the muscular system: the cell & muscle contraction
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
tendons vs ligaments
tendons attach muscles to bones — ligaments attach bones to bones
body composition varies among ppl, but muscles make up approx. __ of the body’s weight
1/3
functions of the muscular system
movement, maintaining posture, stabilizing joints, & generating heat (when ATP is used)
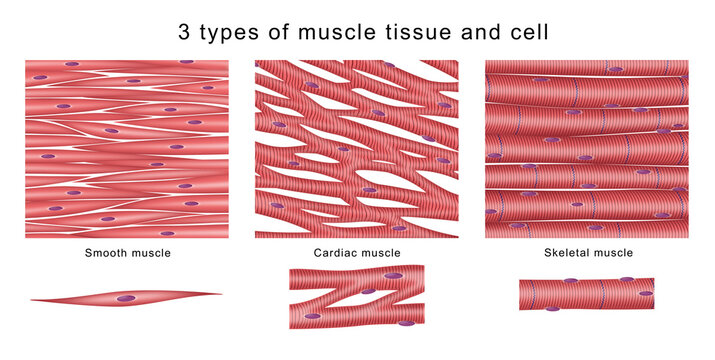
3 types of muscle tissue
Cardiac
Skeletal
Smooth
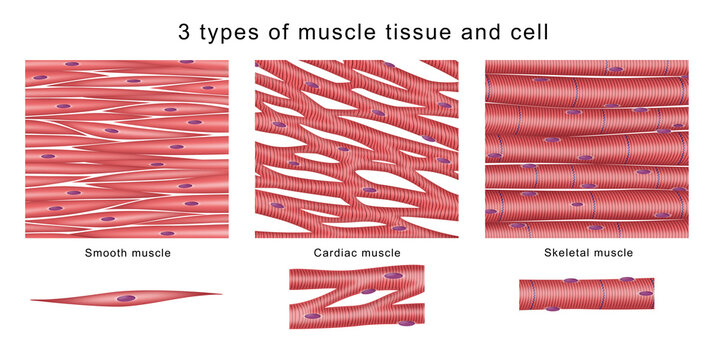
define striated muscle tissue (+ examples)
muscle tissue w/ a striped appearance from sarcomeres—organized arrangement of actin & myosin muscle filament into repeating units
ex. cardiac & skeletal muscles
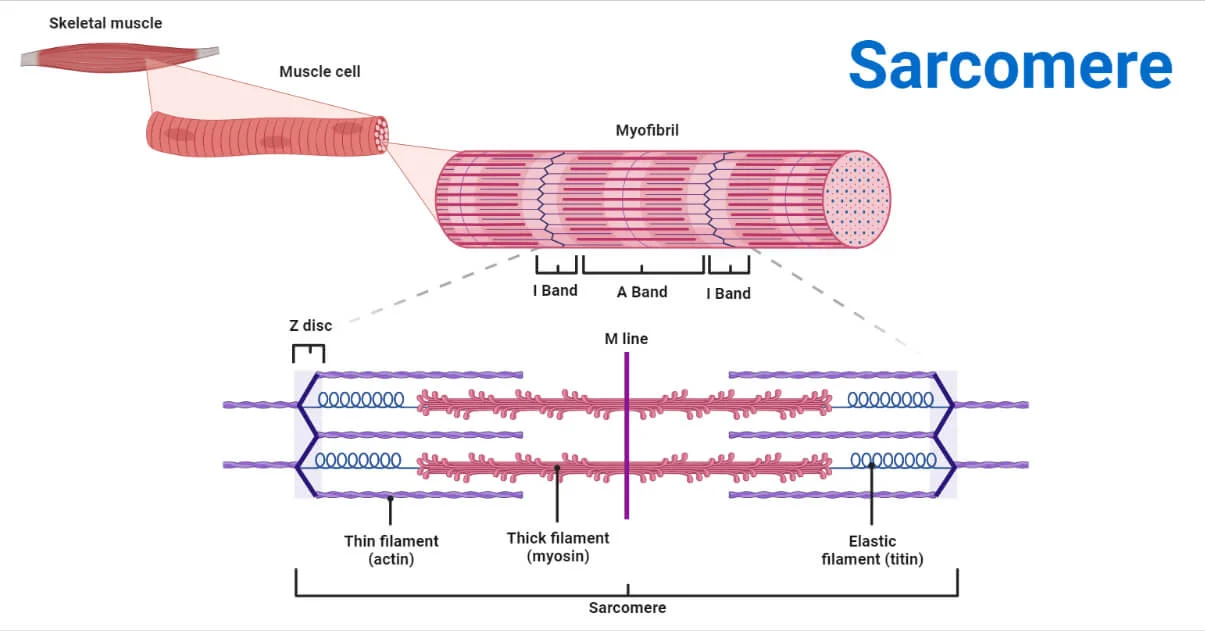
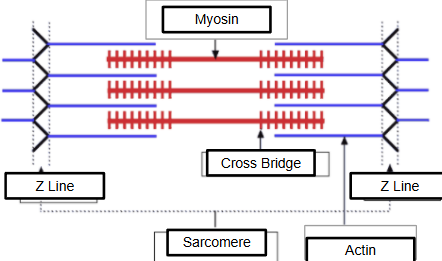
Sarcomeres
