Monetary Policy and Aggregate Demand Curves
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Nominal Federal Funds Rate
Interest rate banks charge each other for loans.
Real Interest Rate
Nominal interest rate adjusted for inflation.
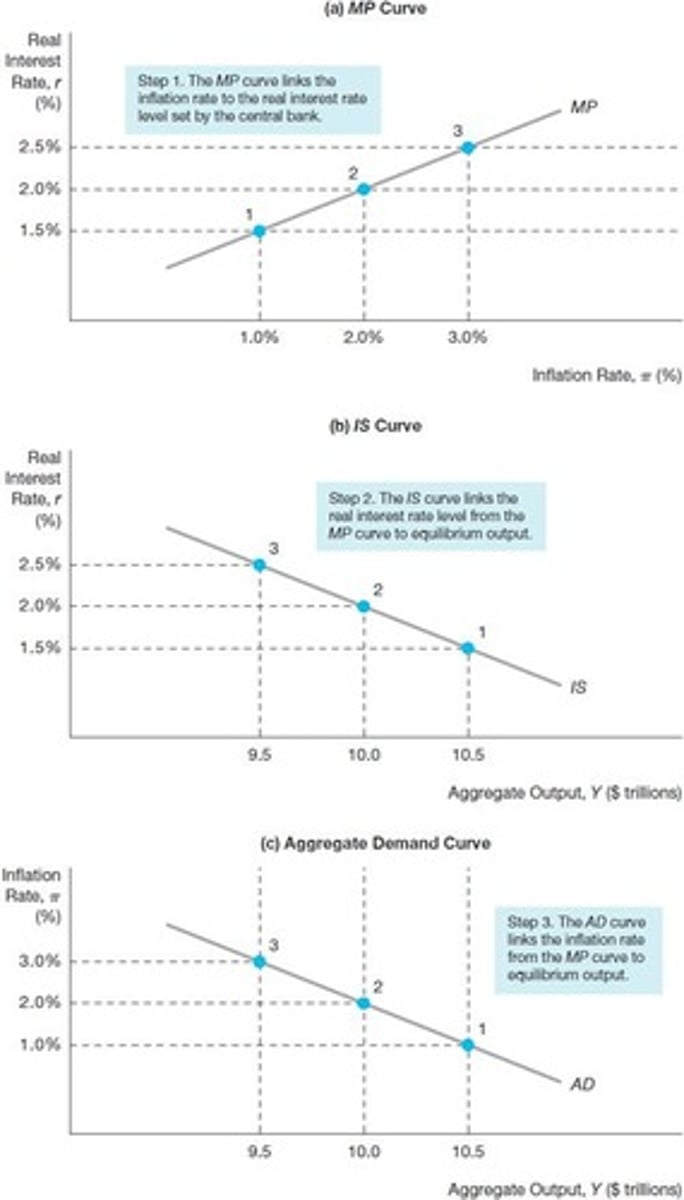
Monetary Policy Curve
Shows real interest rate response to inflation.
Aggregate Demand Curve
Relationship between inflation rate and aggregate demand.
IS Curve
Represents equilibrium in the goods market.
Taylor Principle
Nominal rates must rise more than inflation increases.
Upward Sloping MP Curve
Real interest rates increase with rising inflation.
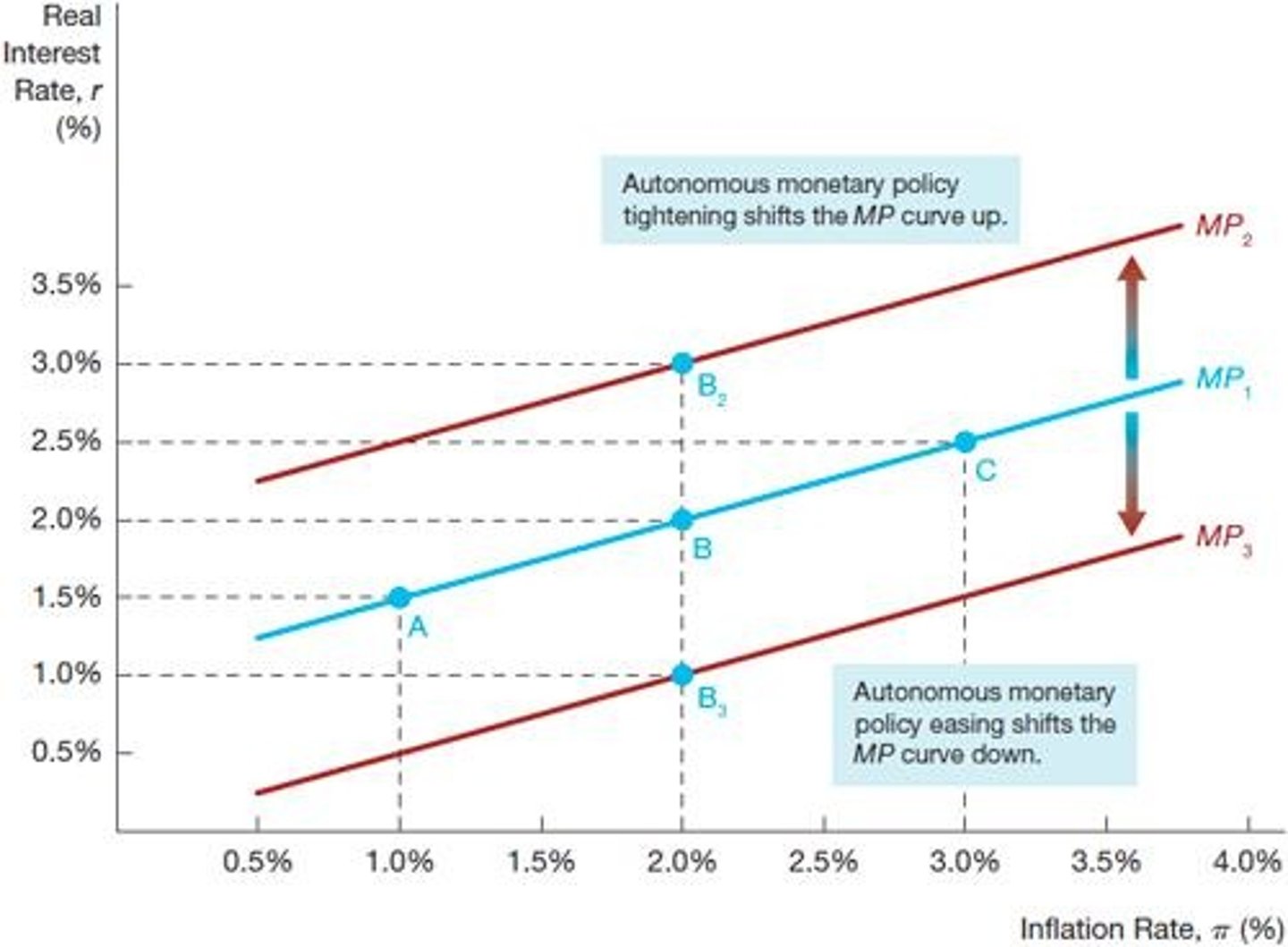
Shifts in MP Curve
Changes in monetary policy affecting interest rates.
Autonomous Tightening
Increases real interest rates to reduce inflation.
Autonomous Easing
Decreases real interest rates to stimulate economy.
