🧬| Chapter 4: Tissue Level of Organization
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from the lecture on tissue types, their structures, and functions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Histology
The study of tissues.
Tissue
A group of similar cells and extracellular products with a common function.
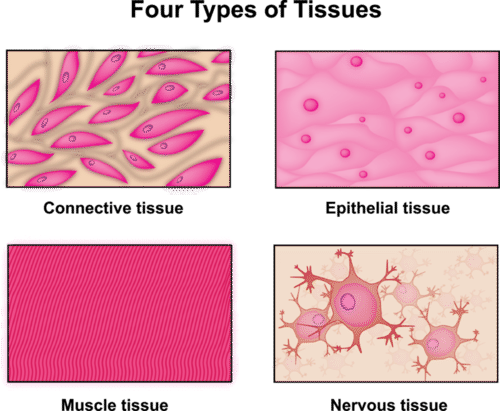
Epithelial Tissue
Tissue that covers surfaces, lines cavities, and forms glands.
Connective Tissue
Tissue that fills spaces, supports, and stores energy.
Muscle Tissue
Tissue for contraction and movement; includes skeletal, cardiac, smooth.
Nervous Tissue
Tissue that conducts electrical impulses and carries information.
Epithelium
A sheet of epithelial cells covering or lining a body surface or cavity.
Basement Membrane
Non-cellular layer anchoring epithelial cells, from epithelium and connective tissue.
