Management Chapter 15
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Behavior
the actions of people
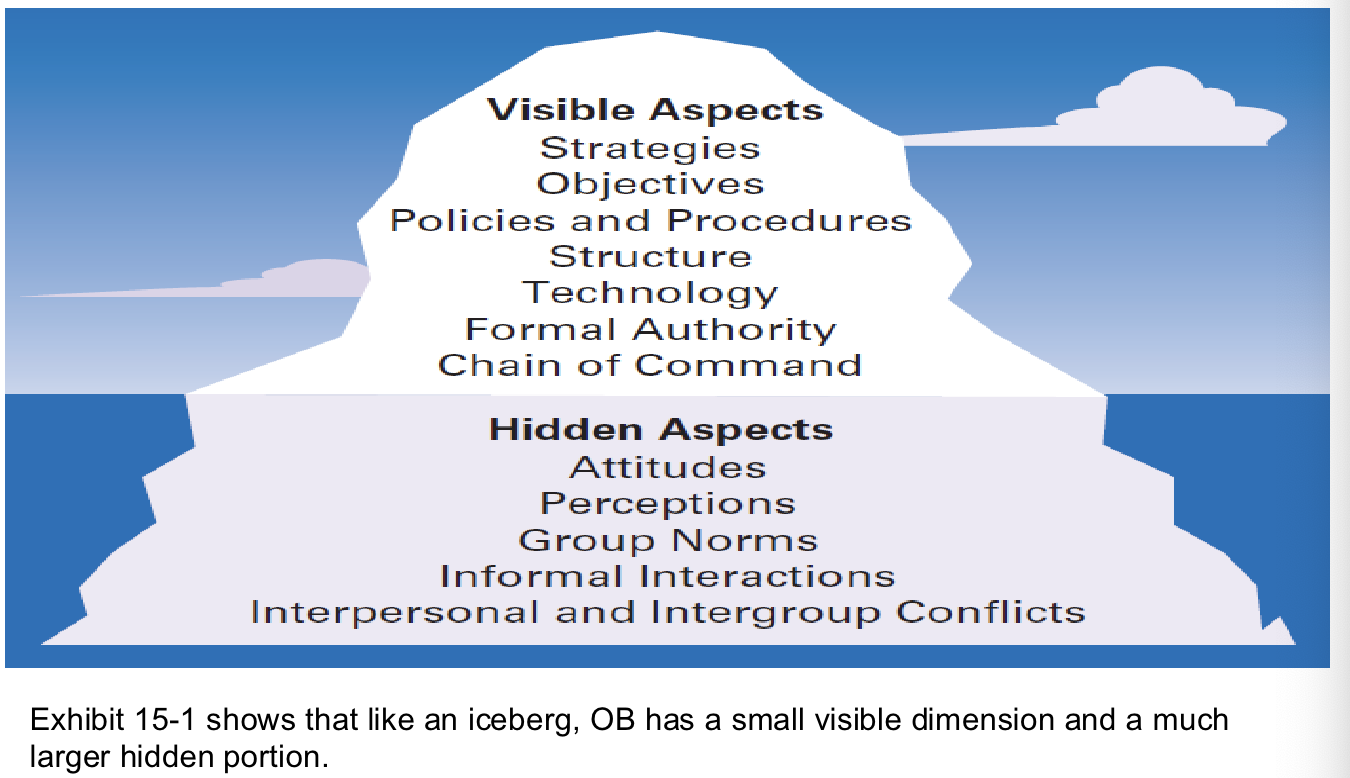
Organizational behavior
the study of the actions of people at work
Focus of organizational behavior
individual behavior
group behavior
organizational aspects
Explain, Predict, and Influence: Employee productivity
a performance measure of both efficiency (most output, least input) and effectiveness (doing it right the first time)
Explain, Predict, and Influence: Absenteeism
the failure to shop up for work
Explain, Predict, and Influence: Turnover
the voluntary and involuntary permanent withdrawal from an organization
Explain, Predict, and Influence: Organizational citizenship behavior (OCB)
discretionary behavior that is not part of an employee’’s formal job requirements, but which promotes the effective functioning of the organization
Explain, Predict, and Influence: Job satisfaction
an employee’s general attitude toward his or her job
Explain, Predict, and Influence: Counterproductive workplace behavior
any intentional employee behavior that is potentially damaging to the organization or to individuals within the organization
Attitudes
evaluative statements, either favorable or unfavorable, concerning objects, people, or events
Cognitive (thinking) component
that part of an attitude that’s made up of the beliefs, opinions, knowledge, or information held by a person
Affective (feeling) component
that part of an attitude that’s the emotional of feeling part
Behavioral (action?) component
that part of an attitude that refers to an intention to behave in a certain way toward someone or something
High level of job satisfaction =
postive attitude
dissatisfaction of job =
negative attitude
Job satisfaction is linked to
job satisfaction High Low
productivity up down
absenteeism down up
turnover down up
customer satisfaction up down
Organizational citizenship behavior up down
Counterproductive behavior down up
Job involvement
the degree to which an employee identifies with his or her job, actively participates in it, and considers his or her job performance to be important to self-worth
Organizational commitment
the degree to which an employee identifies with a particular organization and its goals and wishes to maintain membership in that organization
Perceived organizational support
employees’ general belief that their organization values their contribution and cares about their well-being
