Homeostasis and the Human Endocrine System
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Homeostasis
Maintaining constant internal conditions, so that cells can survive.
Receptors
Cells that detect stimuli, and pass this information along neurones as electrical impulses.
Coordination centre
The central nervous system, which receives and processes information from receptors.
Effectors
Muscles or glands that make changes to restore optimum levels.
Blood glucose concentration
The level of glucose in the blood that is monitored and controlled by the pancreas.
Body temperature
A physical condition that is maintained within narrow limits for cell survival.
Water levels
A chemical condition that is maintained within narrow limits for cell survival.
Nervous system
One of the two automatic control systems in the body.
Endocrine system
The system made of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
Reflex Actions
Quick and short lasting responses that do not involve the conscious part of the brain.
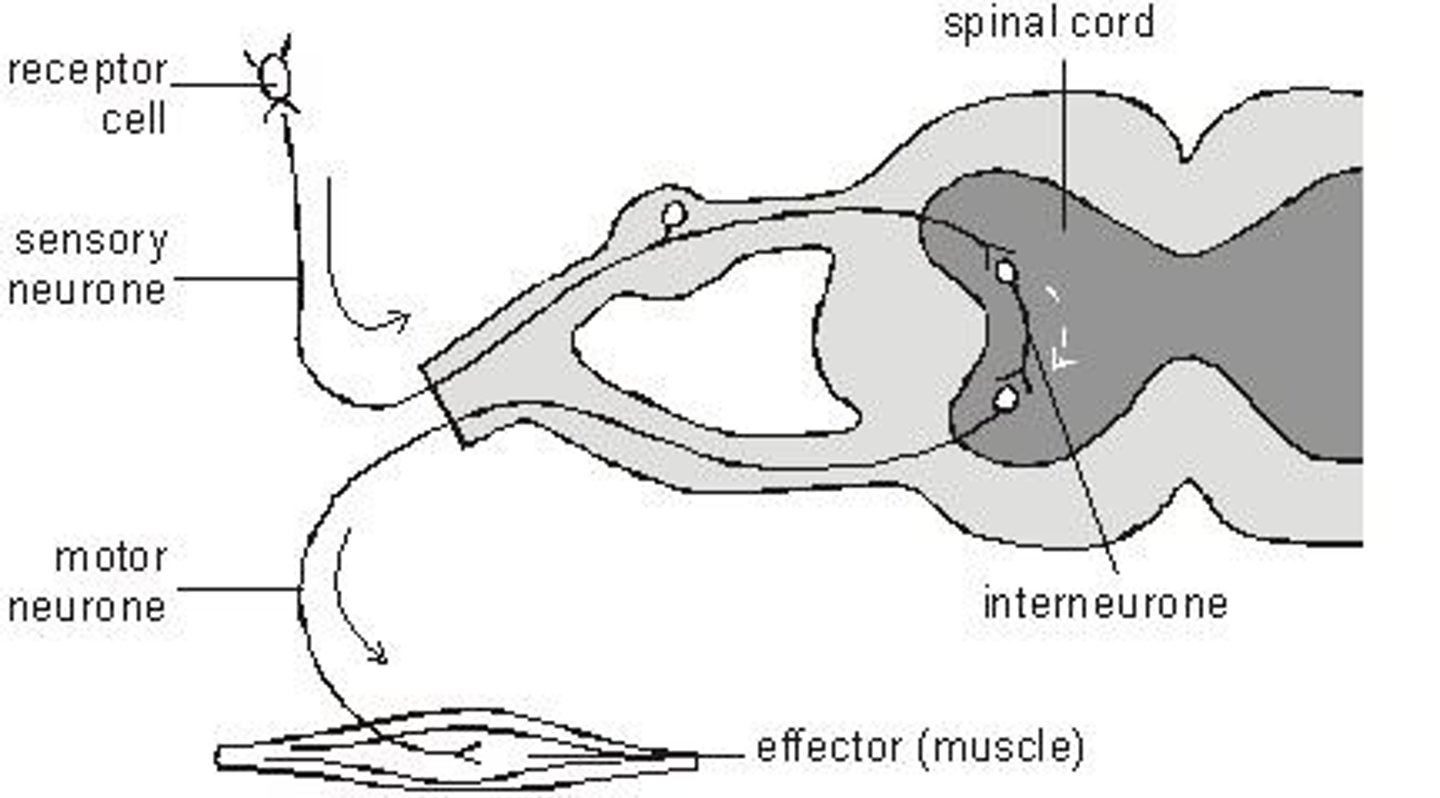
Synapses
Gaps between neurones.
Hormones
Chemicals released by glands into the bloodstream that produce effects on target organs.
Negative feedback
When the body responds to a change in a factor by correcting it.
Insulin
A hormone released by the pancreas that causes glucose to move from blood into cells.
Glucagon
A hormone released by the pancreas that causes glycogen to be converted into glucose.
Type 1 diabetes
A disorder where the pancreas does not produce enough insulin.
Type 2 diabetes
A disorder where cells do not respond to insulin, often associated with obesity.