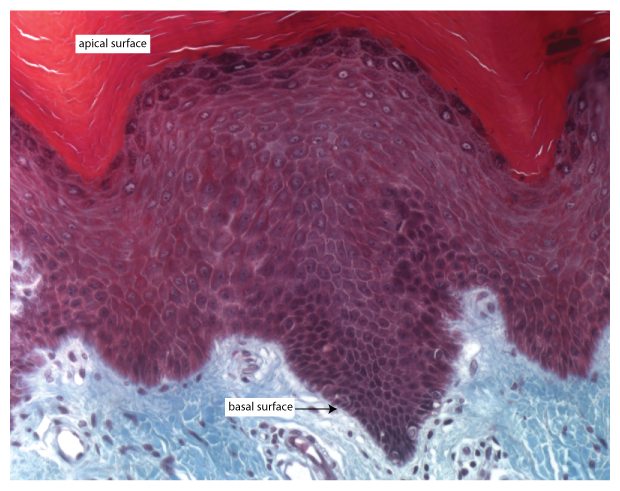
Apical Surface
The free surface of an epithelial cell exposed to the body exterior or cavity interior.
Microvilli
Microscopic, non-motile apical projections for increased absorption surface area.
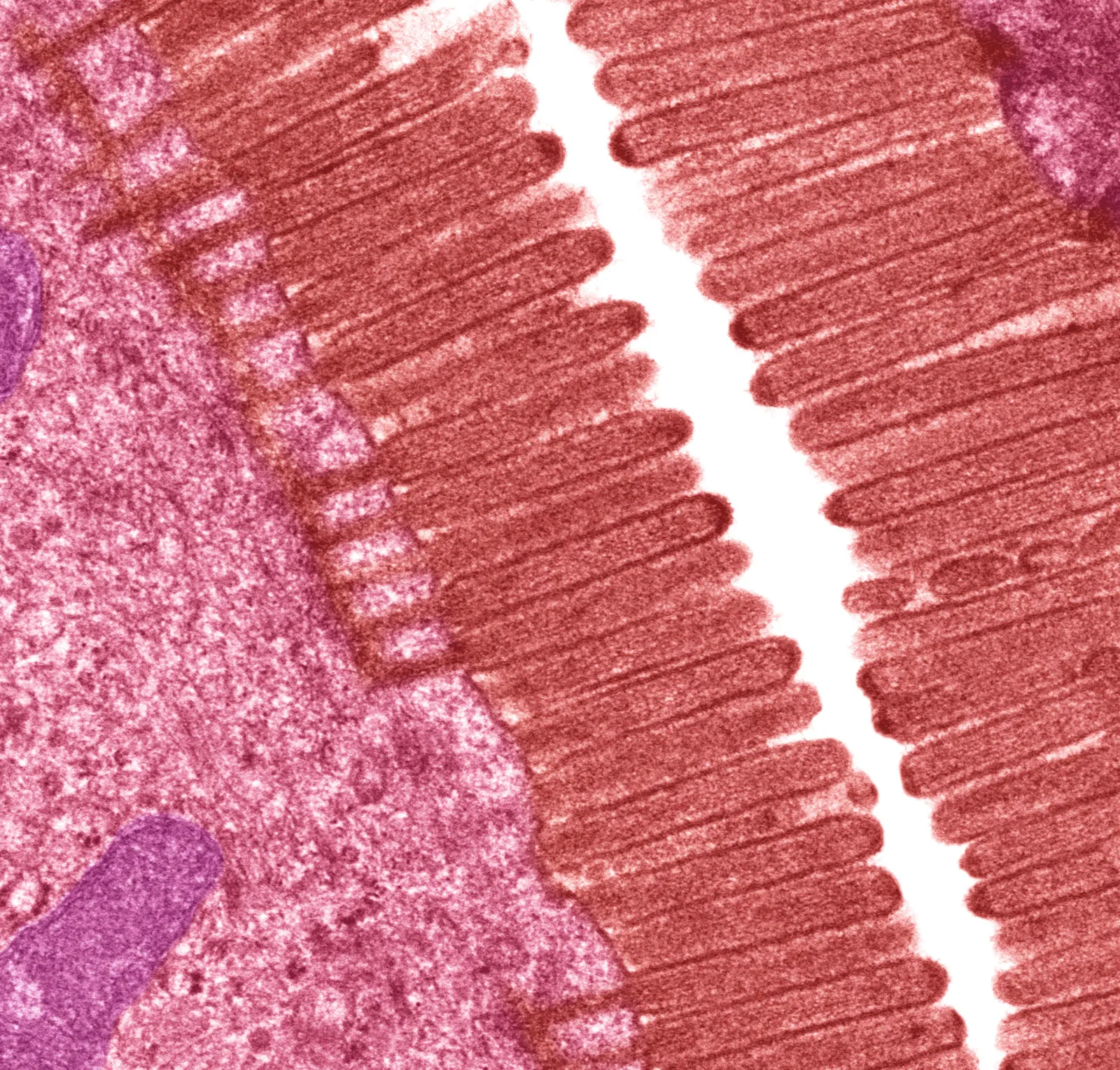
Cilia
Motile, hair-like projections on apical surfaces that move fluid or mucus.
Basolateral Surface
The sides and base of an epithelial cell that attach to neighbors and the basement membrane.
Tight Junction
Intercellular junction that seals adjacent cells to prevent passage of water and solutes.

Gap Junction
Intercellular junction allowing ions and small molecules to pass between cells.
Desmosome
Strong intercellular junction that resists stretching and twisting stresses.
Simple Epithelium
Epithelium with one layer of cells.