Employee engagement
when employees are connected to, satisfied with, and enthusiastic about their jobs
People generally seek consistency among their attitudes and between their attitudes and behavior
they try to reconcile differing attitudes and align their attitudes and behavior so they appear rational and consistent
Cognitive dissonance
any incompatibility or inconsistency between attitudes or between behavior and attitudes
say one thing but do another
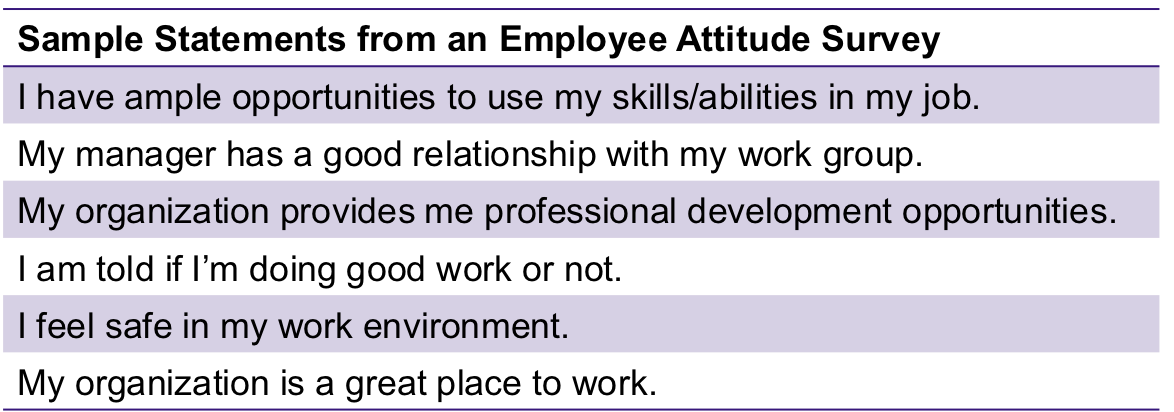
Attitude surveys
surveys that elicit responses from employees through questions about how they feel about their jobs, work groups, supervisors, or the organization
Mangers should be interested in their employees’ attitudes because
they influence behavior
Personality
the unique combination of emotional, thought, and behavioral patterns that affect how a person reacts to situations and interacts with others
The MBTI is a popular personality-assessment instrument
Examples of MBTI personality types
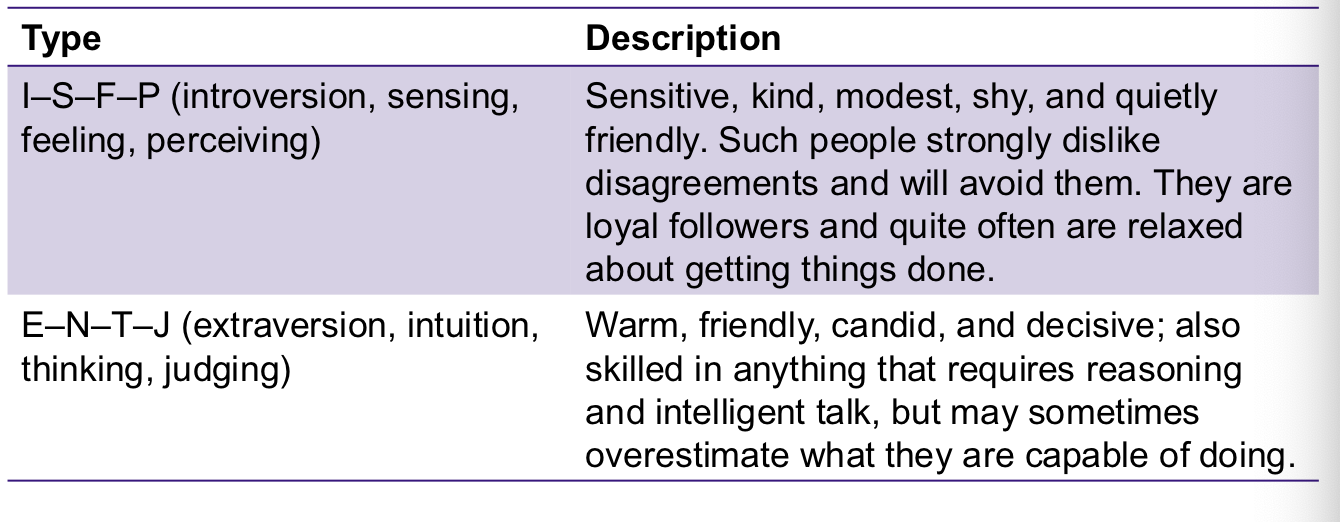
It classifies individuals as exhibiting a preference in four categories:
extraversion or introversion (E or I)
sensing (practical and prefer order) or intuition (more big picture person) - (S or N)
thinking (logical and unemotional) or feeling (don’t like conflict, like harmony) - (T or F)
judging (like control and structure) or perceiving (flexible, adaptable) - (J or P)
Big Five Model
personality trait model that includes extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, emotional stability, and openness to experience
Locus of control
a personality attribute that measures the degree to which people believe they control their own fate
internal - believe you control your own destiny in business
external - luck or chance is a primary factor in your success
Machiavellianism
a measure of the degree to which people are pragmatic, maintain emotional distance, and believe that ends justify means
Self-esteem
an individual’s degree of like or dislike for himself or herself
Self-monitoring
a personality trait that measures the ability to adjust behavior to external situational factors
Proactive personality
a personality trait that describes individuals who are more prone to take actions to influence their environments
Resilience
an individual’s ability to overcome challenges and turn them into opportunities
