Anatomy Final Exam Extra Credit (Ch. 15)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
What are the “5 senses”?
Sight
Taste
Smell
Hearing
Touch
What is the 6th sense?
Balance/equilibrium
The special senses (all but touch) contain distinct ______ modified to be special receptors
Sensory cells
About 70% of the sensory receptors in the body are in the ____
eyes
About 50% of the cerebral cortex is involved in _______
visual perception
Vision requires a ___________ reaction - a change in chemical structure caused by light energy
photochemical
Vision is our _____ sense, and is the perception of objects in the environment by means of the ____ they emit or reflect
dominant; light
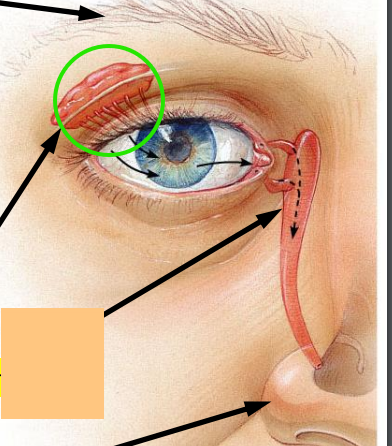
Lacrimal Gland
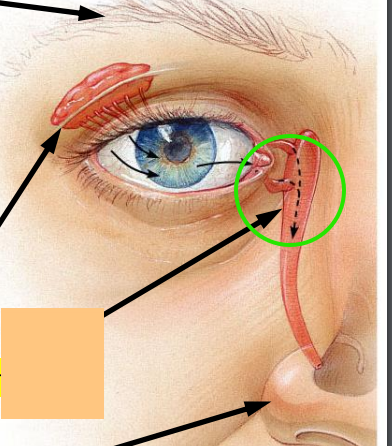
Lacrimal Sac
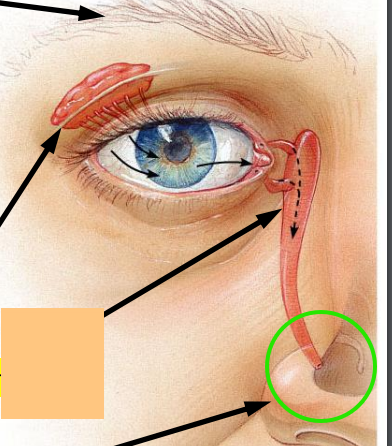
Lacrimal Duct
_________ protect the eye and aid eye function
accessory structures
What are the 5 accessory structures of the eye?
Eyebrows (protection and shade)
Eyelids (protection)
Conjunctiva (lubricating mucous production)
Lacrimal apparatus (team production and spread)
Extrinsic eye muscles (eye movement)
Your nose runs when you cry because your tears exit through the _____.
nose
There are _____ pairs of ocular muscles that control the eye
6
Strabismus (cross-eyed) is caused from _________.
weakness in ocular muscles.
90% of people aged 55+ have eyelash _____.
mites
The eye ____ and ____ separate the eye into
lens and ciliary zonule
the eye is a ________, _______ hollow sphere
slightly irregular, fluid filled
What are the 3 layers (tunics) of the eye?
fibrous, vascular, and inner sensory layer
The fibrous layer of the eye has 2 regions. The _____ and ______
sclera and cornea
The lens is _____, transparent, and ______.
biconvex; flexible
What are the 4 characteristics of the sclera?
opaque posterior region
protects and shapes eyeball
Anchors extrinsic eye muscles
posteriorly, where optic nerve exits, sclera is continuous with dura mater of brain
What are the 3 characteristics of the cornea?
Transparent anterior one-sixth of fibrous layer (forms clear window to let light enter and bends light as it enters)
Epithelium covers both surfaces (outer surface protects from abrasions, inner contains sodium pumps to maintain clarity)
Numerous pain receptors for blinking and tears
what are the 3 regions of the eye’s vascular layer?
Choroid
ciliary body
iris
what are the 3 characteristics of the choroid region?
Posterior portion of uvea
supplies blood to all layers of eyeball
Brown pigment absorbs lite to prevent light scattering, which would cause visual confusion
What is the function of the ciliary body?
to hold the lens in place
The iris is the colored part of the eye that lies between the _____ and _____, continuous with ciliary body.
cornea and lens
The pupil is the central opening that _______ the amount of light entering
regulates
close vision and bright light causes the sphincter pupillae (circular muscles) to contract and pupils _____. Parasympathetic control
constrict
Distant vision and dim light cause dilator pupillae (radial muscles) to contract and pupils to _____. Sympathetic control
dilate
Changes in emotional state, like when subject matter is appealing or requires problem solving skills, cause pupils to ______.
dilate
The inner layer (retina) contains what 3 things?
millions of photoreceptor cells that transduce light energy
neurons
glial cells
The optic disc is the site where the ______ leaves the eye, lacks photoreceptors, so it is referred to as a ______.
optic nerve; blind spot
The retina has a quarter billion photo receptors that are in one of 2 types, ____ and _____.
