Hindlimb Blood, Lymph, and Nerve Supply (Week 3, Mod 7)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the main unit that provides the nerve supply to the hind limbs? What nerves branch from it?
The lumbosacral plexus supplies the nerves for the hindlimbs
Emerging peripheral nerves to the hind limb:
Gluteal nerve
Obturator
Femoral nerve
Sciatic
Tibial / fibular / peroneal branches
Describe the route of the gluteal nerve… what muscles does it supply? What then, is its function? Does it provide cutaneous sensation?
Route:
Runs over the dorsal surface of the BODY of the ilium
Supplies the gluteal muscles
Are hindlimb ABDUCTORS
(hind limb retractor / hip extensor in equine)
Does not supply cutaneous sensation
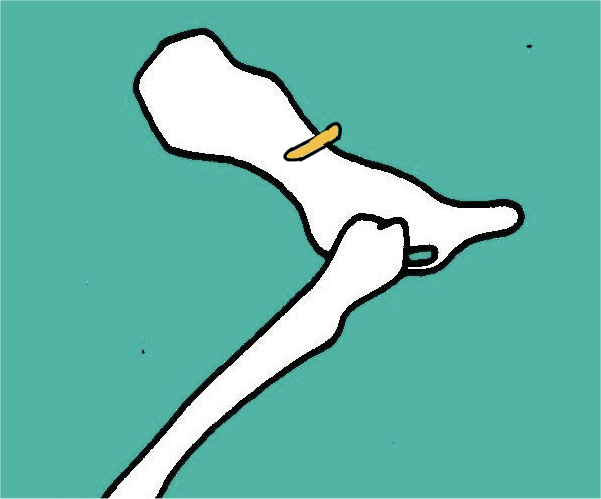
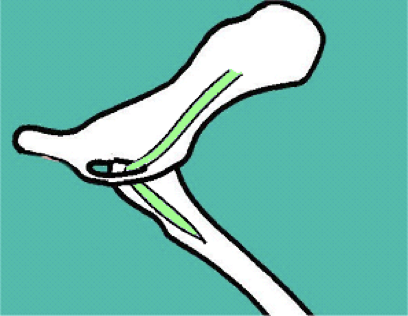
Describe the route of the obturator nerve… what muscles does it supply? What then, is its function? Does it provide cutaneous sensation?
Route:
Passes through the OBTURATOR FORAMEN
Is a short route, passes to medial thigh
Supplies the GAPE muscles (gracilis, adductor, pectineus, and external obturator)
Hind limb ADDUCTORS
Does not provide cutaneous sensation
What is a common problem in dairy cattle that could cause damage to the obturator nerve? What would then happen as a result of this?
Obturator nerve could become damaged in cows during parturition
Due to medial pathway of the nerve; caused by birthing of OVERSIZED CALVES
Have difficulty standing up; “doon coo”
Is not a problem in horses; typically don’t have oversized foals
Describe the route of the femoral nerve… what muscles does it supply? What then, is its function? Does it provide cutaneous sensation?
Route:
Short route to cranial thigh
Supplies the cranial thigh muscles
Iliopsoas
Sartorius
Quandriceps (all heads)
Therefore act as hip FLEXORS, limb PROTRACTORS, and stifle EXTENSORS
Gives sensory supply to the entire medial aspect of the hind limb
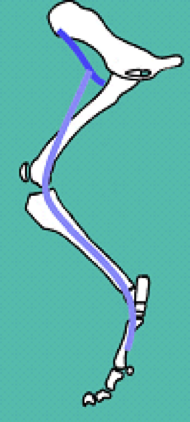
What branch of the femoral nerve is responsible for cutaneous sensation on the inside of the hind limb? What specific anatomical region does it pass through?
The saphenous branch
Passes through the FEMORAL TRIANGLE
Region in the upper, medial thigh where the femoral nerve, femoral artery, and femoral vein all pass through
What nerve is responsible for the “patellar reflex”? If this nerve is damaged, what happens to the hindlimb?
