OBGYN PATHO 6
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Neisseria gonorrhea
gram negative organism, known to cause PID
Chlamydia trachomatis
Atypical intracellular bacterium
infects epithelial cells —> infection
urine tests and swabs from genital sites
Syphilis
treponema pallidum
sexual and congenital transmission
serologic testing
(+ patient history ofc)
diagnosis of syphilis?
Primary stage of syphilis
single papule undergoes ulceration —> painless chancre
highly contagious
Secondary stage of syphilis
occurs in 25% of untreated syphilis
rash (involving trunk, extremities, palms and soles of feet)
highly contagious
Lues maligna
more severe ulcerative form of secondary syphilis
seen in in patients with HIV
secondary syphilis
moth eaten appearance of patchy, scalp hair loss is associated with?
Latent syphilis
contagious, but less than other stages of syphilis (early)
not considered infectious to sexual partners (late)
gumma formation
macrophages attempting to control the disease in untreated syphilis leads to?
Neurosyphilis
rare complication
can occur at any stage
CNS infection
Argyll Robertson pupil
no pupil constriction to light, but constricts for focusing on other obejcts
Neurosyphilis
Argyll Robertson pupil is a sign of?
Exocervix
visible portion of the cervix
Endocervical canal
lined with columnar epithelial cells that produce and secrete mucus
Nabothian cysts
small, dome shaped nodules that are either translucent or opaque
caused by trapped mucus in mucosal glands
benign, most don’t require tx
RARELY grow large, so they don’t cause obstruction of the cervix
menarchial
A
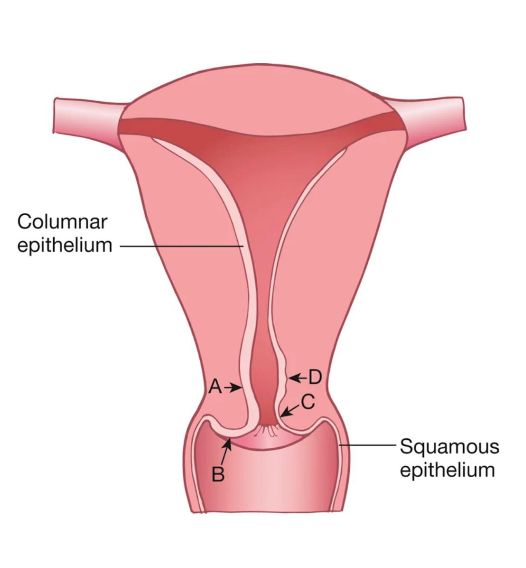
Age
Location of the squamocolumnar junction (SCJ) varies by?
Menstruating
B
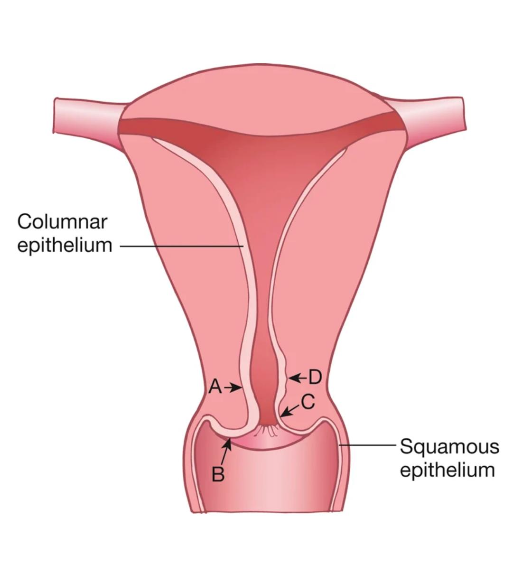
Menopausal
C
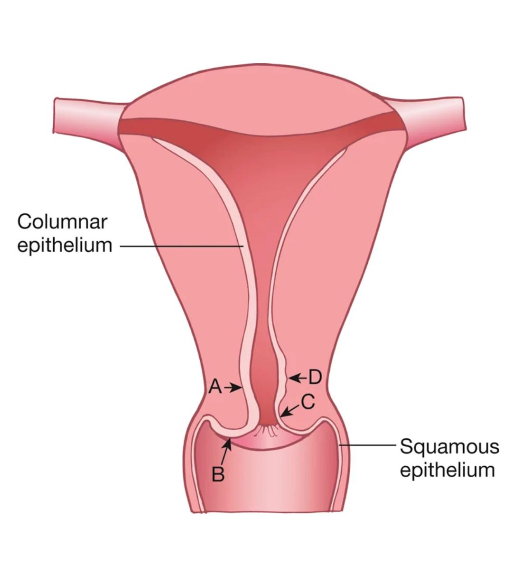
Postmenopausal
D
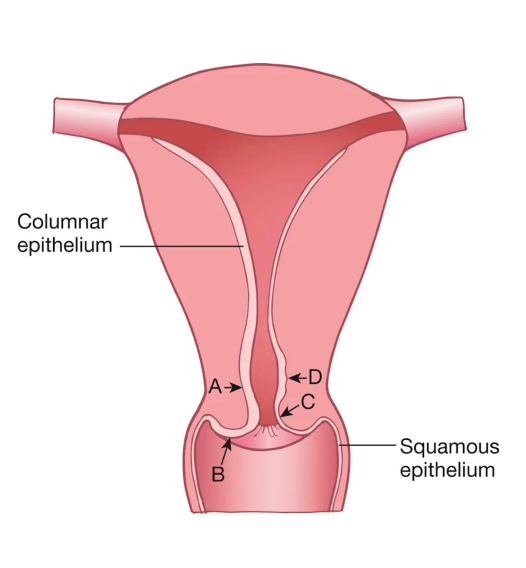
Transformation Zone
where columnar epithelium is being replaced by squamous epithelium (squamous metaplasia)
Transformation Zone
Area most likely to develop into cancer
Transformation Zone
Located between the original SCJ and the new SCJ
Cervical Cancer
readily detected
if detected early —> most easily cured of all reproductive cancers!
ages: 35-44, avg age 50
HPV vaccine
Rates declined in women 20-24, possibly reflecting signs of cancer prevention from what?
