Buffer solutions
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is a buffer solution?
a system that minimises pH changes on addition of small amounts of an acid or base
How do you prepare a buffer solution? (The 2 ways)
a weak acid and a salt of the weak acid
Excess of a weak acid and a strong alkali
What is an example of forming a buffer solution from a weak acid and salt of the weak acid?
CH3COOH and CH3COONa
How is a buffer solution prepared by partial neutralisation of the weak acid?
adding an aqueous alkali solution such as NaOH to an excess of the weak acid (CH3COOH)
What is the conjugate acid-base pair? What is an example?
HA(aq)/A-(aq)
E.g CH3COOH / CH3COO-
When preparing a buffer solution from a weak acid and its salt, what is the source of the conjugate base component?
the salt: when the salt is added to water, the salt completely dissolves so is the source of the conjugate base component
What happens when an acid is added to the buffer solution_
[H+] increases
H+ ions react with the conjugate base, A-
Equilibrium shifts to the left to remove H+ ions
![<p>[H+] increases </p><p>H+ ions react with the conjugate base, A-</p><p>Equilibrium shifts to the left to remove H+ ions </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/256a96b8-87df-4fcf-918d-e217b54b9dc9.jpg)
What happens when an alkali is added to the buffer solution?
[OH-] increases
The concentration of H+ ions react with the OH- ions to form H2O
HA dissociates to restore H+ ions
![<p>[OH-] increases</p><p>The concentration of H+ ions react with the OH- ions to form H2O</p><p>HA dissociates to restore H+ ions</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ef13f8b7-c9df-470d-b4fa-7e5b87e017c1.jpg)
A buffer is most effective when what?
there are equal concentrations of the weak acid and its conjugate base
When [HA] = [A-], what is true?
pKa = pH
Ka = [H+]
How do you calculate the pH of a buffer solution?
Using Ka
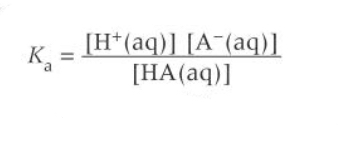
The pH of the blood needs to be maintained between which values?
7.35 - 7.45
The carbonic acid-hydrogencarbonate buffer system operates how when an acid is added?
[H+] increases
H+ ions react with the conjugate base, HCO3-
Equilibrium shifts to the left
![<p>[H+] increases</p><p>H+ ions react with the conjugate base, HCO<sub>3</sub>-</p><p>Equilibrium shifts to the left</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c4aa9ab2-f49a-4f81-8076-e46cc5c49696.jpg)
What happens when an alkali is added to the carbonic acid-hydrogencarbonate buffer system?
[OH-] increases
H+ ions react with OH- ions to form H2O
H2CO3 dissociates so equilibrium shifts to the right
![<p>[OH-] increases</p><p>H+ ions react with OH- ions to form H2O</p><p>H<sub>2</sub>CO<sub>3</sub> dissociates so equilibrium shifts to the right </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e1a5b277-22a3-41da-aaa1-2d6827441208.jpg)
Why does excess of a weak acid and a strong base create a buffer solution?
partial neutralisation of the weak acid
contains both the weak acid and the conjugate base