The FEMORAL NERVE is responsible for the patellar reflex (hammer to knee test)
Should cause involuntary extension to the stifle upon impact
If femoral nerve is damaged, P will be unable to extend stifle (loss of patellar reflex)
Cannot weight bear
No compensatory muscles
Describe the route of the sciatic nerve… what muscles does it supply? What then, is its function? Does it provide cutaneous sensation?
Route:
Dorsal surface of ilium → passes CAUDAL to hip (very close to hip joint) → runs DEEP to biceps femoris
Supplies the CAUDAL thigh muscles:
Biceps femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranous
Therefore functions as hip EXTENSORS / limb RETRACTORS, and stifle FLEXORS
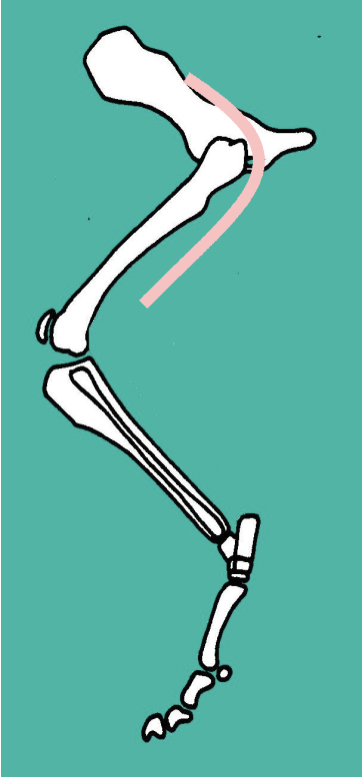
What are the two branches of the sciatic nerve?
1) Tibial nerve
2) Peroneal / Fibular nerve
Describe the route of the tibial nerve (branch of sciatic)… what muscles does it supply? What then, is its function? Does it provide cutaneous sensation?
Supplies the caudal TIBIAL muscles:
Gastrocnemius
Superficial digital flexor
Deep digital flexor
Therefore acts as a hock EXTENSOR and digital FLEXORS
DOES supply cutaneous sensation
To the caudal / plantar aspect of the limb
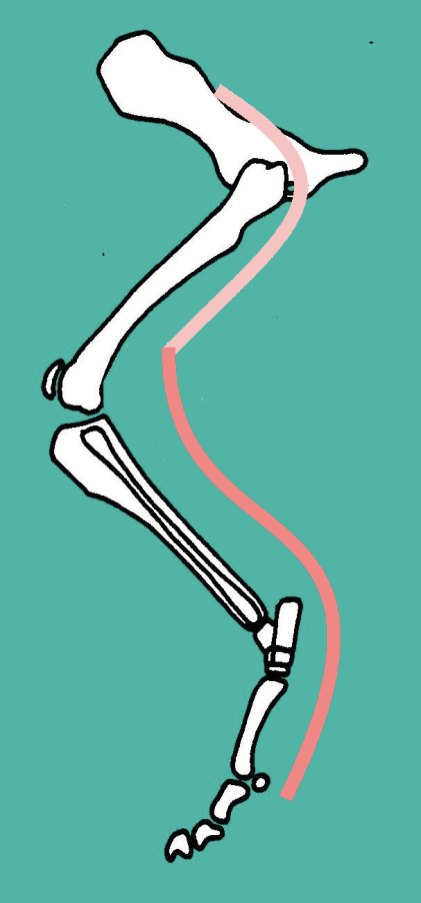
Describe the route of the peroneal / fibular nerve (branch of sciatic)… what muscles does it supply? What then, is its function? Does it provide cutaneous sensation?