Rods and cones.
Signal output travels the _______ direction of light in the eye
opposite.
Rods in the eye see ___ and are your ____
dim light, peripheral vision receptors.
Rods are _____ and ______ to light than cones
more numerous, more sensitive
Rods lack ______ but have their numbers greatest in the ______ vision
color vision; peripheral
Cones are vision receptors for _____ and have ________.
bright light; high-resolution color vision.
The fovea centralis is a tiny pit in the center of the macula lutea that contains all ____.
cones
Diabetic retinopathy causes _____ in vision due to damaged blood vessels
dark spots
Glaucoma causes blindness due to lack of _________ drainage, putting pressure on the retina and optic nerve
aqueous humor
Cataracts occur when _____ precipitates on the lens, clouding vision
protein
Chemical senses are ______ and _____
olfaction (smell) and gustation (taste)
The chemoreceptors respond to chemicals in _____ and are complimentary
aqueous solution
in smell, substances are dissolved in _____.
mucus
In taste, substances are dissolved in _____.
saliva
Smell is the ______ sense to develop in the embryo
first
An infant can recognize their mother by _____ old
7 days
Smell acts as an ________ for things like bad food, chemical fumes, fire.
early warning system
Smell has a _____ factor in taste
strong
smell can trigger _____ and may have a role in ______.
memories; reproduction.
olfactory receptor cells are specialized _______.
bipolar neurons
olfactory cells are the ____ cells able to reproduce every 60 days
only
mucus captures ______ substances for detection
inhaled
Naegleria fowleri can follow ______ to the brain and can cause death.
olfactory nerves
there are about ______ tastebuds on the tung, in peg like papillae
10,000
different types of papillae may have different ____, but all contain tastebuds
shapes
all parts of the tounge can taste _____ taste sensations
ALL
what are the 5 basic taste sensations?
-sweet - (sugar)
-Salt - (metal ions)
Sour - (hydrogen ions, acids)
Bitter - (alkaloids)
Umami (savory, elicited by the amino acid glutamate)
To be tasted, what must happen to a chemical
Dissolved in saliva → Diffuses into taste bud pore → Touches gustatory hair → Release of synaptic vesicle contents from gustatory cell, triggering a nerve signal
Adaptation of a taste occurs within __ to __ minutes, which is why food tastes best when you start eating.
1-5
what is the pathway for taste?
Taste buds → Medulla oblongata → Thalamus, hypothalamus and limbic system (appreciation of taste) → Gustatory cortex (recognition of taste)
Taste triggers the hypothalamus to trigger what 3 things?
salivation
Stomach secretions/motility
If foul or rancid food - vomiting center
Taste is ___ smell
80%
________ is the feeling when something that is though to be tasted is actually just smelled.
Retronasal olfaction
Aroma _____ taste
enhances
Nasal congestion _____ taste.
decreases
sound is an audible _____ of molecules
vibration
Sound can be transmitted through ____, ____, and ____, but not ____.
Water, Solids, Air; But not a vacuum.
The _______ vibrates and moves the ossicles
tympanic membrane
Ossicles _____ sound and ___ fluid within inner ear
amplify; move
What are the 4 steps in hearing?
sound waves vibrate the tympanic membrane
Auditory ossicles vibrate, pressure is amplified
Pressure waves created by stapes pushing on the oval window move through fluid in the scala vestibuli
4a. Sound with frequencies below hearing level go through the helicotrema and do not excite hair cells
4b. Sound in the hearing range go through the cochlear duct, vibrating the basilar membrane and deflecting hairs on inner hair cells.
vestibules or maculae maintain a _____ and can sense ______.
static equilibrium; linear acceleration
Semicircular canals maintain _____ planes, and can sense _______.
X, Y, and Z planes; rotational acceleration.
Hair cells in the ear ____ with the fluid movement in inner ear, speed and direction of it is interpreted by the _____
bend; brain
Motion sickness is caused by _______ confusing integrative centers. Ears say the body is moving, Eyes say the body isn’t, etc.
conflicting sesnory input
Benign positional vertigo (“Otoconia“) is caused by the detatchment of the ____.
otolith