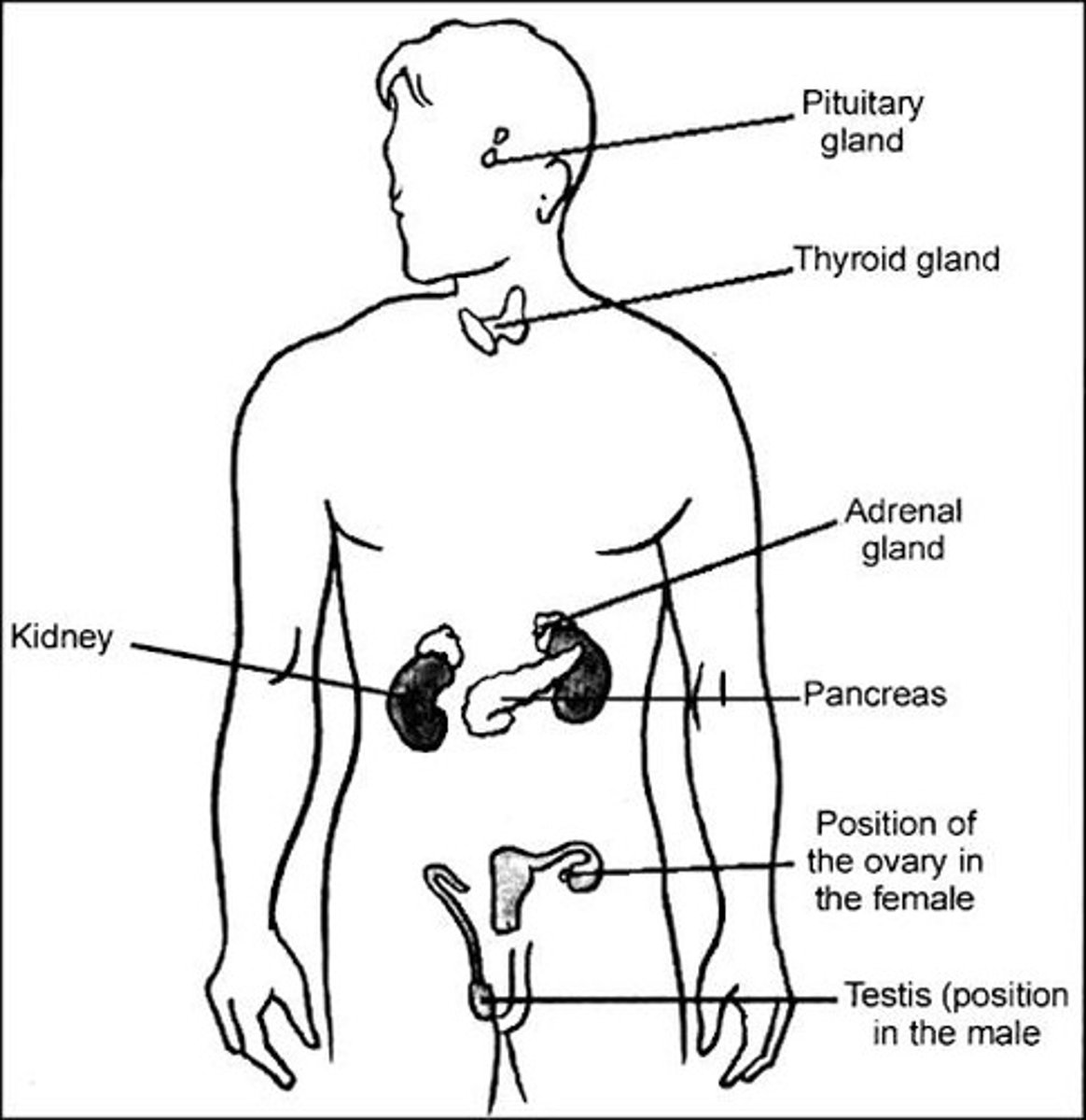
Adrenaline
A hormone produced by the adrenal glands in times of fear or stress that increases heart rate.
Thyroxine
A hormone produced by the thyroid gland that stimulates the basal metabolic rate.
Testosterone
The main male hormone produced by the testes that stimulates sperm production.
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
A hormone produced by the pituitary gland that causes an egg in the ovary to mature.
Luteinising hormone (LH)
A hormone produced by the pituitary gland that causes the mature egg to be released into the oviduct.
Oestrogen
A hormone produced by the ovary involved in thickening the lining of the uterus and inhibiting FSH.
Progesterone
A hormone produced by the ovary involved in maintaining the thickened lining of the uterus.
Fertility drug
A medication given to women to increase their chances of becoming pregnant, containing FSH and LH.
FSH
Follicle Stimulating Hormone, a hormone involved in the maturation of eggs.
LH
Luteinizing Hormone, a hormone that works with FSH in the fertility treatment process.
IVF
In vitro fertilization, a process where eggs are collected from the mother and fertilized by sperm in a laboratory.
Success rate of fertility treatment
The likelihood of achieving pregnancy through fertility treatments, which is noted to be not high.
Multiple births
A condition that can arise from fertility treatments where more than one embryo is implanted, posing risks to the babies and mother.
Contraception
Methods used to control fertility and prevent pregnancy.
Hormonal contraceptives
Birth control methods that contain hormones to inhibit FSH production, preventing egg maturation.
Non-hormonal contraceptives
Methods that do not involve hormones, such as barrier methods and surgical sterilization.
Barrier methods
Contraceptive methods like condoms and diaphragms that prevent sperm from reaching an egg.