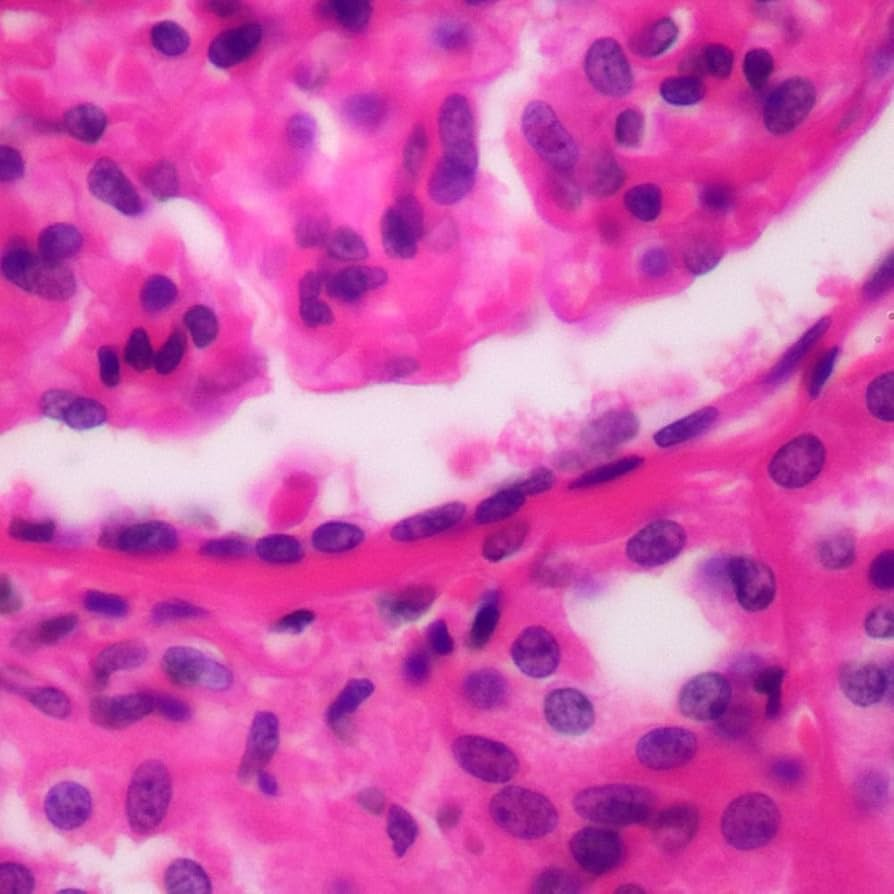
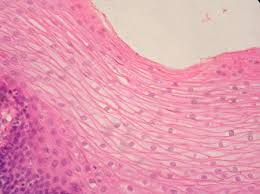
Stratified Epithelium
Epithelium with two or more layers of cells.
Squamous Cell
Epithelial cell wider than tall; plate-like.
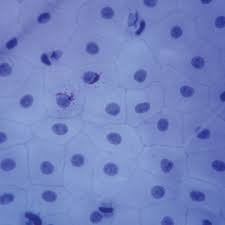
Cuboidal Cell
Epithelial cell as tall as wide; cube-shaped.
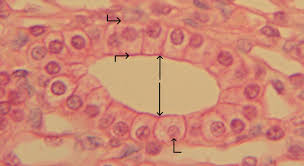
Columnar Cell
Epithelial cell taller than wide; column-shaped.
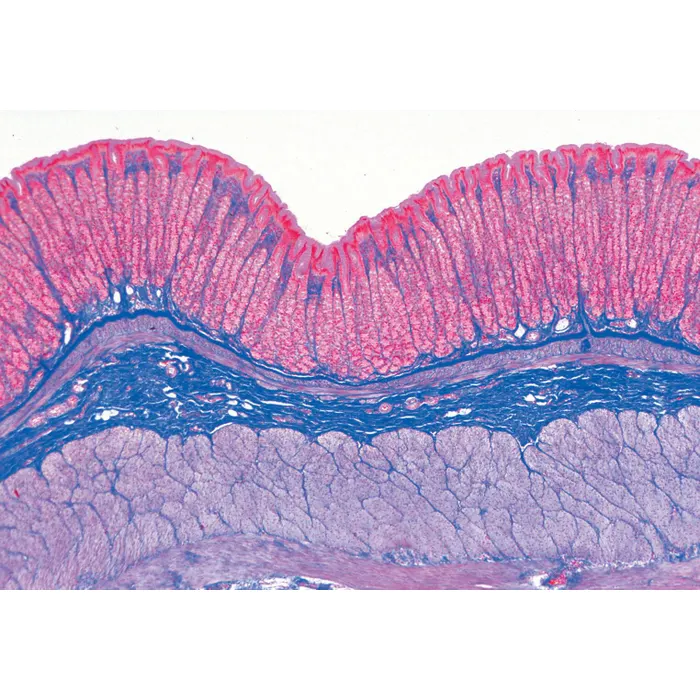
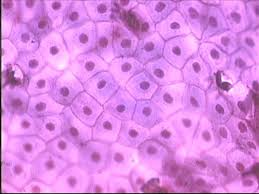
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Single layer of flat cells; permits diffusion/filtration and secretes lubricants.
