astrophysics and paper 3
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
what characteristic makes an image virtual
the rays focus on the same side of the lens that they enter
define a black hole
an object with escape velocity greater then the speed of light
what are some features of a refracting telescope (positive and negatives)
chromatic abberation, hard to make the lenses, magnification proportional to focus length
what are some features of a reflecting telescope (positive and negatives)
less distortion as mirrors can be supported better, spherical abberation
what is a CCD - what does it do?
a small chip divided into light sensitive pixels, when photons hit the face, they trigger the photoelectric effect, causing electrons to be emitted creating a digital signal
Why are CCD’s better then the human eye at detecting planets
they have greater quantum efficiency and resolution
what is quantum efficiency?
the ratio of incident to detected photons
what is collecting power proportional to
the diameter squared
the one formula for intensity and magnitude
i2/i1 = 2.51^m1-m2
In the acronym OBAFGKM, what are the temperature ranges for each letter
50-25 25-11 11-7.5 7.5-6 6-5 5-3.5
In the acronym OBAFGKM, what are the colours for each letter
blue blue blue-white white yellow-white orange red
on the HR diagram, what goes on the vertical axis (give name of it and numbers from bottom to top)
apparent magnitude 15 -10
on the HR diagram, what goes on the horizontal axis (give name of it and numbers from start to finish)
temperature 50000 2500
give the formation of a star
an interstellar dust cloud collapses under gravity
the gpe decreases and kinetic energy increases increasing temperature
at 10 million kelvin, hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium
radiation and gas pressure cause gravity
give the life of a star like the sun
protostar/gas cloud, main sequence, red giant, white dwarf
whats one big characteristic of a neutron star
very high density very small size
state hubbles law in words
recession speed of a galaxy is proportional to its distance from earth
whats an astronomical unit
the distance from the earth to the sun
whats a parsec
the distance when 1 astronomical unit subtends a parallax angle of 1 arcsecond
define absolute magnitude
the apparent magnitude an object would have if viewed from 10 parsecs away from earth
define apparent magnitude
a stars brightness as measured from earth, it depends on the luminosity of the star and how far away it is from earth
state an advantage of a large diameter telescope
minimum angular resolution
state the rayleigh criterion
the minimum angle required for the maximum of one diffraction pattern to coincide with the first minimum of the other, allowing for two sources to be just resolved.
whats spherical abberation
when two rays dont converge onto a single point
whats chromatic abberation
when different colours are refracted by different amounts
how do you take an uncertainty for a measurement
you take + or - the smallest unit in the measurement
how do you calculate uncertainty of a gradient
(gradient of best line - gradient of worst line)/best gradient (gradient of worst line could be steepest or shallowest gradient)
when taking the log of a data value, what does the number of sigificant figures of the data value represent
the number of decimal places in the logged values answer
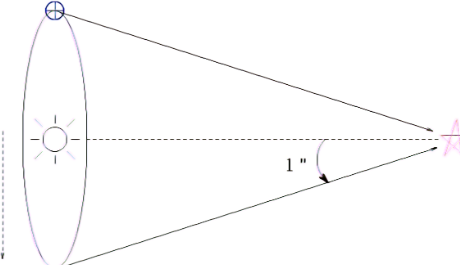
what does this diagram represent
the parsec
when do gamma ray bursts occur and what forms soon after
when a big star runs out of fuel and collapses under gravity forming a black hole and a neutron star
what is meant by normal adjustment on an astronomical telescope
the image is formed at infinity
what combo gives largest angular magnification (eg. large converging objective lens, small diverging eyepiece lens etc)
large converging objective lens and small converging eyepiece lens
give a quick definition of the transit method
detects a dip in a stars brightness as a planet passes infront of it
give a quick definition of the radial velocity method
as a planet orbits, it moves towards and away from the observer, causing a doppler shift
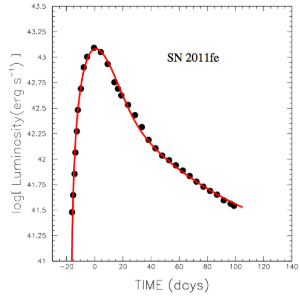
what does this graph represent
a supernova
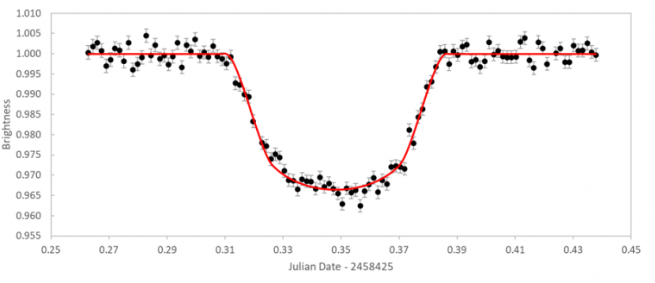
what does this graph represent
a transit light curve
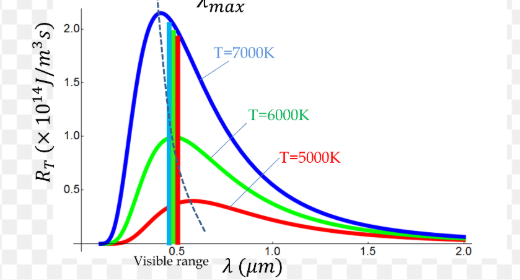
what does this graph represent
a black body radiation curve
why are some telescopes located in space
because the wavelengths it aims to detect are smaller then visible light and so are absorbed by the ozone layer
how does a quasar form
when a giant black hole is feeding on nearby matter
what is collecting power proportional to
area
give some benefits and negatives of a reflecting telescope
spherical abberation, shorter so easier to transport
give some benefits and negatives of a refracting telescope
chromatic abberation, magnification proportional to focal length
define a standared candle
a distant object with known absolute magnitude
give percentage of quantum efficiency of a CCD and an eye
80 percent, 1 percent
define a supernova
an object that produces a rapid increase in brightness
whats dangerous about supernovas
they emit gamma ray bursts
how can i use a mirror to avoid parallax errors (errors caused by the angle your viewing something like a needle)
move position until needle is aligned with its position in the mirror
why are quasars easily discovered
they are high power radio emitters