Spermicidal agents
Substances that kill or disable sperm to prevent fertilization.
Abstinence
Choosing not to engage in sexual intercourse during the time an egg may be present.
Ecosystem
The interaction of a community of living organisms with the non-living parts of their environment.
Adaptation
Features that enable organisms to survive in their natural environment.
Community
A group of species that live in the same place.
Interdependence
The reliance of each species in a community on other species for resources such as food and shelter.
Stable community
A community where all biotic and abiotic factors are in balance, and population sizes remain constant.
Abiotic factors
Non-living components of the environment that affect living organisms, such as light intensity and temperature.
Biotic factors
Living components of the environment that affect organisms, including availability of food and presence of predators.
Food chain
A linear sequence showing feeding relationships, starting with a producer.
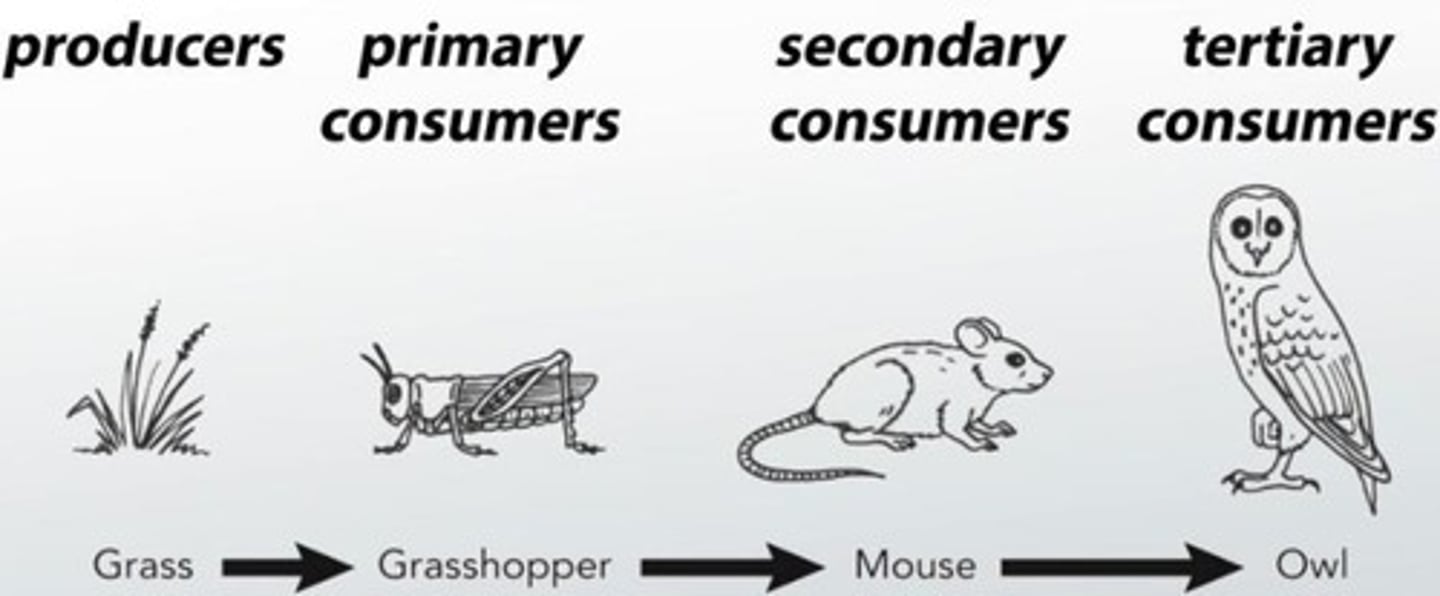
Producers
Organisms that synthesize molecules, typically green plants or algae that make glucose through photosynthesis.
Primary consumers
Organisms that eat producers in a food chain.
Secondary consumers
Organisms that eat primary consumers in a food chain.
Tertiary consumers
Organisms that eat secondary consumers in a food chain.
Environmental changes
Alterations in abiotic factors that affect the distribution of species in an ecosystem.
Carbon Cycle
Carbon moves from the atmosphere into organisms through photosynthesis and is released back to the atmosphere through respiration.
