Polymers
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is a polymer?
A very large organic molecule made up of small repeating units
How are polymers formed?
From reactions between small organic molecules called monomers in a process called polymerisation.
What are addition polymers and draw the polymerisation process of ethene?
They are formed from certain alkenes (containing a C=C bond)
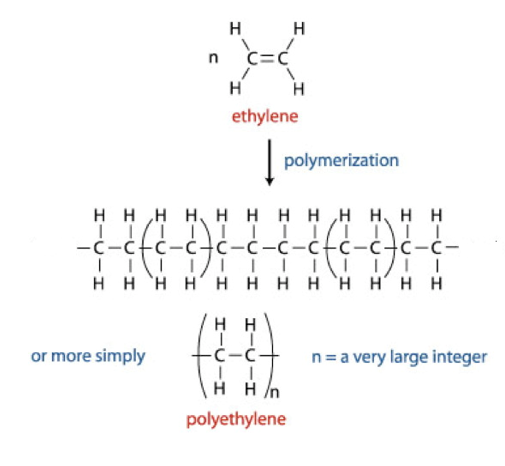
Is addition polymerisation a spontaneous reaction?
No it is not spontaneous and requires high temperatures and high pressures.
What is the side affect of using high pressure and temperature for polymerisation?
A short chain of polyethene form and branch off the main polymer chain. These polymers have low densities and are loosely packed and are more flexible.
How can we reduce the number of side chains caused by high pressure and temperature polymerisation?
Use a catalyst and therefore lower temperature and pressure. This will have less branches, tightly packed and called high-density polymers.
How are condensation polymers formed?
From monomers containing two reactive functional groups.
a carboxylic acid and alcohol
a carboxylic acid and amine
What is produced in a condensation polymer reaction?
The polymer and water
What is a polypeptide?
A large number of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds
What is a peptide bond?
The bond formed between the two amino acids
What is nylon?
A condensation polymer that consists of polyamides
Properties of nylon
It is strong and elastic
It is easy to launder
It dries quickly
It retains its shape
It is resilient and responsive to heat setting
Polyester
Polyesters are long-chained polymers composed of ester groups in the main chain formed from a dicarboxylic acid and a diol.
What is the most common polyester?
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) made from benzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid and an alcohol, ethane-1,2-diol
PET fibres
The molecules are mainly arranged in one direction
PET film
They are in two directions and for packaging, they are in three directions
Uses of PET
capacitators, graphics, film base and recording tapes
fibres for a very wide range of textile fibres
bottles
food packaging
electrical components
magnetic tape
backing for adhesive tape
sail cloth
Properties of PET
Can be produced with varying degrees to crystallisation providing a range of rigidity absorbs very little water
Good gas barrier
Excellent moisture barrier
Chemically resistant to acids, oils, alcohol
Highly transparent and colourless
High mechanical strength
Low density
Impact resistant