Cervical Cancer risk factors
early age at first intercourse
multiple sexual partners
smoking
Hx of STI’s
WSW due to delayed screening
Cervical cancer
Evidence suggests a causal ling between HPV infection and what cancer?
Gardasil
Prevents infetion with HPV subtypes 16, 18, 6 and 11
condyloma accuminata (genital warts)
HPV subtypes 6 and 11 and MC associated with?
HPV 16 and 18
Which 2 HPV strains are responsible for 70% of cervical cancer?
HPV 6 and 11
Two most common benign strains, account for 90% of genital warts
5 years
HPV testing is recommended every?
cervical dysplasia
65 year old with no hx of ——- ——- and the following
can discontinue screening:
3 neg pap test results
2 neg HPV tests in a row
2 neg co-test results in a row within the past 10 years
3 years
Cytology alone every?
5 years
HPV testing plus cytology every?
Primary testing
HPV testing alone, without cervical cytology
Co-testing
HPV and cytology are collected, and results are provided together
Reflex testing
HPV testing performed automatically on a sample when the cytology result returns positive for atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance
Self collection
When access to a speculum examination is limited or for those who are reluctant to undergo a pelvic exam, —— may be used for select HPV tests
Transformation zone
critical area of development of cervical cancer
Carcinoma
Untreated dysplasia can develop into ?
Metaplasia
During ——, newly developed squamous epithelial cells are vulnerable to development of dysplasia
(reason behind why transformation zone is associated with cancer development)
Colposcopy
follows an abnormal pap test and involves a biospy
premenopausal
Presence of endometrial cells is NORMAL in?
postmenopausal
Presence of endometrial cells is ABNORMAL in
ASC- US (atypical squamous cells of undetermined sginificance)
Most common abnormal pap smear finding? (1 in 15 tests)
cells did not look normal but did not meet criteria for lesion
cancer is unlikely
What are ASC-US?
Repeat pap smear in 6-12 months
If it persists —> colposcopy
If you find ASC-US, how to proceed with care?
Dysplasia
Term for disordered growth of development of cell
Low grade intraepithelial lesions (LGSIL)
mild dysplasia on surface of cervix
minor abnormalities observed
often CIN I on biopsy
High grade squamous intraepithelial lesions
(HGSIL)
more severe, higher cancer risk
associated with CIN 2 or CIN 3
colposcopy
CIN I
mild dysplasia or atypical changes
well differentiated
initial 1/3 of epithelial layer is involved
CIN II
moderate dysplasia
initial 2/3 of epithelial layer
less well-differentiated lesion
CIN III
severe dysplasia
carcinoma in situ
full-thickness involvement
undifferentiated lesion
squamous cell carcinomas
90 % of cerivcal cancers are ?
Glandular lesions
atypical glandular cells (AGC)
less common
needs investigation for glandular intraepithelial neoplasm (GIN) or adenocarcinoma
Koilocytes
abnormal squamous epithelial cells
characterized by a clear, halo-like area (perinuclear
vacuole) surrounding a dense, often hyperchromatic nucleus
Koilocytes
Which cells are strongly associated with HPV?
Abnormal patterns of cell division
Abnormal mitotic figures = ?
Pleomorphism (aka aniskaryosis)
variability in size and shape of cells and their nuclei
Methods for diagnosing cervical cancer
Pap smear (demonstrating SIL)
Colposcopy
Biopsy sample
cervix, vagina, and vulva
In colposcopy:
Colposcope is used to examine the —-, —- and —-
colposcopy
has significant interperformer variability and poor reliability
Methods of removing lesion for early treatment of cervical cancer
Local cautery
Electrocautery, cryosurgery, or carbon dioxide laser
therapy used to treat moderate to severe dysplasia
limited to the exocervix
Therapeutic conization
If the lesion extends into endocervical canal?
removes a cone shaped piece of tissue
using scalpel, laser or LEEP
surgery (hysterectomy), radiation, chemotherapy
Polyps
soft, velvety red lesions that can develop anywhere in the endometrial cavity
Glandular epithelial hyperplasia
Polyps usually arise from —- —- ——, with the tip of the polyp often exhibiting squamous metaplasia.
Polyps
-Usually develop as a result of inflammatory
hyperplasia of the endocervical mucosa
▪Mutations, overexpression of endometrial
aromatase, age related gene mutations KRAS,
PTEN, and TP53
Bleeding
MC presentation of polyp?
Polyp
Typically asx, may have associated poistcoital bleeding
Most are benign but should be removed and examined
Risk factors for polyps
• Tamoxifen
• Obesity
• Hormone replacement therapy
• Lynch and cowden syndrome: hereditary cancer predisposition syndromes
autosomal dominant genes
Lynch and cowden syndrome are both?
Oral contraceptives
Also Levonorgestrel Intrauterine System (LNG IUS)
use is associated with decreased rates of endometrial polyps
Transvaginal US (TVUS)
first line imaging study of choice for polyps
followed by sonohysterography or diagnostic hysteroscopy
Staphylococcal Toxic Shock syndrome
rapid onset fever, rash, hypotension, multisystem involvement
Toxin production
— — plays in important role in the patho of STSS.