No personality type is common for a given country,
yet a country’s culture influences the dominant personality characteristics of its people
Emotions
intense feelings that are directed at someone or something
Emotional intelligence
the ability to notice and to manage emotional cues and information
Five Dimensions of emotional intelligence
self-awareness
self-management
self-motivation
empathy
social skills
Managers are likely to have higher-performing and more satisfied employees if
consideration is given to matching personalities with jobs
Perception (thoughts)
process by which we give meaning to our environment by organizing and interpreting sensory impressions
beware: make sure you see the whole picture
Attribution theory (actions)
a theory used to explain how we judge people differently depending on what meaning we attribute to a give behavior
Attribution depends on three factors:
distinctiveness
consensus
consistency
Fundamental attribution error
the tendency to underestimate the influence of external factors and to overestimate the influence of internal or personal factors
Self-serving bias
the tendency of individuals to attribute their successes to internal factors while blaming personal failures on external factors
Assumed similarity
the assumption that others are like oneself
Stereotyping
judging a person based on a perception of a group to which that person belongs
Halo effect
a general impression of an individual based on a single characteristic
Managers need to recognize that their employees
react to perceptions, not to reality
Learning
any relatively permanent change in behavior as result of experience
Operant conditioning
a theory of learning that says behavior is a function of its consequences
learned by making rewards contingent; if rewarded likely to repeat, if punished or ignored less likely to be repeated
Social learning theory
a theory of learning that says people can learn through observation and direct experience
attention, retention, motor reproduction, reinforcement
Shaping behavior
the process of guiding learning in graduated steps using reinforcement or lack of reinforcement
Pavlov’s dogs
can be positive, negative, punishment or extinction/elimination
don’t confuse with operant conditioning
Employees are going to learn on the job:
are managers going to manage their learning through the rewards they allocate and the examples they set, or allow it to occur haphazardly?