ANAPHY: U10.2 Cardiovascular System (Heart)
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Heart
4-Chambered muscular organ that pumps blood through the blood vessels of the body
Pulmonary Circulation
Type of circulation done by the right side of the heart; pumps blood to lungs and back to left side of heart
lungs; left side of the heart
The right side of the heart pumps blood to ___ and back to the ___ ___ __ __ ___
Systemic Circulation
Type of circulation done by the left side of the heart; pumps blood to all other tissue of the body and back to the right side of the heart
all other tissues; right side of the heart
The left side of the heart pumps blood to __ ___ ___ and back to the ___ ___ __ __ ___
BROS
Acronym for 4 Main Functions of the Heart
Blood Pressure Generation
Routing Blood
Ensures One-Way Blood Flow
Regulating Supply of Blood
4 Main Functions of the Heart
Blood Pressure Generation
One of the four main functions of the heart; heart contractions generate blood pressure which forces blood through the blood vessels
Routing Blood
One of the four main functions of the heart; heart separates pulmonary and systemic circulation, ensuring oxygenated blood flows to tissues
Ensures One-Way Blood Flow
One of the four main functions of the heart; valves of the heart ensure one-way blood flow through heart and blood vessels
Regulating Blood Supply
One of the four main functions of the heart; changes in heart rate and force of contraction matches blood flow during rest, exercise, and change in body position
Size of a closed fist
What is the size of the heart?
In mediastinum, protected by the thoracic cage
Where is the heart located?
Pericardium
Sac consisting of fibrous and serous pericardia
Fibrous & Visceral Pericardium
2 Types of Pericardium
Fibrous Pericardium
Type of pericardium; outer layer lined by the parietal pericardium
Visceral/Epicardium
Type of pericardium; lines outer surface of heart
R & L Atria
Part of External Anatomy of the heart; 2 structures located at the base of the heart
Coronary Sulcus
Part of External Anatomy of the heart; Groove around the heart that separates the atria from ventricles
R & L Ventricles
Part of External Anatomy of the heart; 2 structures separated by interventricular sulci anteriorly and posteriorly
Superior and Inferior Vena Cava
Part of External Anatomy of the heart; enter the right atrium
Pulmonary Trunk
Part of External Anatomy of the heart; exits right ventricle
Aorta
Part of External Anatomy of the heart; exits left ventricle
R & L Atrium, R & L Ventricle
4 Chambers of the Heart
Atria
Part of the internal anatomy of the heart; separated by the interatrial septum, serves as reservoirs (receiving chamber only); contraction completes ventricular filling
Ventricles
Part of the internal anatomy of the heart; main pumping chambers that are separated by the interventricular septum
Ventricles
Part of the internal anatomy of the heart; main pumping chambers separated by interventricular septum
Pulmonary Trunk
Where does the right ventricle pump blood into?
Aorta
Where does the left ventricle pump blood into?
Valves
Part of the internal anatomy of the heart; ensures one-way blood flow
Atrioventricular & Semilunar Valves
2 Main Types of Heart Valves
Tricuspid & Bicuspid/Mitral Valve
2 Types of Atrioventricular Heart Valves
Tricuspid Valve
Type of Artrioventricular Valve; separates RA and RV
Bicuspid/Mitral Valve
Type of Atrioventricular Valve; separates LA and LV
Pulmonic & Aortic Valve
2 Types of Semilunar Valves
Pulmonic Valve
Type of Semilunar Valve; separates RV and pulmonary trunk
Aortic Valve
Type of Semilunar Valve; separates LV and aorta
Pulmonary Arteries
Only artery that doesn’t carry oxygenated blood
Right Side
Side of the heart that always has deoxygenated blood
Papillary Muscles
Attached by chorda tendineae to cusps, adjust tension on valves; prevent atrioventricular valves from stretching too much
Chorda Tendineae
What are papillary muscles attached to?
Coronary Arteries
Arteries that originate from the base of the aorta and are filled when the heart relaxes
Left Coronary Artery
Artery that supplies most of the left ventricle and anterior heart wall
3
How many branches does the left coronary artery have?