Mesothelium
Simple squamous epithelium lining pericardial, pleural, and peritoneal cavities.
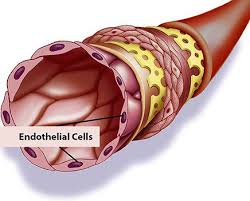
Endothelium
Simple squamous epithelium lining heart and blood vessels.
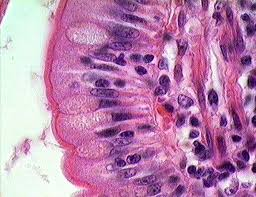
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Single layer of cube-like cells; functions in secretion and absorption.
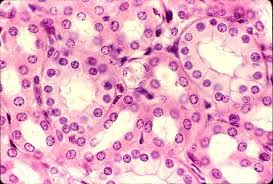
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Single layer of tall cells; involved in absorption and secretion; ciliated form propels mucus.
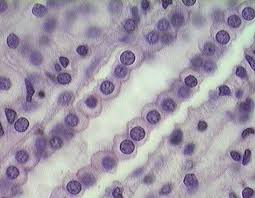
Goblet Cell
Unicellular exocrine gland that secretes mucin to form mucus.
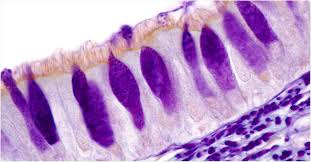
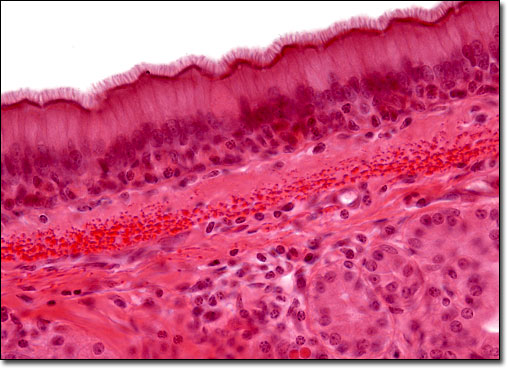
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium
Appears stratified but all cells touch basement membrane; cilia move mucus.
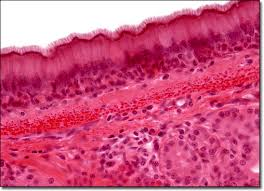
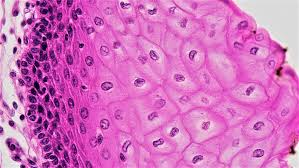
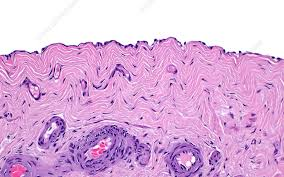
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Multiple layers of cells; protects against severe mechanical or chemical stresses.
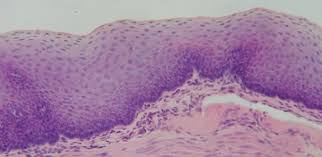
Keratinized Epithelium
Stratified squamous epithelium with surface layers packed with keratin, making it tough and water-resistant.
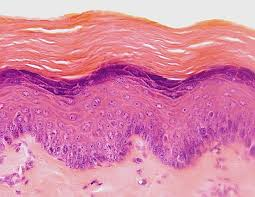
Nonkeratinized Epithelium
Stratified squamous epithelium lacking surface keratin; must remain moist.
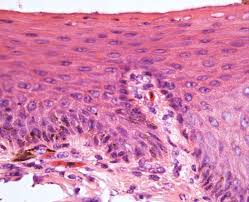
Transitional Epithelium
Stratified epithelium that stretches; lines urinary bladder, ureters, and proximal urethra.
