urinary system
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
osmolarity
water/salt ratio
blood osmolarity balance
monitor electrolyte/ions and H2O balance: + hormones ADH
waste excretion
urea → via deamination of amino acids (remove nitrogen)
PH regulation
via H+ ion secretion & reabsorb of HCO3- (bicarbonate)
blood pressure regulate
renin, angiotensin II, aldosterone (Na+) → blood volume
erythropoietin
(EPO) secretion to make RBCs → red marrow
H+
proton = acid
reabsorb
take from urine back to blood
secretion
from blood into kidney tubes/urine
location
retroperitoneal space, has capsule of adipose (fat) & adrenals on top (superior)
hilum
depression where vessels enter/exit
regions
cortex & medulla containing parts of nephrons and pyramids
nephrons
filtering units
pyramids
concentrate urine
calyx
cup regions, collect urine from pyramids
renal pelvis
funnel, forms superior ureters
ureters
empty into bladder
bladder
muscle, stores urine, anterior to uterus & anterior to rectum, male prostate gland = inferior
epithelial
lines organs
detrusor (smooth muscle)
aids micturition/voiding
trigone muscle
triangle, acts as valve, aids continence
continence
ability to hold and use
internal sphincters (relaxing fills urethra)
circular muscle: regulate release of urine to urethra involuntarily (autonomic)
external sphincter
skeletal/somatic muscle, control → micturition from urethral meatus
meatus
opening to a tube/canal
micturition
to pee
urethra transports…
urine out of body
mucosa
trap stuff
men have
one opening, urethra passes through prostate, serves as a semen transport
afferent
into a location
efferent
away/exit
renal artery
afferent arteriole → feeds glomerulus
nephron glomerulus (capillaries)
HI hydrostatic pressure & gradients, filter out substances thru capillary fenestrations into Bowman’s Capsule
filtrate
liquid to become wee & includes: H2O, glucose, urea, H+, electrolyte/ions. RBCs and proteins not filtered
efferent arteriole
drains blood to renal vein → vena cava
peritubular capillaries & vasa recta
vessels is @ nephrons to reabsorb H2O & nutrients & secrete wastes into nephron that will become pee
vasa recta
caps @ loop henle
osmotic/colloidal pressure (solutes) in Bowman’s law is low
hydrostatic is driving force to make filtrate
125 mL/min filtrate made
180L / day
99% of filtrate reabsorbed by…
nephron under influence of gradients, hormones, etc.
uresis =
urinate
1-2 L
urine output/day
albumin is like a…
osmotic sponge that absorbs water
if albumin escapes into Bowman’s via inflammation…
increases osmotic pressure (solutes/salt) in Bowman’s and nephron
over time, systemically, there is…
lower osmotic pressure in blood and more H2O (hypotonic)
edema (swelling)
H2O diffuses thru capillaries into tissues
passive/simple diffusion
no ATP, things move down gradient HI - Lo concentration
facilitated
still passive but uses carrier protein to move glucose b/c of size
active transport
shows antiport, ions moving in opposite directions using ATP
Secondary active transport
shows symport as 2 molecules diffuse together, using a transport protein and gradient
power in electromechanical [Na+] gradients as…
it flows Hi-Lo, draws things with it, not all movement needs ATP
Proximal convoluted tube (PCT)
majority of reabsorption HERE!