Anterior Interventricular Artery, Circumflex Artery, Left Marginal Artery
3 Major Branches of the Left Coronary Artery
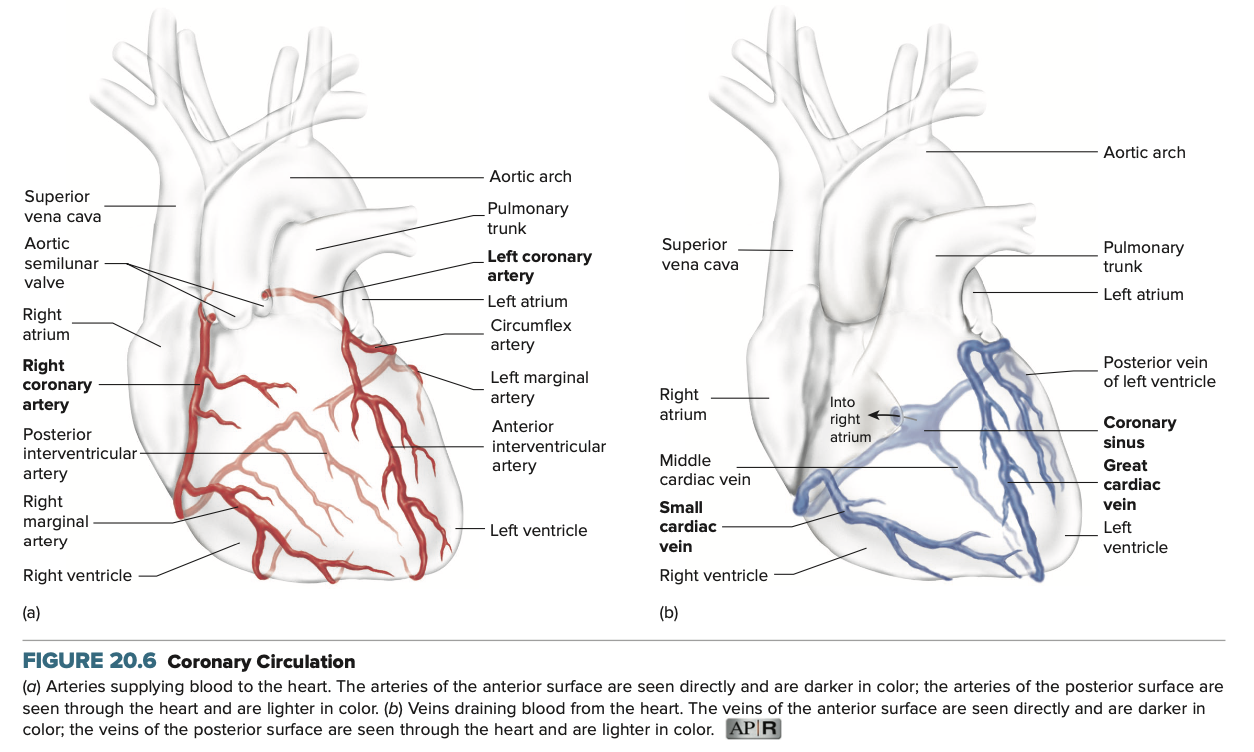
Right Coronary Artery
Artery that supplies most of the right ventricle and the posterior surface of the heart
2
How many branches does the right coronary artery have?
Posterior Interventricular Artery & Right Marginal Artery
2 Major Branches of the Right Coronary Artery
(1) cardiac veins (2) coronary sinus (3) right atrium
Blood returns from the heart tissue through (1) ___ ___, (2) ___ ___, then to the (3) ___ ___
Outer Epicardium, Middle Myocardium, Inner Endocardium
3 Layers of the Heart Wall
Intercalated Disks
What component of cardiac muscle allow for action potentials to be propagated in the heart?
ATP
What does cardiac muscle depend on for energy and aerobic metabolism?
(1) Coordinated sequence of cardiac muscle is stimulated
(2) Contraction of atria
(3) Contraction of ventricles
(4) Cardiac muscle contracts then relaxes completely
4 Steps in the Movement of Blood through the Heart
Sinoatrial (SA) Node, Atrioventricular (AV) Node, Antrioventricular (AV) Bundle
3 Specialized Cardiac Muscle Cells
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
One of the specialized cardiac muscle cells; pacemaker of the heart that initiates action potential and spread to myocardium of the right atrium and left atrium, causing atrial contraction
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
What is considered the pacemaker of the heart?
(1) myocardium (2) right atrium (3) left atrium (4) atrial contraction
The Sinoatrial Node initiates action potential and spread to (1) ___ of the (2) ___ ___ and (3) ___ ___, causing (4) ___ ___.
Atrioventricular (AV) Node
One of the specialized cardiac muscle cells; spreads action potential slowly until it reaches the atrioventricular bundle that allows the atria to complete contraction before it goes to ventricles
(1) atrioventricular bundle (2) atrium (3) ventricles
The Atrioventricular (AV) Node spreads action potential slowly until it reaches the (1) ___ ___ that allows the (2) ___ to complete contraction before it goes to the (3) ____.
Atrioventricular Bundle
One of the specialized cardiac muscle cells; subdivides into the left and right bundle branches, which have inferior terminal branches, called Purkinje Fibers, which are located from the apex to the ventricular walls
Left and Right Bundle Branches
What does the atrioventricular bundle subdivide into?
