Pathology, Radiology, Hair, Fiber, Fingerprints- Unit 5
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Final Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Visible Prints
Seen with unaided eye. Blood, ink, paint, oil transfers

Latent Prints
Invisible prints. Dusting powder with a brush to help visualize print

Impression Print
Clay, putty, wax, playdoh impression

How to preserve fingerprint
Prints are photographed to scale. Use tape to carefully lift up and preserve evidence.
Different types of fingerprint patterns
Arch, loop, whorl patterns

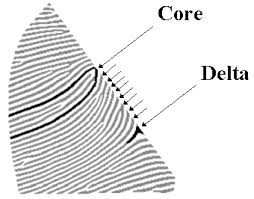
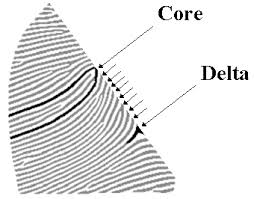
Delta
Point of ridge divergence meeting looping ridges (triangle shaped area)

Core
Where a loop pattern reaches its farthest point towards the middle of print and starts to turn back
Different minutiae patterns
Bifurcation, ridge ending, ridge dot, lake, hook, bridge, island
How fingerprint analysis is done and its limitations
Expert compares F.P. found at crime scene with known fingerprint by examining the minutiae patterns.
Limitation- Not always will there be a full, neat fingerprint to examine, don’t know if it is relevant to the crime scene (was it there before, during, or after?), examiner bias
FBI fingerprinting database
IAFIS
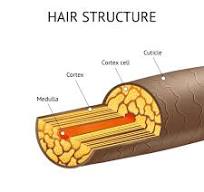
3 parts to hair
Cuticle- outermost layer of hair shaft
cortex-Lower layer under cuticle
medulla- innermost component of hair
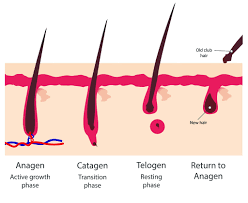
3 stages of Hair Growth
Anagen- Active growth occurs
Catagen- Transitional phase
Telogen- Resting period for follicle
(Exogen- Loss of hair shaft from follicle)
How is hair evidence collected/preserved?
Collected with tweezers, tape lifting, or vacuuming
2. Each hair is packaged separately in paper bags sealed and labeled
How hair analysis is done and its limitations
Experts use a stereo microscope to view the surface of hair shaft or a light microscope for viewing the medulla.
Limitations- Can’t specify who’s hair it is, potential bias
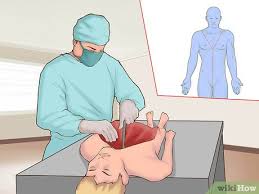
Autopsy
Helps pathologists examine internal and external parts of body
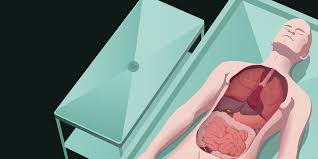
Steps of an autopsy
1- External examination (tattoos, scars, birthmarks…)
2- Internal examination (Y incision is made to expose organs from shoulder-breastbones)
3- Viewing internal organs (ribs sawn off to expose internal organs)
4- Removal of organs (Rokitansky method (removing all organs at once))
5- Removal of brain (Incision made in the back of scalp from ear-ear)
6- Examining organs (All organs except stomach and intestines are weighed)
7- Returning organs to body (organs returned to body except for small tissue frags. for microscope examination)
8- Sewing up the body (Incisions stitched up like a baseball)
Questions to be answered in death investigation
Manner, cause, time of death (PMI)
Manner of Death
Classification of death- Homicide, suicide, natural, accidental, undetermined
Homicide- Death caused by another person (murder or manslaughter)
Suicide- Someone kills themselves
Accidental- Arise from violent, unexpected death
Natural- Heart disease, cancer, stroke

Cause of Death
Medical reason for death
Mechanism of Death
Actual biochemical means by which someone dies