Downward Sloping AD Curve
As inflation rises, aggregate output falls.
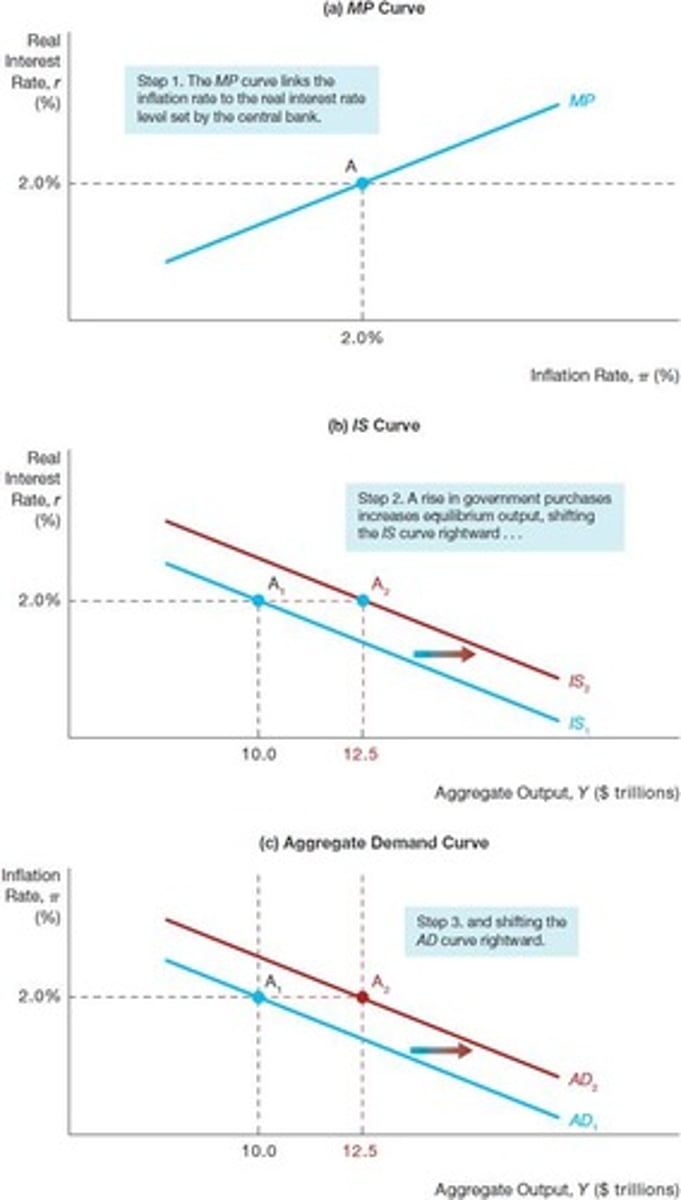
Factors Shifting AD Curve
Changes in consumption, investment, government spending, taxes.
Equilibrium Aggregate Output
Level of output where goods market clears.
Inflation Rate
Percentage increase in price level over time.
Short-run Fluctuations
Temporary changes in output and inflation levels.
Monetary Policy Actions
Decisions by central banks affecting money supply.
Federal Reserve
U.S. central bank responsible for monetary policy.
Automatic Changes
Adjustments in rates based on Taylor principle.
Autonomous Changes
Deliberate policy shifts affecting the MP curve.
Consumption Expenditure
Total spending by households on goods and services.
Investment Spending
Business expenditures on capital goods.
Net Exports
Exports minus imports influencing aggregate demand.