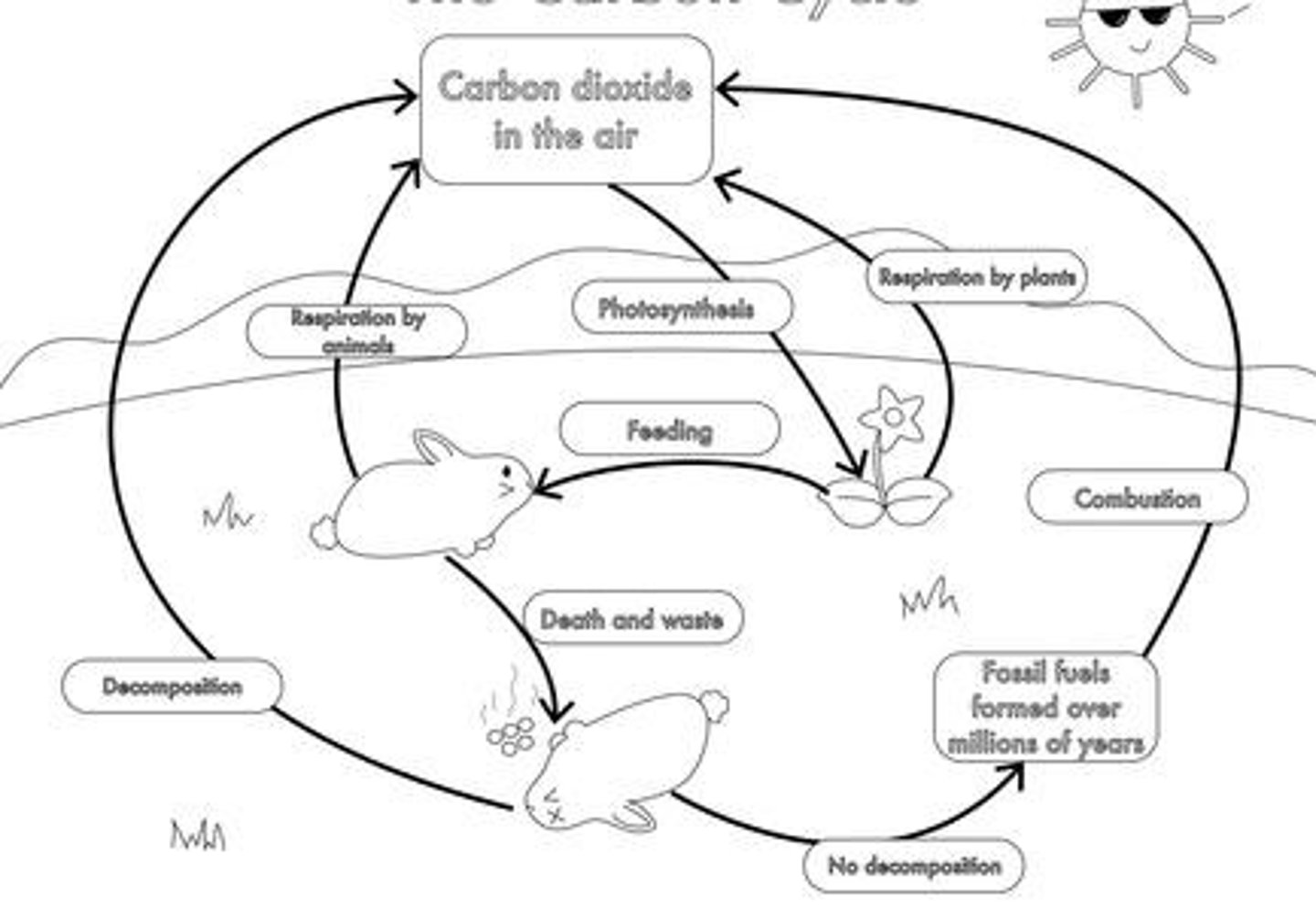
Respiration by microorganisms
When living things die and decay, microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) break chemicals down, returning carbon dioxide to the atmosphere and mineral ions to the soil.
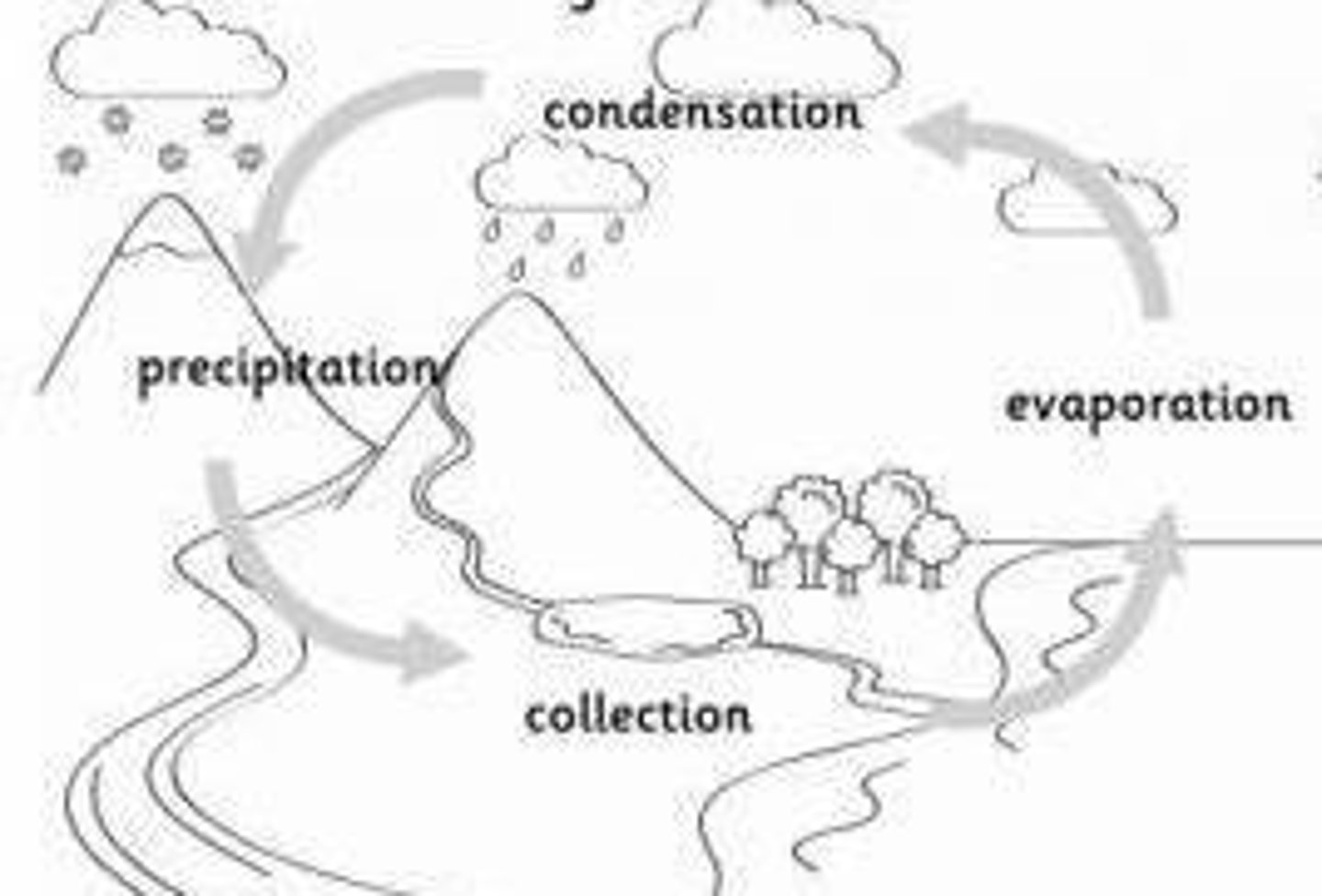
Water Cycle
Rain provides fresh water for plants and animals on land, which drains into the sea through rivers, with continuous evaporation and precipitation of water.
Biodiversity
The variety of all the different species of organisms on earth, or within an ecosystem.
Global warming
The increase in global temperatures due to elevated levels of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere.
High biodiversity
Good for the stability of ecosystems, reducing the dependence of species on one another for food and shelter.
Human activities reducing biodiversity
Human actions have led to increased pollution, habitat loss, food loss, and the spread of disease, reducing biodiversity.
Pollution in water
Caused by sewage, fertiliser, or toxic chemicals, leading to reduced biodiversity.
