L2 - Acids, Bases & Buffers
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
osmolarity and ionic strength: - are necessary when working with cells and macromolecules
salts
cells exert osmotic pressure, preventing -
animal cells, lacking cell walls, need to be maintained in - solutions to avoid osmotic shock
hypotonic shock
isotonic
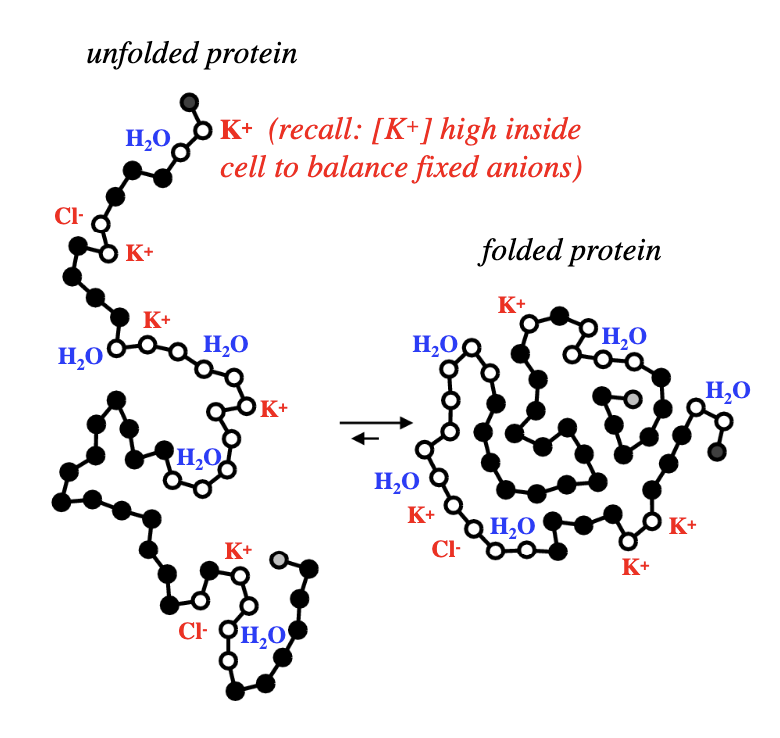
why is water and counter ions near open circles?
open circles = polar or charged aa residues, located near surface of folded proteins
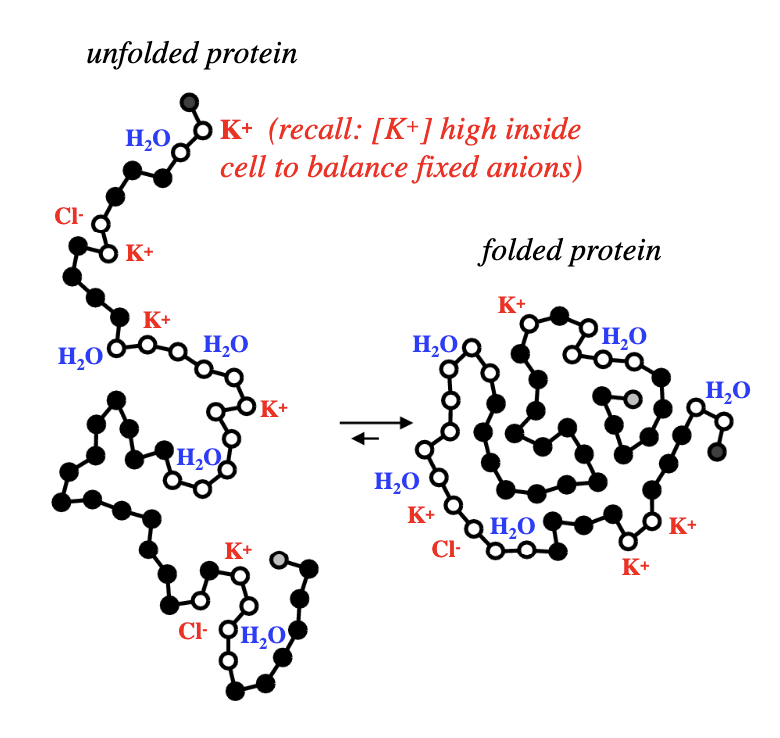
which amino acids are typically protonated at neutral pH?
basic aa are protonated
which amino acids are de-protonated at neutral pH?
phosphodiester bonds of both DNA and RNA will - in acid
hydrolyze
strong acids at high temperatures are capable of breaking a - into its components
polynucleotide chain
weak acid can cause - of DNA
RNA is - (less/more) susceptible to de-purination
de-purination
less
at alkaline pH, dsDNA is denatured into - but the polynucleotide chains are stable
2 single strands
at alkaline pH, RNA is -
hydrolyzed
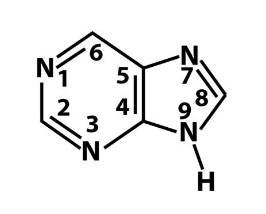
what is this?
what bases are this?
purine
adenine and guanine
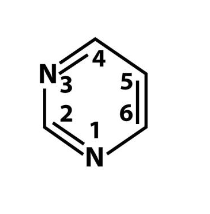
what is this?
what bases are this?
pyrimidine
cytosine and thymine
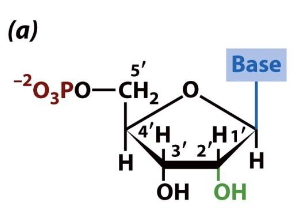
what is this
5’ ribonucleotide
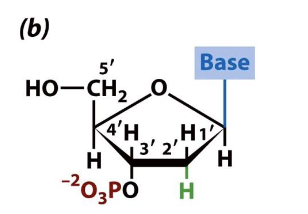
what is this
3’ deoxynucleotide
water can donate or accept H+ ions in solutions, acting as either - or -
acid, base
proton jumping via H bonds is much - (slower/faster) than hydrolysis of H2O into H+ and OH-
which explains - (slow/rapid) rate of acid-base catalyzed reactions in aqueous solutions
faster
rapid
acid is a substance that can - a proton
base is a substance that can - a proton
donate
accept

acid reacts with base to form - and -
conjugate acid, conjugate base of acid
henderson-hasselbach equation?
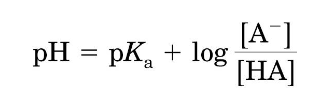
at equilibrium, [H+] = -
pH = -
Ka
pKa
minor additions of OH- or H+ to weak acids or bases at equilibrium/close to pKa - (do/don’t) shift pH value
this is why weak acids/bases are used in biological buffers
don’t
buffering acids are typically provided as -, they serve s counter ions for the acid/base but don’t contribute to its buffering properties
- = ionic strength of buffer
salts
salt concentration
polyprotic acids can donate - proton during acid-base reactions
more than one
glycine is a key component of the discontinuous buffer system in SDS-PAGE because of its - properties
zwitterionic
at low pH, both carboxyl and amino groups of glycine are - and glycine is a -
at neutral pH, carboxyl group is -, amino group is - and glycine is both anionic and cationic but net neutral and glycine is a -
at high pH, both carboxyl and amino group - and glycine is -
protonated, cation
de-protonated, protonated, zwitterion
de-protonated, anionic
for SDS-PAGE, the stacking gel has pH 6.8, and the glycine - stack nicely
zwitterions
for SDS-PAGE, the separating gel has pH 8.8, once glycine enters the gel, anionic glycine predominates and migrates - of proteins, allowing proteins to freely separate according to their -
ahead, MW