Research methods year 13
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Define Case study?
an in depth investigation and analysis of a single individual, institution or event
Define content analysis?
a research technique that indirectly studies behaviour through communications like written forms in texts or emails or spoken interactions involving words or speech to draw conclusions
Define coding in terms of content analysis?
the stage of content analysis in which the communication to be studies is analysed by identifying each instance of the chosen categories
Define thematic analysis?
a form of content analysis which produces qualitative data and involves the identification of themes
Evaluate case studies(A03)?
STRENGTHS:
they are able to offer rich, detailed insights
Contribute to our understanding of typical functioning e.g.HM(Memory)
Can generate hypothesis for future studies
WEAKNESSES:
Findings cannot be generalised due to small sample size
Personal accounts from the participants and their family and friends may be prone to inaccuracy and memory decay therefore decreased validity
Evaluate content analysis (A03)?
STRENGTH:
can get around ethical issues associated with psychological research as most of the material being studied may already exist in the public
WEAKNESS:
People tend to be studied indirectly so the communications they produce are usually analysed outside of the context that they occurred
Define reliability?
A measure of consistency
What 2 ways do psychologists use to test reliability?
test retest
Inter observer reliability
Define test retest reliability?
Administering the same test or same questionnaire to the same person or people on different occasions if the test or questionnaire is reliable then the results obtained should be the same
Define inter observer reliability?
The extent to which there is agreement between 2 or more observers involved in the observations of a behaviour
Measured by correlating the observations of 2 or more observers
Define validity?
whether a psychological test, observation or experiment produces legitimate results
Define internal validity?
whether the effects observed in an experiment are due to the manipulation of the independent variable and not any othe rfactoe
Define external validity?
the extent to which findings of a study can be generalised to other situations, settings people or times
State and explain the 2 types of external validity?
Ecological validity→ the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalised to other settings and situations
Temporal validity→ the extent to which findings from a research study can be generalised to other historical times and eras
State and explain the 2 ways in which validity can be assessed?
Face validity→ whether a test or research tool appears to measure what it’s supposed to measure
Concurrent validity→ the extent to which a new test or measure a,igns with an existing validated measure for the same concept when both are administered at the same time
Draw the stat's test table?
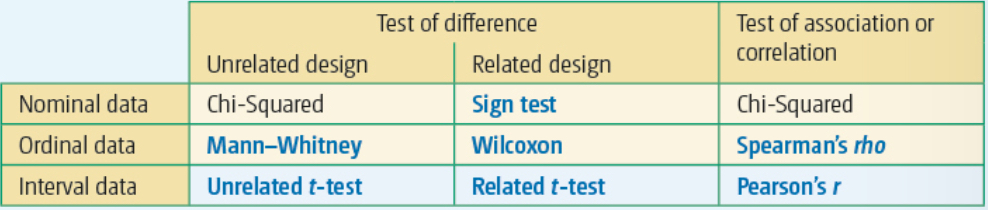
State the 3 factors used to determine what stats test to use?
difference or correlation
Experimental design
Level of measurement
Define nominal data?
categorical data
Define ordinal data?
subjective data which is ordered
Unsafe data as lacks precision
Define interval data?
data that includes units of equal , most precise
What does a null hypothesis state?
there is no difference
Define the critical value?
the cut off point between accepting or rejecting the null hypothesis
Define type 1 error?
the incorrect rejection of a true null hypothesis, false positive
Define type 2 error?
the failure to rejects a false null hypothesis, false negative
Define significance?
how sure we are that a difference or correlation exists
What is the usual level of significance in psychology?
0.05
Why did psychologists come up with 0.05 level of significance?
even when the researcher claims to have found a significant difference/ correlation, there is still up to 5% chance that it isn’t true for the target population which the sample was drawn from
Cannot be 100% certain
This conventional level is prepared to accept that results occurred to chance