Pollution in air
Caused by smoke and acidic gases, leading to reduced biodiversity.
Pollution on land
Caused by landfill and toxic chemicals, leading to reduced biodiversity.
Land use
Humans use land for building, quarrying, farming, and dumping waste, which reduces the land available for animals and plants.
Breeding programmes
Initiatives aimed at protecting endangered species to help stop the decline in biodiversity.
Rare habitats protection
Efforts to protect and regenerate rare habitats to support biodiversity.
Compost
Increases food production and is a result of decaying organic matter.
Deforestation
The reduction in size of forests, primarily a problem in tropical areas, often for agricultural purposes.
Genetic variation
Differences in the characteristics of individuals in a population, caused by genetic and environmental factors.
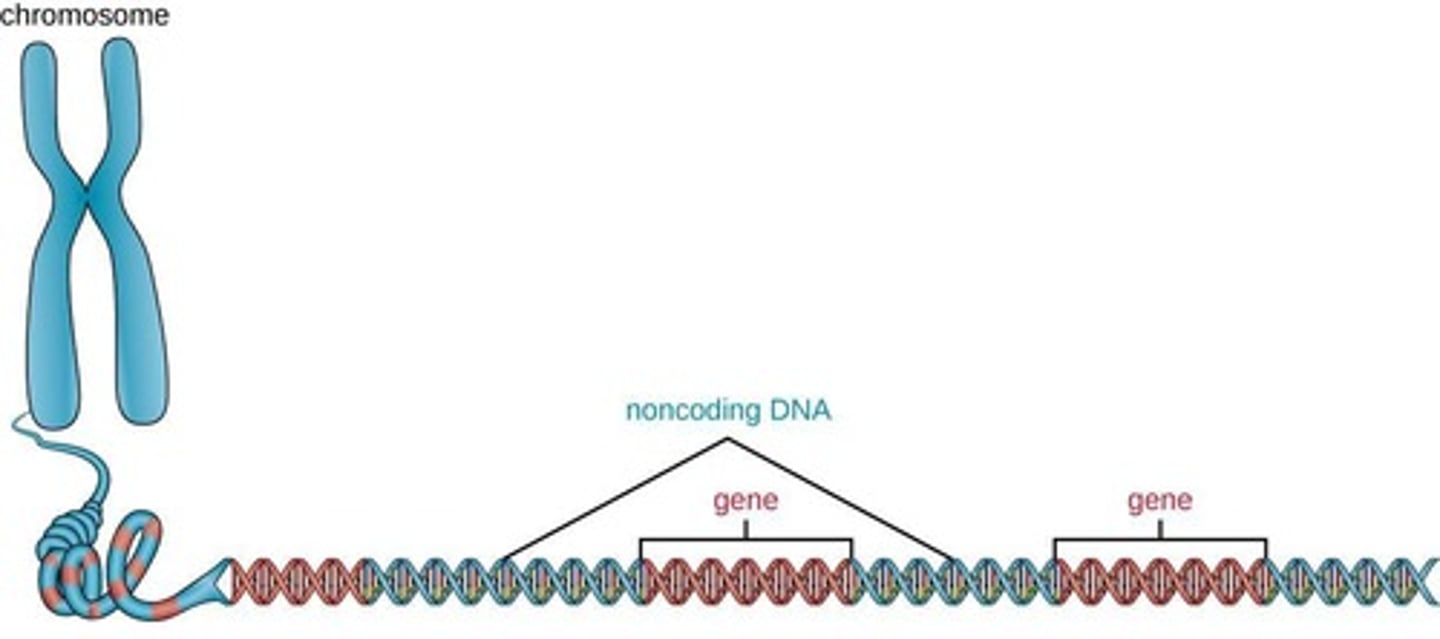
Gene
A short section of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a sequence of amino acids, making a specific protein.