muscle contraction units in organized arrangement of actin & myosin muscle filament into repeating cycles of relaxed & contracted muscle fiber — present in striated muscle tissues such as cardiac & skeletal
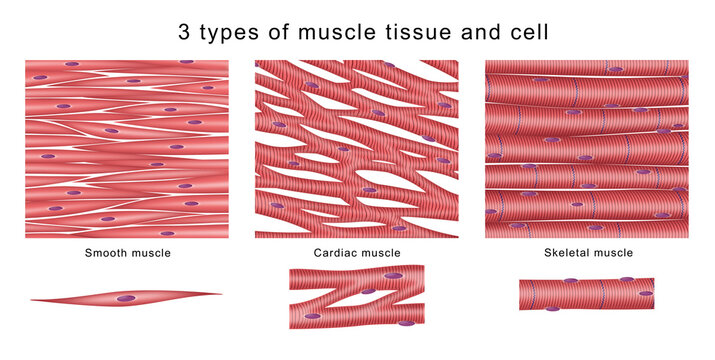
cardiac muscle tissue
branch-shaped cell tissue that pumps blood
involuntary controlled
located near the heart
mononuclear
striated
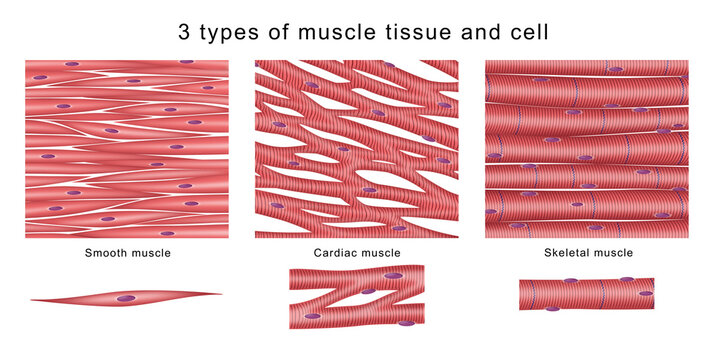
smooth muscle tissue
diamond-shaped cells that aid body functions by surrounding internal passages & pathways to regulate flow of substances (ex. air, food, blood)
involuntary control
located in hollow organs
mononuclear
not striated
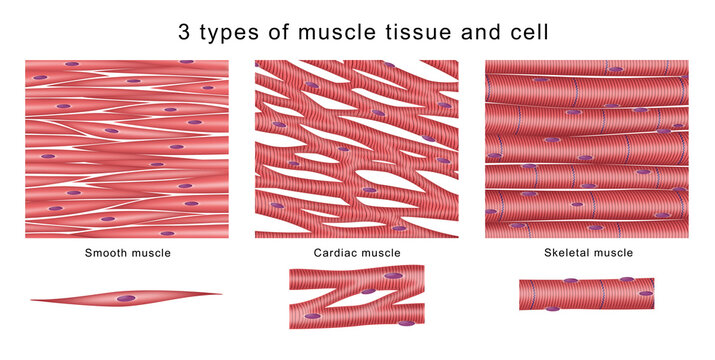
skeletal muscle tissue
cylinder-like cells responsible for movement
voluntarily controlled
attached to bones
multinuclear
striated
myofilaments (types?)