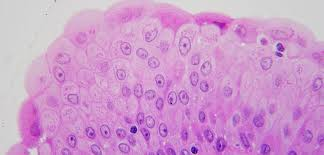
Glandular Epithelium
Epithelial tissue specialized for secretion forming exocrine and endocrine glands.
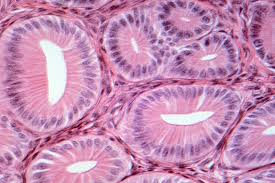
Exocrine Gland
Gland that releases secretions into ducts leading to epithelial surfaces.
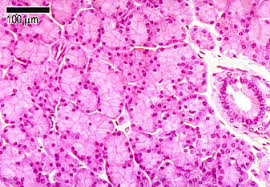
Endocrine Gland
Ductless gland that releases hormones into the bloodstream.
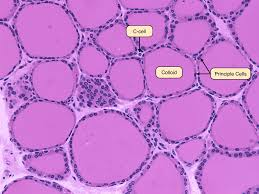
Connective Tissue Proper
Connective tissue with diverse cells, fibers, and syrupy ground substance.
Areolar Tissue
Loose connective tissue with all cell types; widely distributed packing material.
Adipose Tissue
Loose connective tissue of adipocytes that stores fat and insulates the body.

Reticular Tissue
Loose connective tissue with reticular fibers forming a stroma in lymphoid organs.
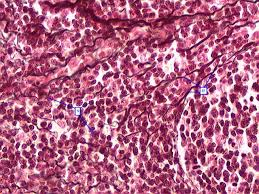
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
Connective tissue with parallel collagen fibers; forms tendons and ligaments.
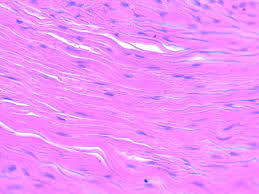
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
Connective tissue with thick, interwoven collagen bundles; found in dermis and organ capsules.
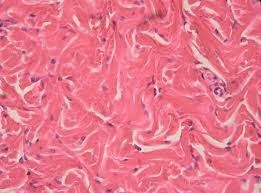
Elastic Tissue
Connective tissue rich in elastic fibers; allows stretch and recoil in arteries and ligaments.

Plasma
Fluid blood matrix suspending formed elements.
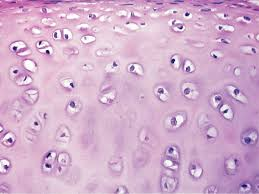
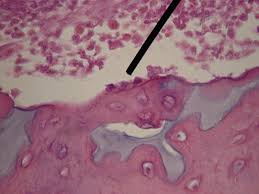
Cartilage
Supporting connective tissue with chondrocytes in lacunae and a firm, avascular matrix.
Chondrocyte
Mature cartilage cell occupying a lacuna.
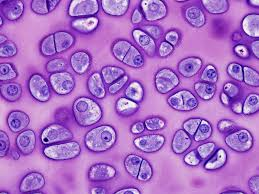
Lacuna
Small cavity in cartilage or bone matrix housing a cell.
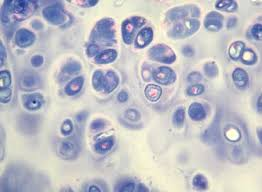
Perichondrium
Dense irregular connective tissue membrane surrounding cartilage.
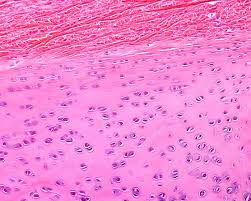
Hyaline Cartilage
Common, stiff-flexible cartilage; reduces joint friction.
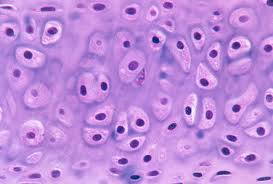
Elastic Cartilage
Cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; tolerates distortion and returns to shape.