Genome
The entire genetic material of an organism.
Eukaryotic cell
A cell in which genetic material is found in the nucleus and contained in chromosomes.
Non-coding DNA
Parts of DNA that do not code for proteins but can switch genes on and off, affecting gene expression.
Mitosis
A process of cell division in body cells where the number of chromosomes remains the same.
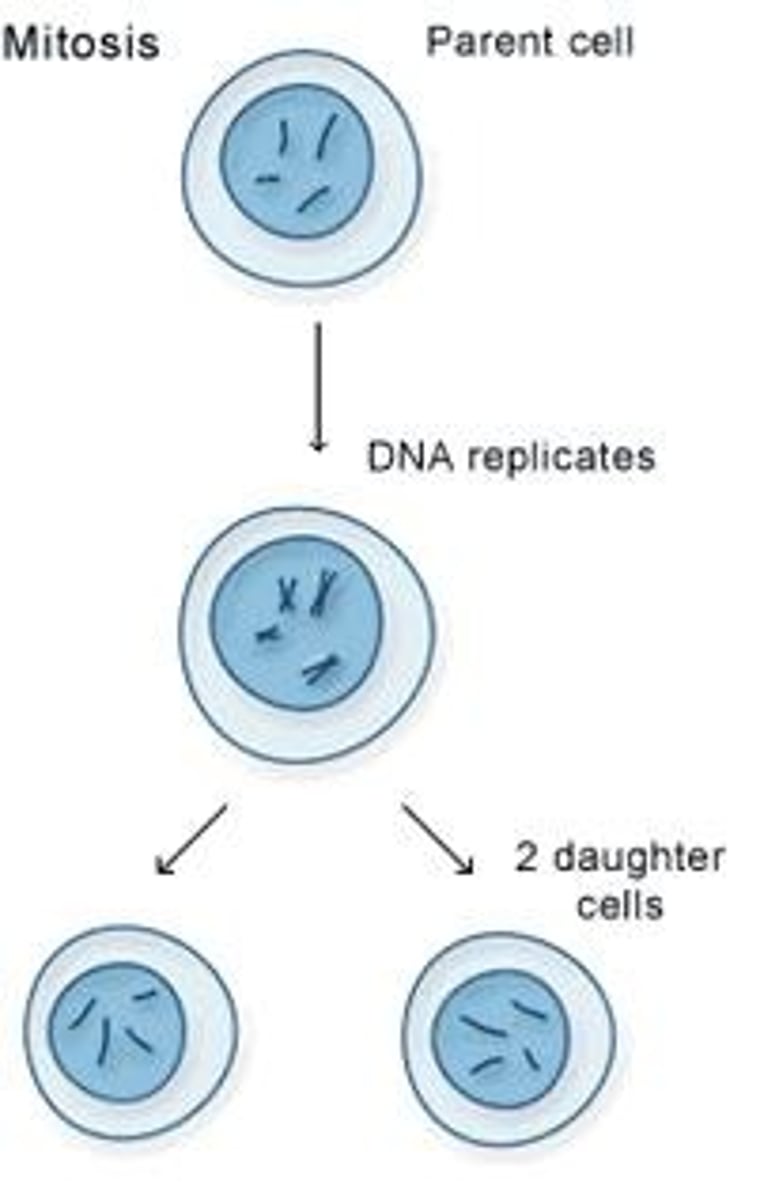
Cell cycle stage 1
The cell grows, the DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome, and new mitochondria and ribosomes are made.
Uses of cell division by mitosis
Growth, Repair of tissues, Asexual reproduction.