Apical cell side
faces nephron lumen & filtrate
basal
faces interstitial/ tissue
Filtrate passes into PCT, most active reabsorb area of :
Na+, electrolytes, H2O, glucose
Na+ symport: apical side:
transports glucose out of nephron filtrate → glucose then diffuses into peritubular capillary
NA/K ATP pump (active trans)
pumps 3 Na+ into interstitial & then Na+ diffuses into peritubular caps… H2O will diffuse Hi-Lo gradient b/c of this
Na+/H+ antiport
secrete H+ into filtrate = acidic (Low pH) wee + Na+ adds to gradient for H2O to follow
HCO3- (bicarbonate)
important for pH balance, is symported with Na+ ions = buffer blood
ions: Cl-, Mg, Ca2+…
use symport proteins from filtrate
loop of henle
reabsorb Na+ & H2O into vasa recta capillaries
as H2O lost in loop of Henle…
osmolarity increases down in loop (increased concentration)
Ascending loop
thick portion impermeable to H2O, BUT Na+ actively transported (Na/K+ ATP pump) into interstitial space @ loop
hyperosmotic
lots of solutes/salt
ascending is vital b/c…
it forms hyperosmotic gradient so H2O can diffuse out of descending loop
countercurrent
against
THIS = COUNTERCURRENT EXCHANGE
H2O diffuse out as we move down, Na+ is transported out as we move up
urea (nitrogen waste)
byproduct of the breakdown of Amine (NH2) group of amino acids via liver
urea diffuses into…
descend loop lumen
When H2O leaves
more concentrated (more salt than water) higher number
When salt leaves
less concentrated (more water than salt) lower number
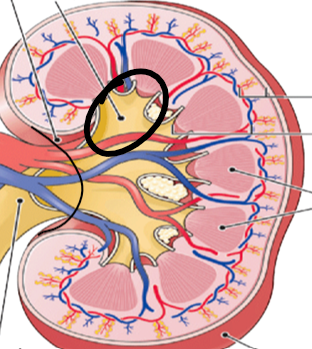
calyx (pic)
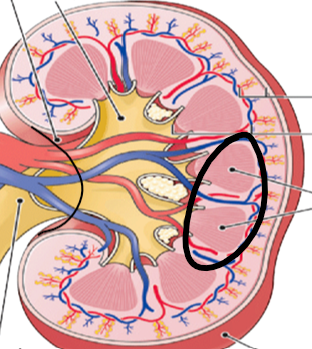
renal pyramids (pic)
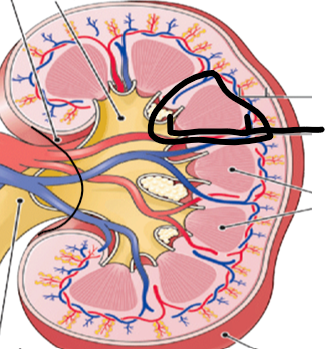
renal medulla (pic)
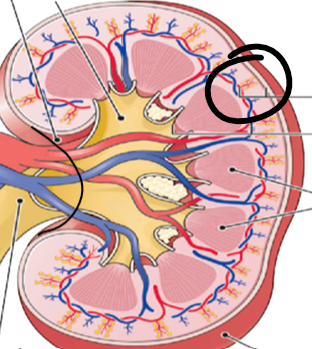
renal cortex (pic)
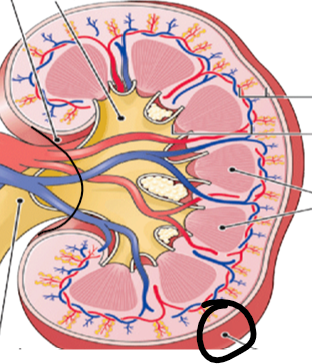
renal capsule (pic)
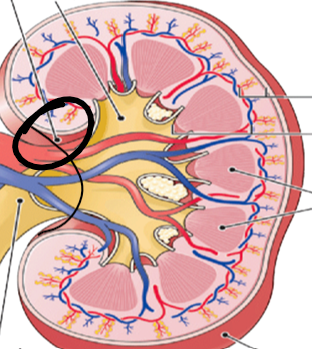
hilum (pic)
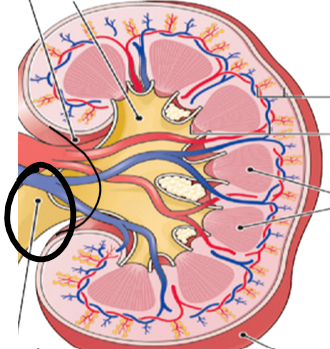
renal pelvis (pic)