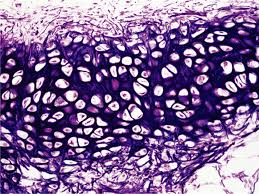
Fibrocartilage
Cartilage with dense collagen; resists compression and limits movement.
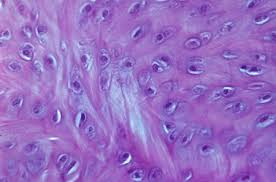
Bone (Osseous Tissue)
Supporting connective tissue with calcified matrix and collagen fibers.
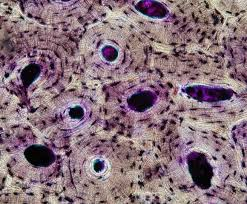
Osteoblast
Bone-forming cell that secretes bone matrix.
Osteocyte
Mature bone cell residing in a lacuna; maintains bone matrix.
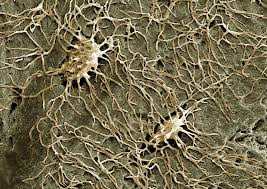
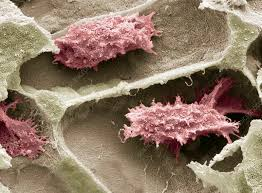
Osteoclast
Large, multinucleated cell that resorbs bone matrix.
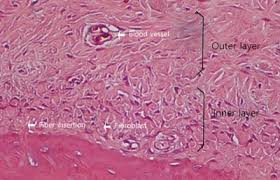
Periosteum
Dense connective tissue membrane covering bone surfaces except at joints.
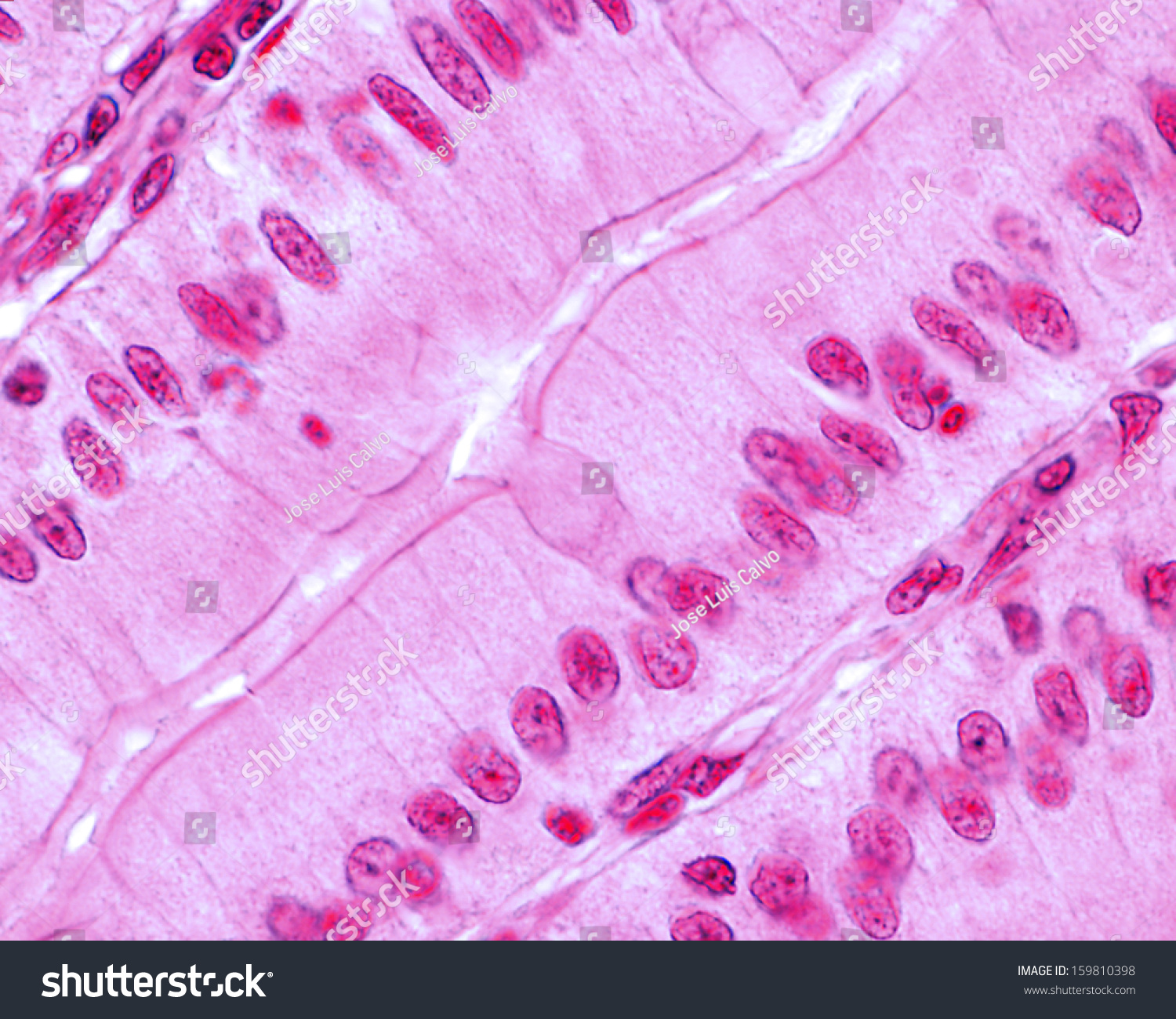
Muscle Fiber
Elongated muscle cell capable of contraction.

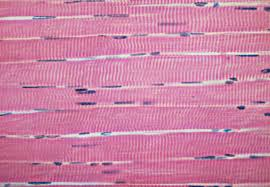
Skeletal Muscle
Striated, multinucleated voluntary muscle attached to bones.