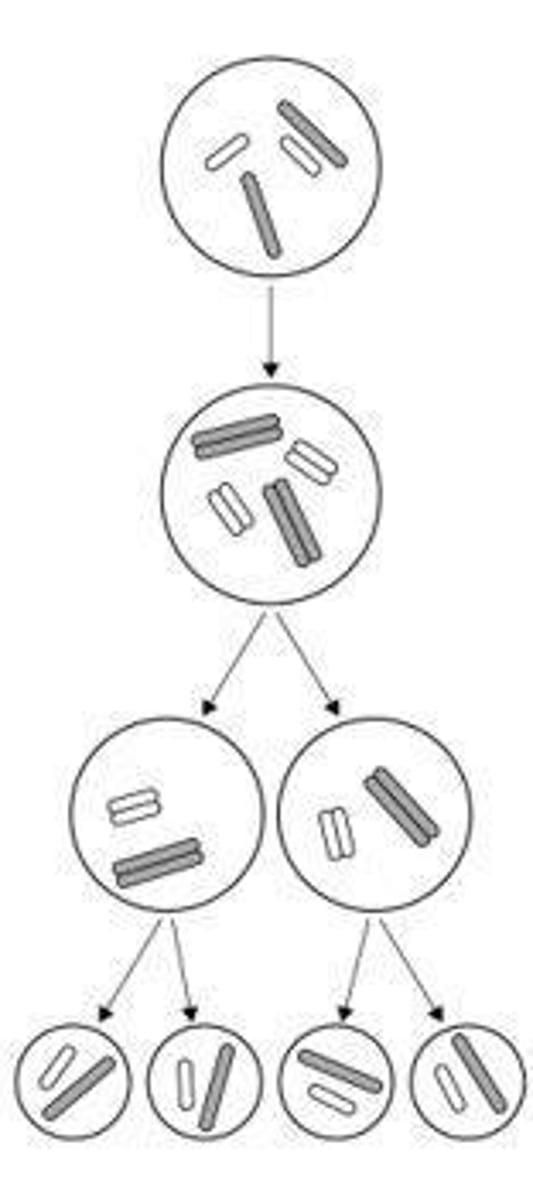
Meiosis
Happens in reproductive organs: ovaries and testes. In meiosis, the number of chromosomes is halved.
Fertilisation
The full number of chromosomes is restored when the male and female gametes fuse.
Cell cycle stage 2
Meiosis: the chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles twice. Male and female gametes join.
Cell cycle stage 3
The cytoplasm and cell membranes divide twice. There are now four genetically different gametes (sex cells).
Asexual reproduction
Involves only one parent.
Sexual reproduction
Involves the fusion of male and female gametes.
Polydactyly
Causes extra fingers or toes.
Allele
Version of a gene e.g. blue eyes, brown eyes.
Cystic fibrosis
A disorder of cell membranes, causing mucus to block narrow passages such as the bronchioles.
Genotype
The alleles that an organism has e.g. AA, Aa or aa.
Phenotype
The characteristics that an organism has e.g. tall, dimples, red flowers.
Dominant allele
A dominant allele is always expressed, even if there is only one copy.
Recessive allele
Two copies of a recessive allele are required for it to be expressed.
Homozygous
Two of the same alleles for a gene e.g. AA or aa.
Heterozygous
Two different alleles for a gene e.g. Aa.
Punnett Squares
A method to predict the probability of offspring genotypes.
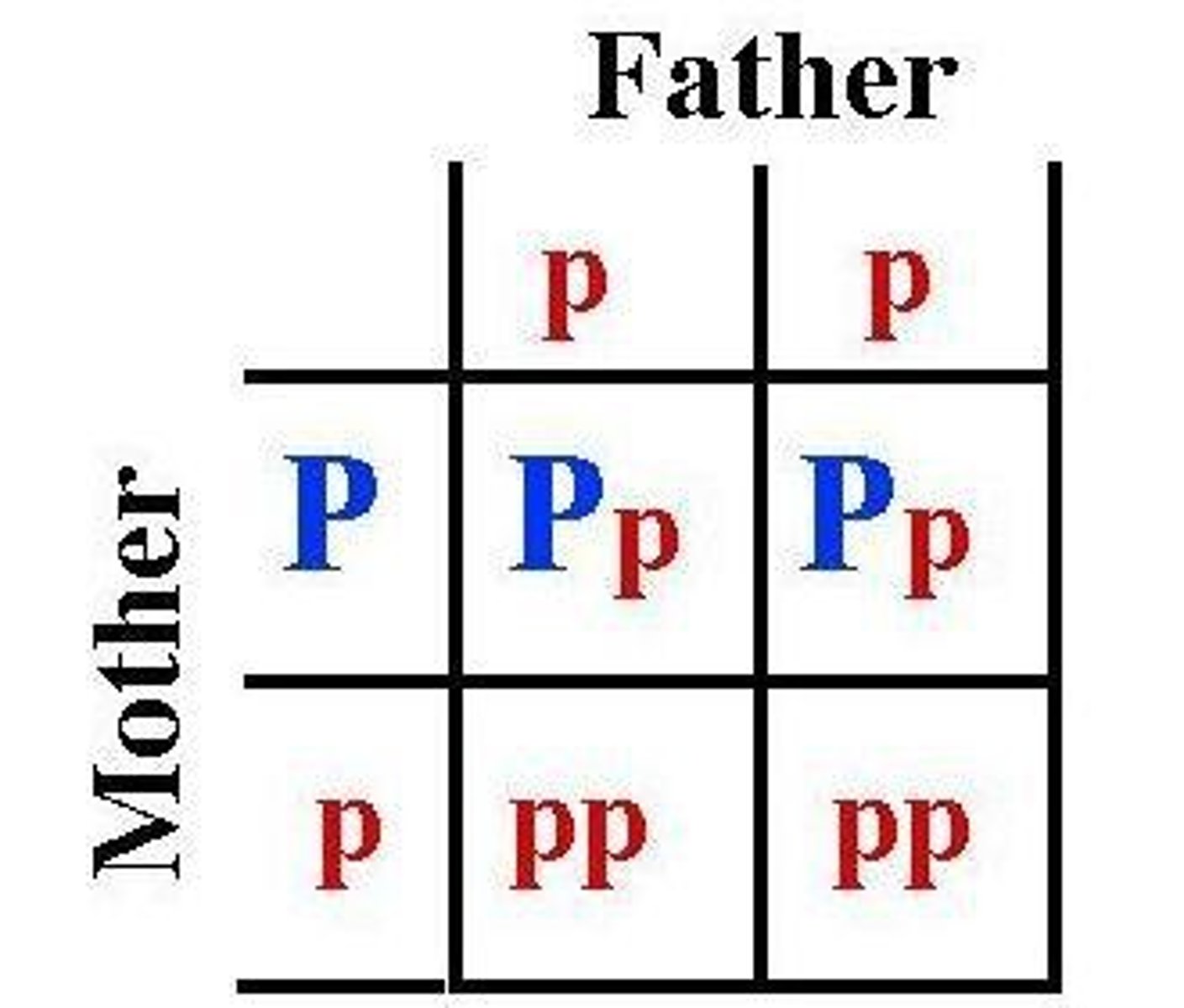
Chance of offspring being pp
1 in 4 or 25%.
