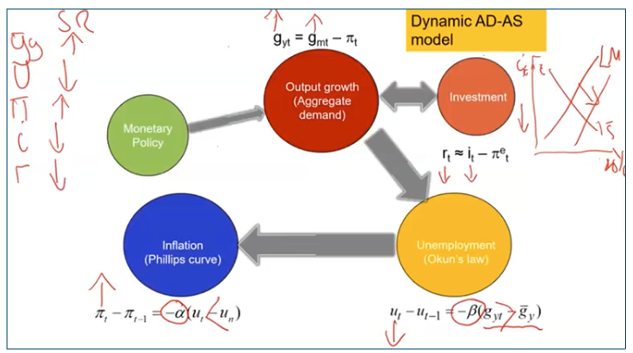
How MP affects Dynamic AD/AS in MR
gy returns to the natural rate + u → un
pi = gm - gy → Increase in money growth = increase in inflation
(true only for permanent increase to gm)
i + Pi increases, so r unchanged in MR → composition of Y unchanged → Monetary Policy affects Pi but not Y, nor its composition (the neutrality of money)

FP in dynamic model SR
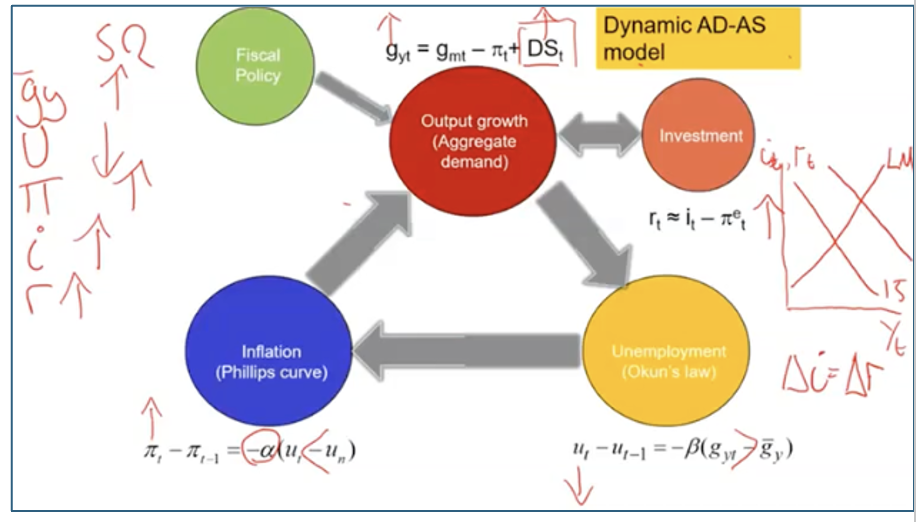
FP in dynamic model MR
Y & U → Yn & Un
PiMR = gm - gy
Nominal (and therefore) Real i increase
I fallen compared to G → Y composition changed
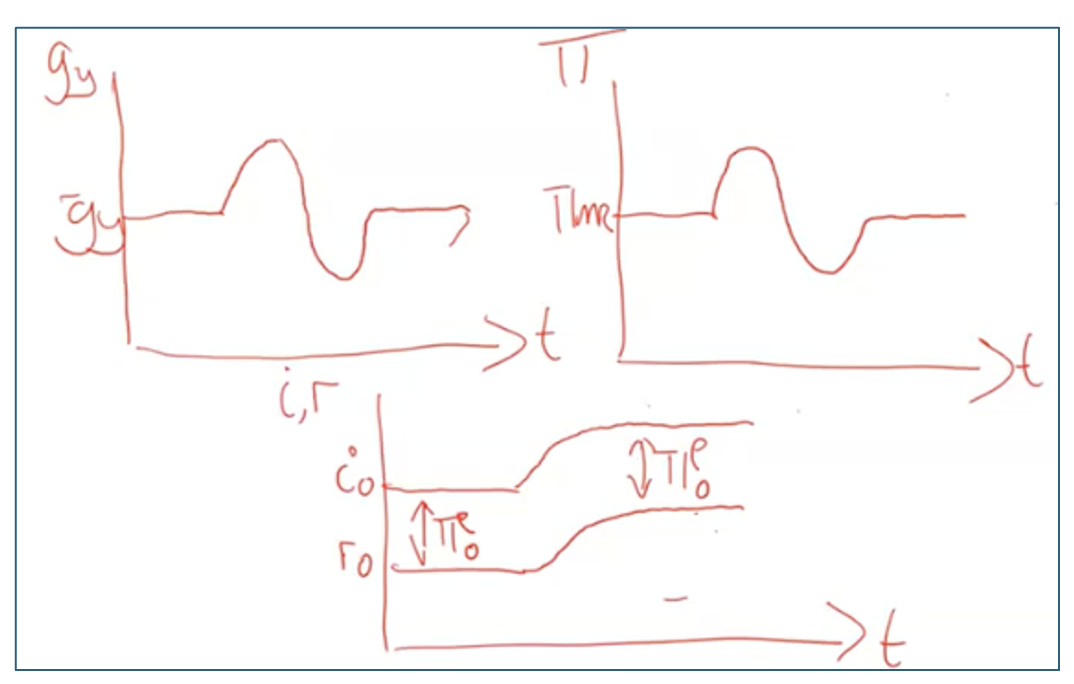
FP and crowding out
Crowding out always happens with FP – real i change causing the crowding out