Side PanelExpand side panel Topic 6 Cultivation
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
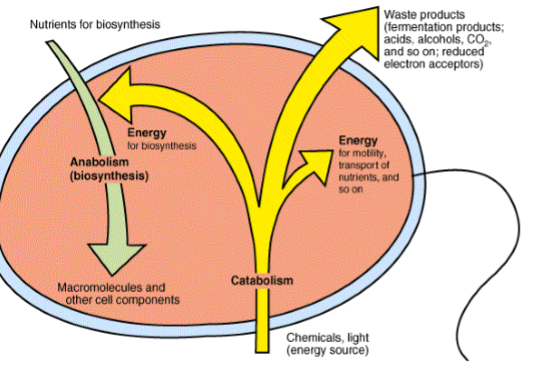
Cell Metabolism
Catabolism
Anabolism
Catabolism
releases energy (think catalyze)
Anabolism
Consumed energy (
Cell matabolism visual
Nutritional Requirements
macronutrients
micronutrients
macronutrients
• required by ALL cells to build macromolecules
• C, N, P, S, O, H
micronutrients
• required by some cells
• includes Fe, Cu, Na, Mg, Mn, and others
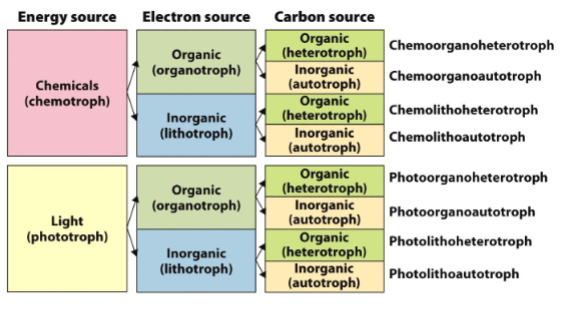
Fundamentals of Nutrition
1. ENERGY SOURCE
2. ELECTRONS
3. CARBON SOURCE
1. ENERGY SOURCE
(for oxidation, providing electrons for ETC)
Photo (photosynthetic; organic or inorganic e-)
OR
Chemo (organic or inorganic)
2. ELECTRONS
organo
(e.g., H2, NH3, S0, NO2-)
litho
(e.g., glucose, acetate)
3. CARBON SOURCE
(for cell maintenance and division)
Fixed organic (C-C bonds)
heterotroph
Greek heterone = (an)other and trophe = nutrition
OR
Gaseous inorganic (CO2)
autotroph
Greek autos = self and trophe = nutrition
Funamentals of Nutrition Naming Visual

Appropiate Naming System for Metabolism Visual
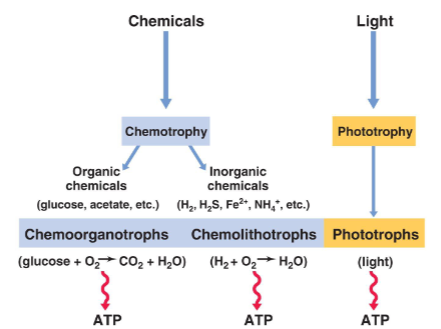
Energy sources (3)
Chemoorganotrophs
Chemolithotrophs
Phototrophs
Chemoorganotrophs
energy from oxidation of organic compounds and electrons
Chemolithotrophs
energy from oxidation of inorganiccompounds
found only in prokaryotes
Phototrophs
energy from light captured by pigments
may be oxygenic or anoxygenic
Carbon Sources
Carbon is a major requirement for all organisms
heterotroph
autotroph
Carbon Source - heterotroph
primary producers”
fix C directly from CO2
Carbon Source - Heterotrophs
use organic molecules produced by autotrophs
Conservation Energy Visual - Carbon focused
Idea - energy stored within chemicals “saved up”
ATP - high energy bonds
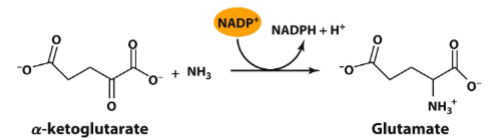
Acquisition of Nitrogen
Microorganisms must be able to incorporate nitrogen into a usable form.
Assimilation of ammonia into glutamate/glutamine most common
Glutimate
Glutamite
Acquisition of Nitrogen - Critical to making numerous macromolecules
amino acids
nucleic acids
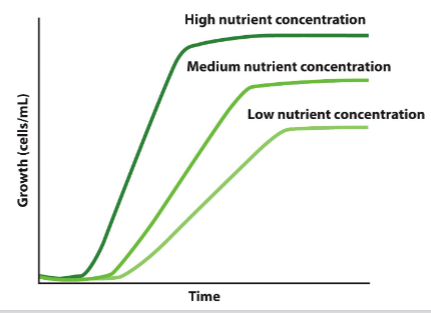
Nutrient Concentration
growth rate depends on amount of nutrients available
key nutrient available in the lowest amount will limit growth
Effects on Oxygen - condition
aerobic growth uses oxygen
anaerobic growth occurs without oxygen
Aerobic growth
obligate aerobes require O2
microaerophiles grow best in low levels of O2
anaerobic growth
• aerotolerant anaerobes aren’t harmed by O2 but don’t use it
• obligate anaerobes facultative cannot grow when O2 is present
• facultative anaerobes
facultative anaerobes
can grow in the absence of O2 but grow better when it is present
Toxic Oxygen Species
impact of O2 respiration on a cell depends on a cell’s available defenses
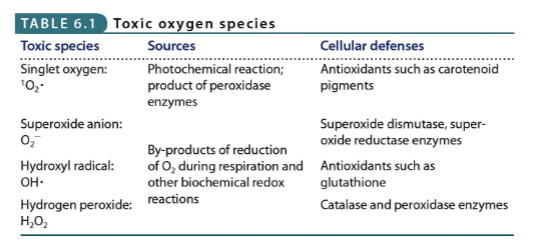
Toxic Oxygen Species - Singlet Oxygen
Toxic Oxygen Species - Superoxide anion
Toxic Oxygen Species - Hydroxyl radical and Hydrogen Peroxide
Catalase Test
Some microbles produce catalase
H2O2 + H2O2 → 2H2O + O2