Cardiac Muscle
Striated, branched involuntary muscle of the heart with intercalated discs.
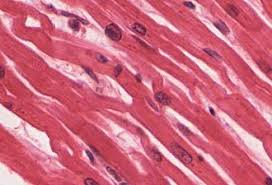
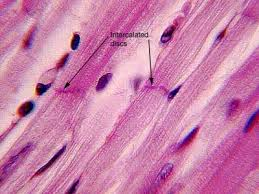
Intercalated Disc
Specialized junction of cardiac muscle; synchronizes contraction.
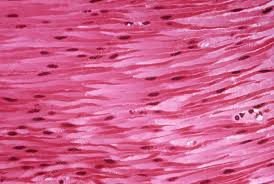
Smooth Muscle
Non-striated involuntary muscle in walls of hollow organs and blood vessels.
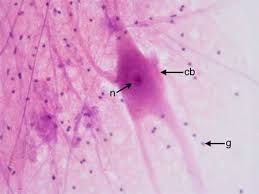
Neuron
Excitable cell that transmits electrical impulses.
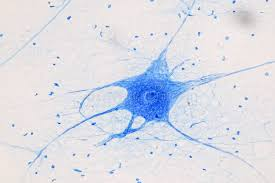
Soma
Cell body of a neuron containing the nucleus.
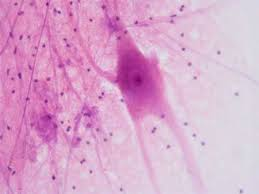
Dendrite
Branched neuronal process that receives signals.
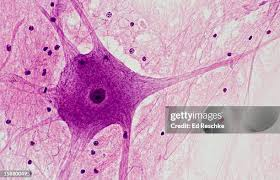
Axon
Long neuronal process that conducts impulses away from the soma.
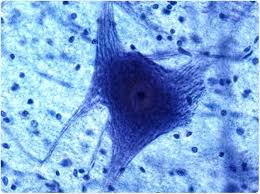
Neuroglia (Glial Cells)
Supporting cells nourishing, protecting, and insulating neurons.