Blood Components
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on some slides on Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells, and Platelets. This is a combination of three flashcard sets; see my profile for the individual sets.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Red blood cells
Blood cells that carry oxygen and nutrients throughout the body; uses structure to grab iron and oxygen for transport
Shaped as a biconcave disc at 5 million per cc and no nuclei
White blood cells
Blood cells with an immune function
Splenomegaly
Enlargement of the spleen
Causes:
Leukemia
Mononucleosis (viral)
Sickle cell disease
Beta thalassemia
Malaria
Thrombocytopenia
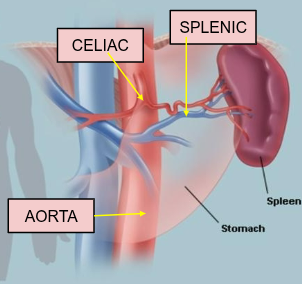
Spleen functions
Blood filtration
RBC and iron recyclation
Antibody production
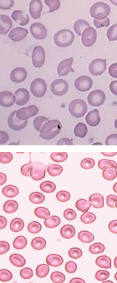
Hypochromia
The loss of color usually with pale/less RBCs
Phlebotomist
Person trained to draw blood from a patient
Coney’s anemia (beta thalassemia)
An recessive inherited disorder inferfering with the blood’s ability to carry oxygen, leading to hypochromia (requires regular transfusions)
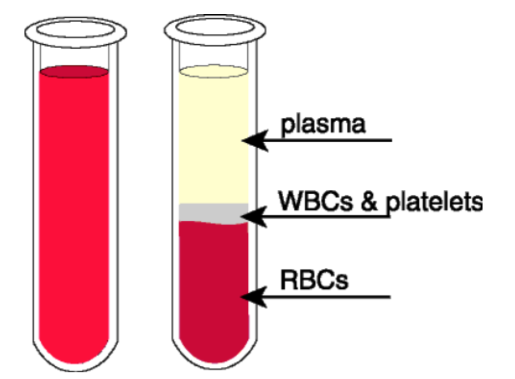
Blood components
Cells (RBCs, WBCs, platelets) at 45%
Plasma (water, protein, amino acids) at 55%
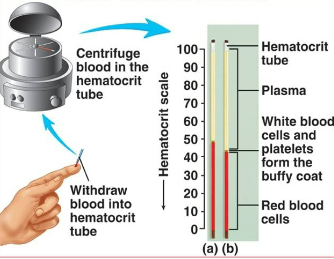
Centrifuge
Device that spins blood samples to allow cells to settle to determine percentages
Hematocrit
The percentage of blood and plasma; usually at 45-55 balance
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells
Leukocytes
White blood cells
Thrombocytes
Platelets
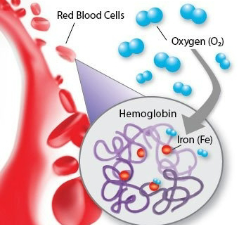
Hemoglobin
A protein that contains iron to transport oxygen
Iron-deficient anemia
Anemia caused by a low amount of iron
Hematopoiesis
The formation of blood cells within the bone marrow
Erythropoietin
A hormone that increases red blood cell levels, sometimes used as a performance-enhancing drug
Oxyhemoglobin
Hemoglobin with more oxygen; appears bright red
Deoxyhemoglobin
Hemoglobin with less oxygen; appears dark red
Veins
Vessels which return blood to heart
Arteries
Vessels which send blood to tissues from heart
Sickle cell disease
Genetically recessive disorder with abnormally-shaped RBCs; caused by DNA mutation with incorrect hemoglobin formation
Symptoms include splenomegaly, fatigue, pain, strokes, shortness of breath
Leukemia
A type of blood cancer
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
The most common type of childhood leukemia (75% of all cancers), it progresses quickly
Leukocytes
Another name for white blood cells
Granulocytes
White blood cells with granular cytoplasms; inlcudes neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
Agranulocytes
White blood cells without granular cytoplasms; includes monocytes and lymphocytes
Neutrophil
Type of granulocyte with multi-lobed nucleus; has active phagocytes for bacteria and makes up 60% of white blood cells (present in pus)
Eosinophil
Type of granulocyte that attacks parasites and makes up 2% of white blood cells
Basophil