Supplies the CRANIAL tibial muscles:
Cranial tibial
Peroneus group
Long Digital Extensor
Therefore, acts as a hock FLEXOR and a digital EXTENSOR
DOES provide cutaneous sensation:
Cranial / dorsal aspect of limb
Also lateral thigh
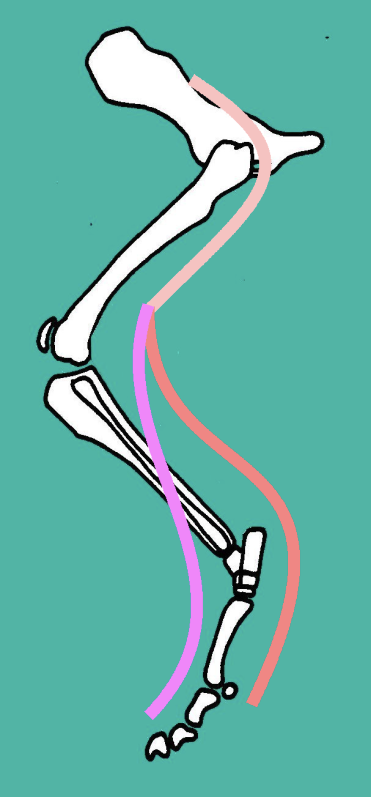
How can the sciatic nerve become damaged? What happens to the hindlimb as a result? Are there any compensatory muscles that would help the limb still function?
Sciatic Nerve damage may result from
Hip trauma / surgery
Femoral fractures
Lose supply to:
Hip extensors/ stifle flexors
Hock extensors/ digital flexors
Hock flexors/ digital extensors
Cutaneous sensation
Still possible to:
Abduct (Gluteals)
Adduct (Obturator N)
Protract limb / flex hip / extend stifle (Femoral N)
** CAN get isolated sciatic nerve damage
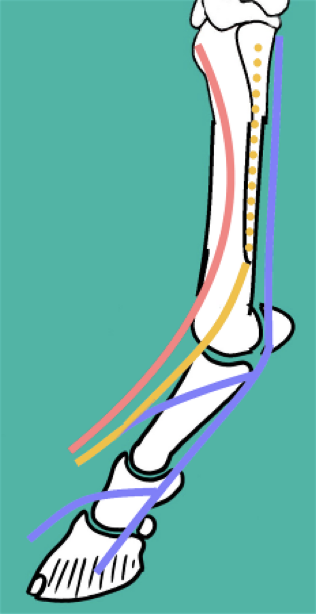
As the tibial and peroneal / fibular nerves descend down the EQUINE hindlimb, what nerves do they branch into?
Tibial Nerve:
Plantar nerves → become plantar digital nerves (1)
Plantar metatarsal nerves (2)
Peroneal / Fibular nerve:
Dorsal metatarsal nerves (3)
Describe the ARTERIAL blood supply of the hindlimb… how is it similar to the blood supply of the forelimb?
ALSO runs as one single major blood vessel, changes names with the region of the hind limb:
External iliac artery leaves abdominal aorta →
Femoral artery runs through the thigh region →
Popliteal artery supplies the distal limb, branches from here
** ALSO crosses the flexor angle of joints
Distal limb ALSO well-vascularized:
The farther you go down the limb, the more the artery branches off, and the thinner the branches get and the more that are produced.
- This is why foot injuries bleed like crazy , because there’s so much vascularization
Describe the VENOUS drainage system of the hind limb… how is it similar to the forelimb?
Has a DEEP and SUPERFICIAL system as well:
Deep system -
Follows arterial blood supply
Vein, artery, and nerve all run together; has the same name as artery
Superficial system -
Consists of the lateral saphenous and medial saphenous veins
Lat. → prominent in dogs; access to circulation
Med. → prominent in cats and horses; access to circulation
What exactly is the femoral triangle, and what are its contents / boundaries?
Contents:
Femoral Vein Artery & Nerve
Pulse – Femoral Artery
Intravascular catheters – Femoral vein
Femoral nerve = saphenous branch
Boundaries:
Caudal - Pectineus (& Adductor)
Cranial - Sartorius
What is the main hind limb lymph node of the dog? Of the cow? Describe how they are clinically significant.
Dog - POPLITEAL
Caudal to stifle
Cow - PREFEMORAL
Cranial to femur
Clinical significance:
Becomes enlarged in response to INFECTION
Can be used to differentiate between localized / systemic diseases
Important in large animals for meat inspection