Addictive Behaviors Quiz 6
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Age group with the highest rate of mental illness
18-25
Age group with the lowest rate of mental illness
50+
Disorders that commonly co-occur with substance misuse
Major Depression, generalized anxiety disorder, ADHD, PTSD, Schizophrenia, CD, Antisocial PD, Borderline PD
Necessary criterion for MDD
depressed mood or anhedonia (diminished interest in all or most activities)
Other criterion for MDD
weight changes, more/less sleep, psychomotor agitation/retardation, fatigue, worthlessness/guilt, concentration issues, thoughts of death
Number of 18-25 year olds reporting a major depressive episode
1 in 5 (20%)
Symptoms tend to be ____ severe among adolescents with MDD or GAD
more
Epigenetics
the study of how environmental and behavioral factors can change gene expression without altering the underlying DNA sequence
Primary prevention
Stopping the development of substance misuse before it happens
Secondary prevention
Stopping the development of substance misuse in the early stages
Tertiary prevention
Minimizing the impact of substance misuse that has already developed (most of focus in US)
Did the first generation of DARE (1980’s and 90’s) reduce substance use?
no
DARE
Drug Abuse Resistance Education
What was different about the second generation of DARE (2010’s)
Science backed, 80 hour training program required for DARE officers, more interactive
What factor largely determines the treatment goal?
Model of therapy (ex: disease model—>total abstinence)
12-step programs (AA, NA)
based on principles of powerlessness over addiction, surrender to a higher power, personal responsibility, and peer support (least evidence based)
self-management and recovery training (SMART)
mutual support group, based on rational emotive behavioral therapy (REBT) and CBT, focus on science and clinical evidence

cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
evidence based, challenges negative thoughts and dysfunctional beliefs to shape behavior
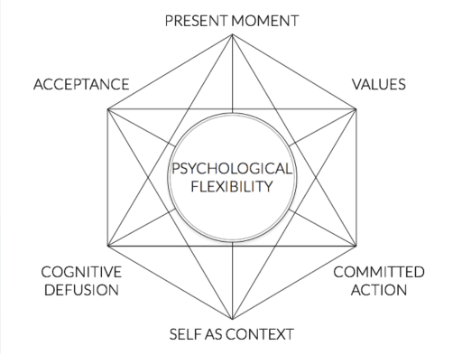
acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT)
seeks to promote psychological flexibility, where behavior aligns with values instead of emotions driving behavior
mindfulness
informed by buddhist traditions of meditation, goal is to bring attention to experiences in the present moment, emphasizes nonjudgemental observation and breathing
motivational enhancement therapy (MET) and motivational interviewing
helps people who are unsure about quitting, empathetic not argumentative
contingency management (CM)
based on principles of operant conditioning, rewards drug abstinence and supportive behaviors, the most effective but not widely implemented