Natural Selection
Evolution is a change in the inherited characteristics of a population over time through a process of natural selection.
Mutation
Causes variation in the population.
Fossils
Evidence for natural selection; remains of organisms from millions of years ago, found in rocks.
Problems with the fossil record
Insufficient evidence for theories of evolution.
Extinction
The process through which species cease to exist, often due to factors like new diseases, new predators, climate change, habitat loss, or catastrophic events.
Antibiotic resistant bacteria
Bacteria that have evolved to survive exposure to antibiotics, serving as evidence for natural selection.
Selective breeding
The process where humans breed plants and animals for particular characteristics.
Genetic engineering
The technological alteration of an organism's genome by transferring genes from one organism to another.
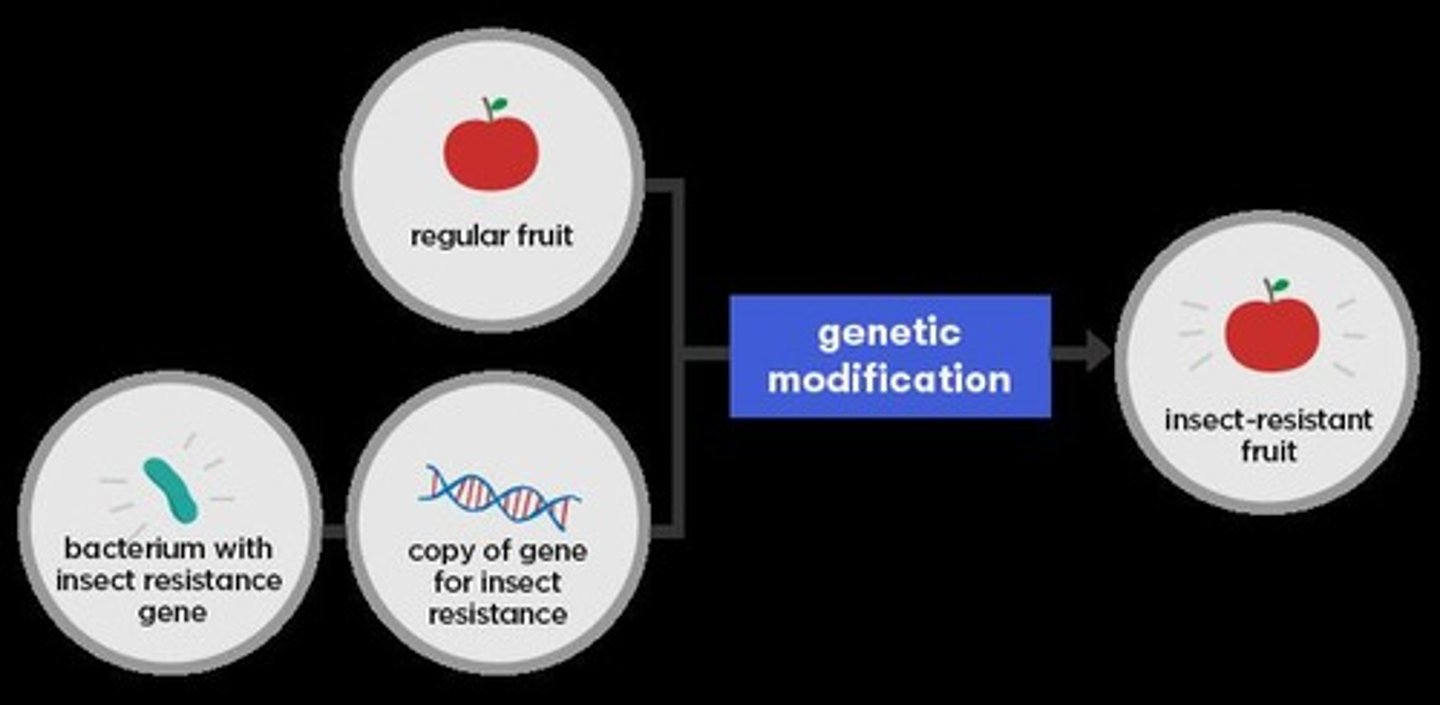
Binomial name
The two-part scientific naming system for organisms, consisting of the genus and species.
Domains
The three new groups proposed by Carl Woese: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukaryota.
Archaea
Bacteria living in extreme environments.