Purkinje Fibers
What are the inferior terminal branches of the left and right bundle branches?
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Record of the electrical events within the heart
P Wave, QRS Complex, T Wave
3 Components of a Normal ECG
P Wave
Component of a normal ECG; represents atrial depolarization/contraction of the atrium
QRS Complex
Component of a normal ECG; represents ventricular depolarization/contraction of the ventricles
T Wave
Component of a normal ECG: represents ventricular repolarization/relaxation of the heart
PQ Interval
Name of the part of the ECG from the start of the P-wave to the start of the QRS complex
QT Interval
Name of the part of the ECG from the start of the QRS complex to the end of the T Wave
Cardiac Cycle
(From the Book)
Term referring to the repetitive pumping process that begins with the onset of cardiac muscle contraction and ends with the beginning of the next contraction
Systole
(From the Book)
Term in the cardiac cycle; means to contract; when used alone, usually refers to that of the ventricular myocardium
Diastole
(From the Book)
Term in the cardiac cycle; means to dilate; when used alone, usually refers to that of the ventricular myocardium
Atrial Systole
(From the Book)
Term in the cardiac cycle; contraction of the atrial myocardium
Atrial Diastole
(From the Book)
Term in the cardiac cycle; relaxation of the atrial myocardium
Ventricular Systole
(From the Book)
Term in the cardiac cycle; contraction of the ventricular myocardium
Ventricular Diastole
(From the Book)
Term in the cardiac cycle; relaxation of the ventricular myocardium
Atrial Systole: Active ventricular filling
Ventricular Systole: Period of isovolumetric contraction
Ventricular Systole: Period of ejection
Ventricular Diastole: Period of isovolumetric relaxation
Ventricular Diastole: Passive ventricular filling
5 Steps of the Cardiac Cycle
70%
When blood returns to the heart and enters the atria with the antrioventricular valves open, what volume of the ventricles are filled?
Atrial Systole
Event in the cardiac cycle in which the atria contract and complete the filling of the ventricles; the semilunar valves remain closed
Ventricular Systole
Event in the cardiac cycle in which the atrioventricular valve closes, ventricular pressure increases, semilunar valve opens and blood flows into the aorta and pulmonary trunk
Lubb; when the atrioventricular valves close during the beginning of ventricular systole
What and when is the first heart sound?
Ventricular Diastole
Event in the cardiac cycle in which ventricular pressure decreases; the semilunar valves close (which prevents backflow to the ventricles); ventricular pressure lowered until atrial pressur increases, atrioventricular valves open and blood fills the ventrivles
Dubb; When the semilunar valves close (during ventricular diastole)
What and when is the second heart sound?
Cardiac Output
(From the Book)
The amount of blood pumped by the heart per minute
Cardiac Output (CO) = Stroke Volume (SV) x Heart Rate (HR)
What is the equation for Cardiac Output (CO)?
Stroke Volume (SV)
Component to calculate cardiac output; volume of blood ejected by the heart per beat
Intrinsic Regulation
Regulation mechanism contained within the heart
Venous Return
(From the book)
Amount of blood returning to the heart from the systemic circulation
Increased stretching
As venous return increases, what occurs to the heart walls?
Preload
(From the Book)
Extent to which the ventricular walls are stretched
Afterload
Pressure against which the ventricles must pump blood
(From Book) Pressure the contracting left ventricle must produce to overcome the pressure in the aorta and move blood into the aorta
Extrinsic Regulation
Regulation mechanism that refers to nervous and chemical mechanisms
Autonomic Nervous System & Baroreceptors
2 Ways of Nervous Regulation of the Heart
Autonomic Nervous System
Way of nervous regulation of the heart; sympathetic nerve fibers cause the heart rate and stroke volume to increase, while the parasympathetic nerve fibers cause them to decrease
Increases
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect heart rate and stroke volume?
Decreases
How does the asympathetic nervous system affect heart rate and stroke volume?
Baroreceptors
Way of nervous regulation of the heart; stretch receptors in carotid arteries and aorta that detect an increase in blood pressure
Stretch receptors/baroreceptors in carotid arteries and aorta sense a BP increase
Cardioregulatory center in medulla oblongata initiates a decrease in sympathetic stimulation of the heart and adrenal medulla (so decreased epinephrine and norepinephrine
Increase parasympathetic stimulation of the heart, causing decreased heart rate and stroke volume
Decreased blood pressure
How do the baroreceptors stimulate a decrease in blood pressure?
Exercise, Emotional Excitement, Stress
What 3 factors can cause the adrenal medulla to release epinephrine and some norepinephrine which cause a sympathetic response, thus an increased heart rate and stroke volume?
60-100 bpm
What is the normal heart rate range?