proteins that myofibrils are made of; 2 types are thick myofilaments (myosin) & thin myofilaments (actin)
myofibrils
tube-like structures within a muscle fiber containing myofilaments such as myosin & actin that aid in muscle contraction w/ ATP — image: the red small bundles parallel to one another
myosin
thick myofilaments that work w/ actin (thin) for muscle contraction
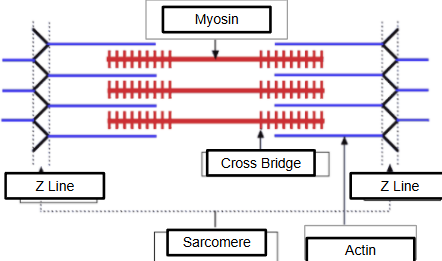
actin
think myofilament anchored to Z-Lines acting as boundaries for sarcomeres giving muscle a striped appearance
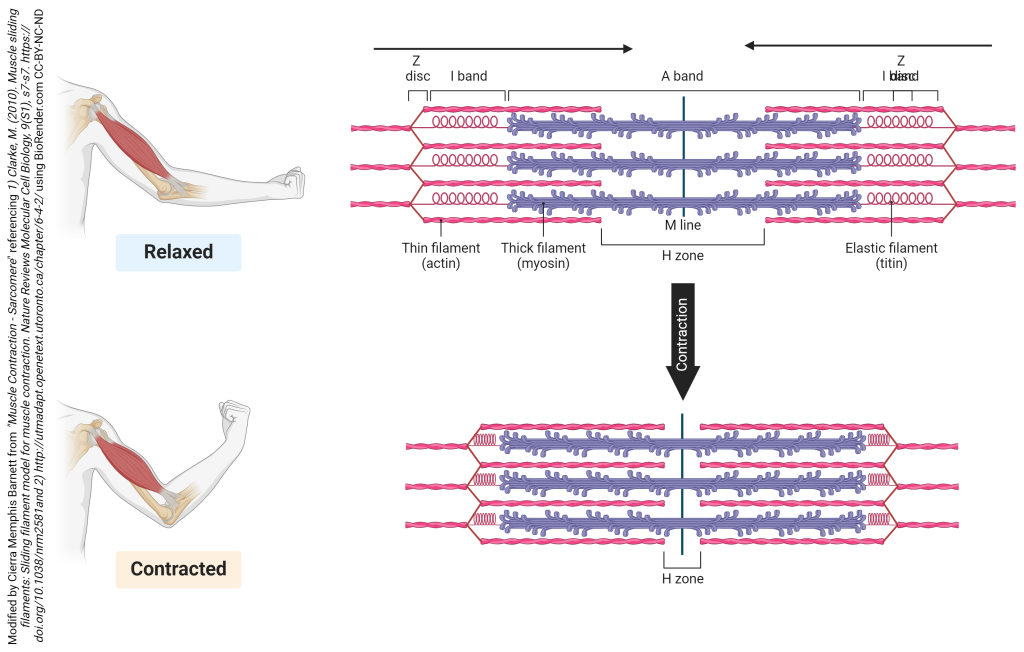
Sliding Filament Theory
explains muscle contraction as the process of synchronized shortening of sarcomeres —> muscle fibers (myosin & actin) sliding past each other —> muscle contracts
neurotransmitter needed to initiate a muscle contraction
acetycholine