Type of granulocyte that produces heparin (a blood thinner) and histamines to increase flow
Dermatographia
Condition where the immune system releases excess histamine, causing welts to appear when lightly scratched
Cold urticaria
Condition where hives or large welts form on the skin due to a cold stimulus
Monocyte
A type of agranulocyte with a large cell and horseshoe shaped nucleus; can become macrophages or dendritic cells (signallers)
Lymphocyte
A type of agranulocyte that is the main defense of the immune system; produces antibodies that are 30% of WBC count
Mononucleosis
Also called “mono” or the “kissing disease,” it’s caused by the Epstein-Barr virus
More lymphocytes enter the bloodstream; the virus is very common and can be solved with rest
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Virus that weakens the immune cells by infecting specific immune cells; not necessarily paired with AIDS
Infection occurs with bodily fluid exposure
AIDS
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome; condition where immune cells fall and can allow opportunistic infections (no cure available)
Leukemia treatment phases
Remission induction
Consolidation
Maintenance
Chemotherapy
The use of drugs that target cancer cells; can also target healthy cells with hair loss, digestive issues, lower red blood cells, and weakened immune systems
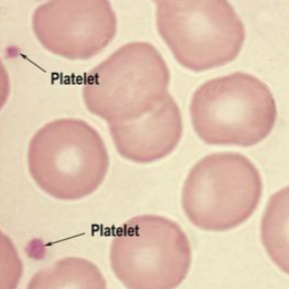
Platelets (thrombocytes)
Help initiate formation of blood clots; they close breaks in damaged blood vessels
Blood plasma
Transports nutrients, gases, vitamins, fluids, and maintains electrolytes and pH
Plasma proteins
Albumins
Globulins
Fibrinogens
Albumin
Plasma protein for blood pressure
Globulin
Plasma protein for antibody transport
Fibrinogen
Plasma protein for blood clotting
Multiple myeloma cancer
Cancer that affects plasma cells by crowding out healthy cells and producing harmful antibodies
Hemostasis
The process of stopping bleeding; involves coagulation and clotting of blood to seal site of damage
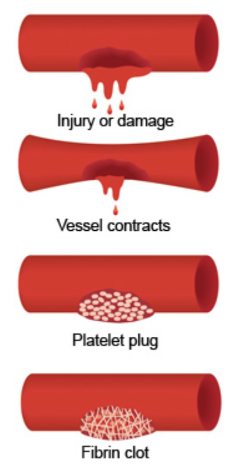
Hemostasis events
Vascular spasm
Platelet plug formation
Coagulation
Serotonin
A vasoconstrictor that aids in the vascular spasm
Thrombin
An enzyme in blood plasma that causes clotting by converting fibrinogen to fibrin
Coagulation
The thickening of blood to form a clot
Hematoma
Another name for a clot
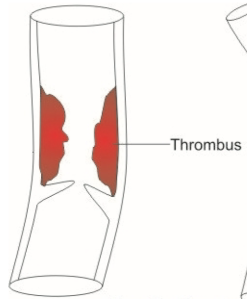
Thrombus
An abnormally placed blood clot, such as within an artery or the heart
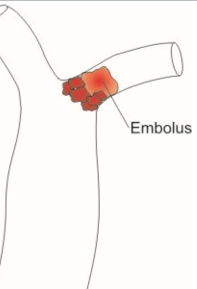
Embolus
When a clot within a vessel moves to another place, thus creating a blockage
Pulmonary embolism
An embolism (movement of blood clot) that moves to the lungs
Cerebral embolism
An embolism (movement of blood clot) that moves to the brain
Vitamin K
Can be injected to prevent deficiency bleeding in newborns
Hemophilia (bleeder’s disease)
Sex-linked recessive condition where blood does not clot
5 L
The amount of blood in the human body
0.5 L
The amount of blood taken in a donation
Blood donation uses
Purposes:
Hemophiliac clotting factor replacement
Sickle cell reduction
Injury or surgery blood replenishment