AGRI FISHERY 2
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LT 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
is the science and practice of cultivation of plants/crops and domestication of animals to provide food, fiber, medicinal substance & other products to sustain & enhance life
AGRICULTURE
According to FAO, it is an activity leading to harvesting of fish
FISHERY
also known as aquafarming, is the farming of fish, crustaceans, mollusks, aquatic plants, algae, and other organisms. It involves cultivating freshwater and saltwater populations under controlled conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish.
AQUA-CULTURE
this refers to cultivation of crops through soils and other medium growing of trees, raising of livestock, poultry, or fish which includes harvesting, processing and marketing of product of farm activities and practices.
AGI-FISHERY
is entrepreneurship that relates to the production and marketing of various agricultural products, as well as agricultural inputs (GFRAS)
Agricultural Entrepreneurship i
The process whereby an individual or group of individuals use organized efforts to pursue business opportunities in order to create value and grow by fulfilling wants and needs of target market through innovation and uniqueness -regardless of personal resource situation
ENTREPRENEURSHIP
is simply combining different aspects of agriculture such as growing crops, fruits and vegetable symbiotically with livestock and aquaculture to achieve the best and optimum production, reduce farm inputs cost, ensure sustainability and increase the total income from the farm, while maintaining a healthy biotic and abiotic environment.
INTEGRATED FARMING
includes plant variety or cultivar selection, doing the necessary seed treatment/vegetative plant part preparation for asexual propagation.
Preparation of Planting Materials
: involves cultivation appropriate for the crops to be planted as well as basal fertilization.
LAND PREPERATION
involves determining the rate of planting, time of planting and the manner of planting – whether directly seeded, transplanted, or other ways of propagation such as marcotting, grafting etc.
PLANTING
is the process of providing sufficient moisture for the plants to grow. There are crops which require more moisture in soil and some require a well-drained soil, hence, water is supplied according the plant requirement and the type of soil and prevailing temperature and humidity.
IRRIGATION
involves removal of any unwanted plant in the field to avoid crop-weed competition.
WEEDING
different kinds of crops and different stages of plant development require different amount and kinds of nutrients depending on the fertility of the land.
FERTILIZATION
different kinds of crops and different stages of plant development require different amount and kinds of nutrients depending on the fertility of the land.
PEST MANAGEMENTS
: involves identifying the pathogen/s based on the physical manifestation (as in signs and symptoms) and preventing its occurrence or if already present, preventing its spread by eradicating infected crops or plots.
DISEASE CONTROL
: involves determining the maturity of plant produce appropriate for harvesting as manifested in the change in color, plumpness, size, firmness, ripe scent, and other characteristics that signify maturity of plant parts to be harvested. T
HARVESTING
: involves cleaning, grading, semi processing of plant produce, packaging and storage or transport of plant produce to ensure that quality is maintained.
POST HARVEST HANDLING
involves activities transforming agricultural produce into products of greater value.
Value addition/value creation
involves proper packaging to maintain the quality of goods.
Packaging and labelling of processed goods
nvolves controlling the temperature and means to protect and maintain product quality.
Storage/Transport of finished products
involves negotiation with distribution centers regarding price, volume requirements, deliveries, proper handling/storage and recalls
Sales and marketing of agricultural products
involves arrangement of products in store/shops, re-stocking of products and product recall for expired, damaged, and contaminated items (based on agreement or contract).
Merchandising of agricultural products
is used in formal landscapes when one side of the landscape is a mirror image of the opposite side (exactly the same, often high maintenance)
SYMMETRICAL BALANCE (BALANCE)
is the strongest element in the design in any given view; the place where the viewer’s eye is first attracted.
FOCAL POINT (FOCALIZATION)
Keeping landscapes simple, not cluttered or fussy is always a good practice
SIMPLICITY
something in the landscape is repeated with a standard interval, a rhythm is established. In landscape design, the interval is usually space.
RHYTHYM AND LINE
the size relationship of all the features in the landscape. This includes vertical, horizontal and special relationships.
PROPORTION
is easily measured if the other five landscape principles have been properly executed throughout the landscape
UNITY
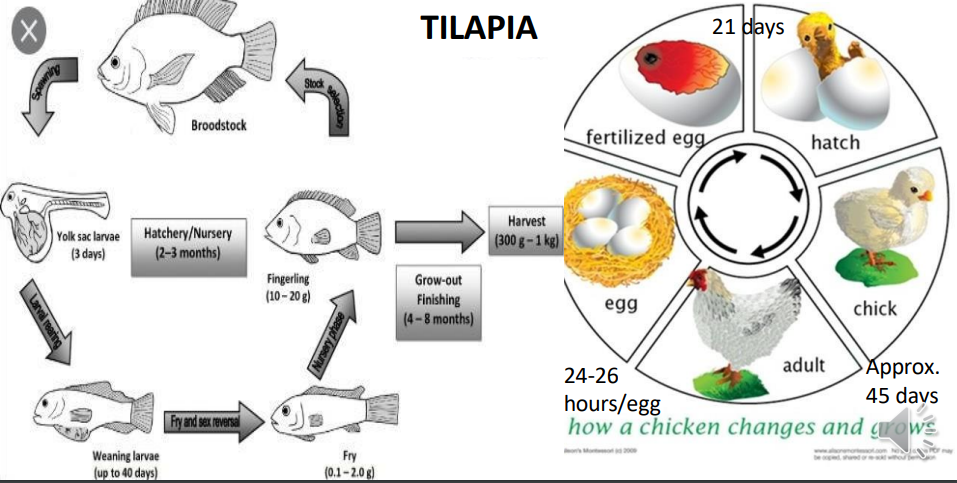
involves activities such as breed selection, animal nutrition, disease prevention and control,stress management, animal housing and care, handling of animals during harvest and breeding and care of young animals
ANIMAL PRODUCTION
The most crucial in animal production are
ANIMAL NUTRITION and FARM MANAGEMENT PRACTICES.
Different animals have different facility requirements. For dairy goats,
QUARANTINE, BREEDING PENS, KIDDING PEN, SICK GOAT PEN, MILKING PARLOR, AND WEANING PENS
is necessary in physiological processes however, critical temperature varies from animal to animal at different stages
TEMPERATURE
the amount of moisture in the air; Highly moist air encourages microorganism growth and multiplication.
HUMIDITY
animal excreta when accumulated could cause the rise in the level of ammonia which is poisonous for animals. Regular cleaning and proper ventilation must be done to avoid this.
LEVEL OF AMMONIA OR C02
different animals require
FARM MANAGEMENT