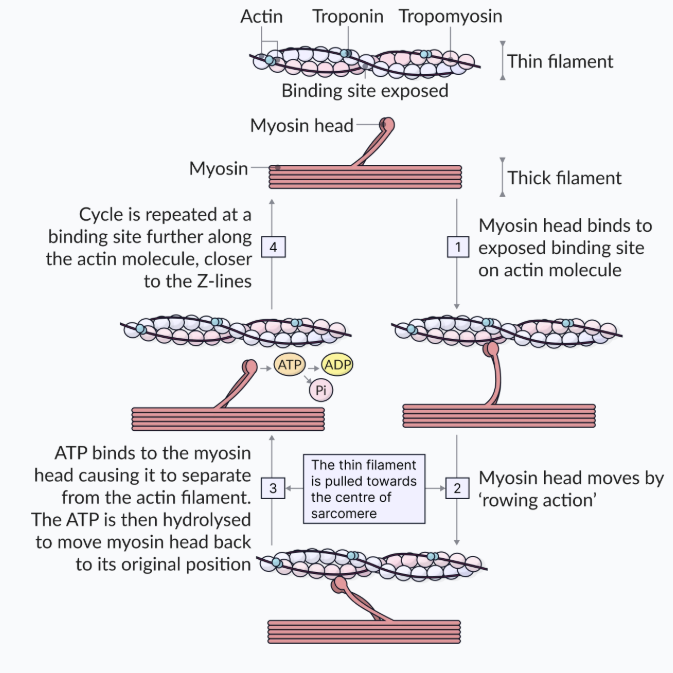
steps of muscle contraction according to the Sliding filament theory
GRAB —> PULL —> RELEASE & RESET
calcium released from sarcoplasm reticulum binds w/ Tropomyosin (changing the shape of the actin), pulling tropomyosin off from covering the binding sites —> connects w/ myosin
GRAB: Myosin head forms cross bridges b/w actin & myosin
PULL: Power stroke causes sarcomere shortening actin filament like rowing motion (muscle contracts)
RELEASE & RESET: ATP breaks cross-bridge & resets myosin to original
calcium is repumped back into SR (can’t function w/o) OR cycle continues as long as calcium is present
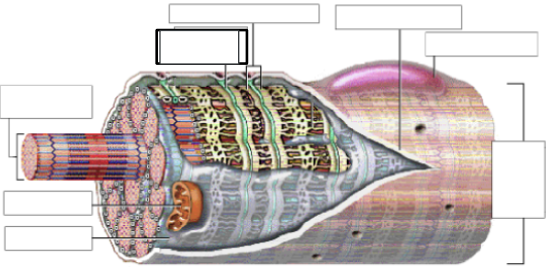
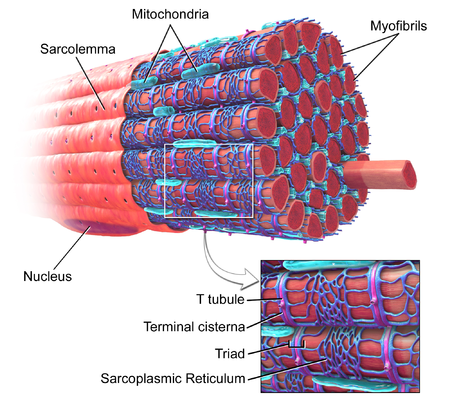
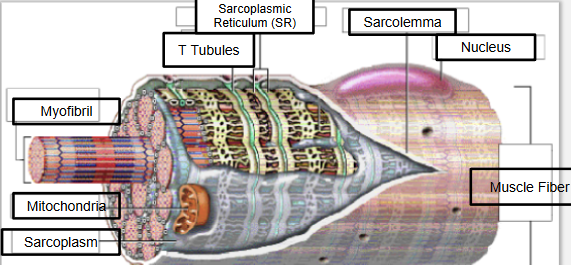
label & define*: nucleus, sarcolemma*, sarcoplasmic reticulum*, t-tubes (transverse tubule system), mitochondria, myofibril*, sarcoplasm
sarcolemma - cell membrane of muscle cell
SR - specialized endoplasmic reticulum that releases Ca
T-tubes - network of tubes that act as calcium releasing channels from the SR & ensuring myofibrils contract simultaneously
myofibril - small tube-like structure containing the contractile filaments
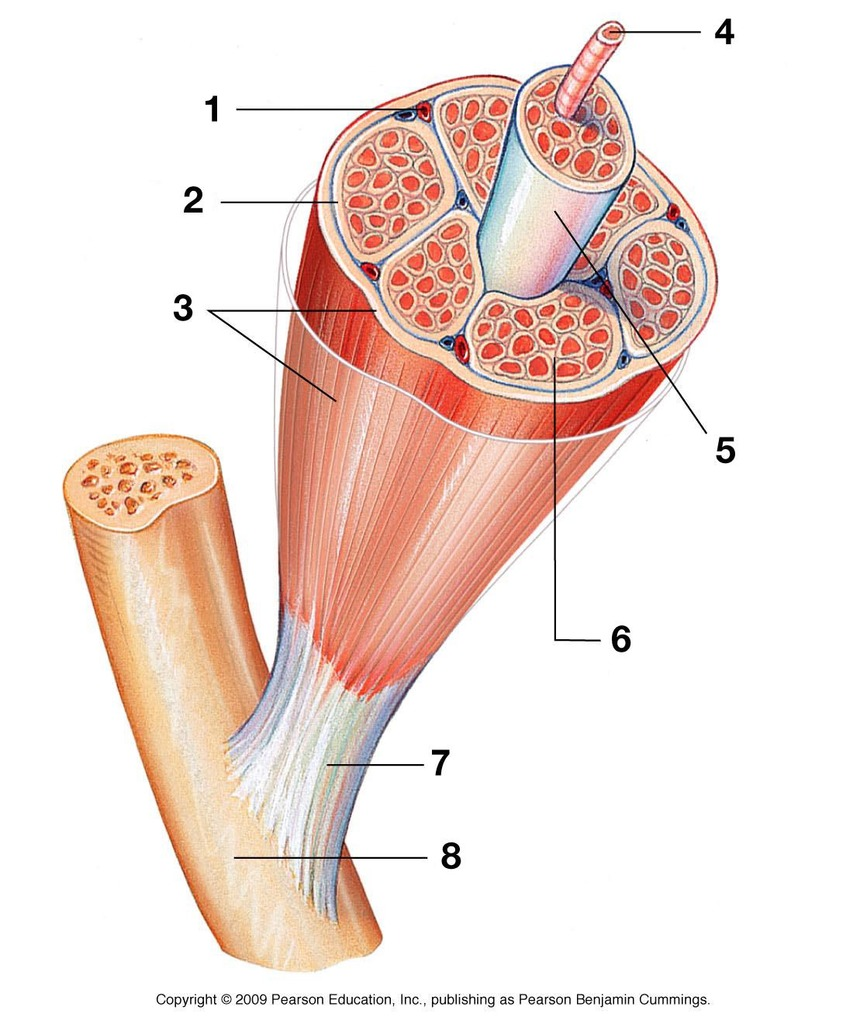
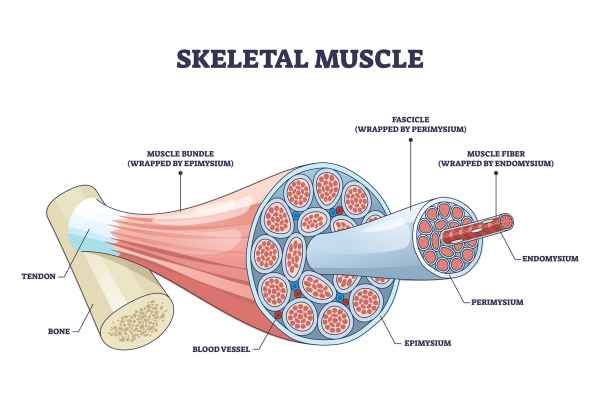
label & define muscle fiber, perimysium, fascicle, epimysium, endomysium, muscle cell
inner to outer
muscle cells (4)
muscle fiber (4) - bundle of individual muscle cells
endomysium (6) - connective tissue covering each muscle fiber
fascicle (5) - bundle of muscle fibers
perimysium (2) - connective tissue covering each fascicle
epimysium (3) - protective layer over the whole muscle (the clusters of fascicles)