ClinChem 1 Lab 3 - Operation of the Centrifuge & Serum Sample Preparation (In progress)
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
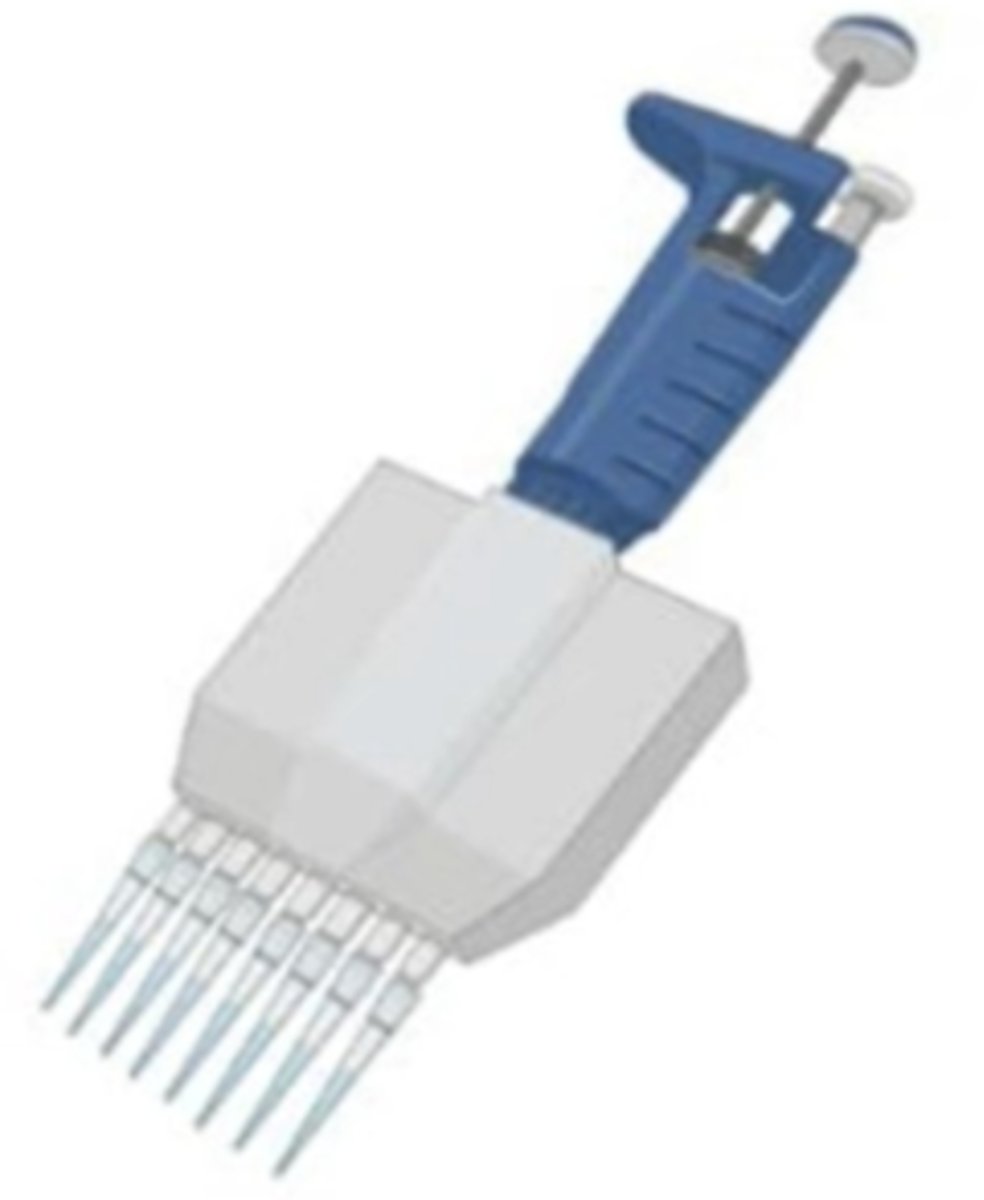
Multichannel Pipette
it's called a such because there are different channels and each channel has its own pipet tips
Multichannel Pipette
can only dispense one type of solution per procedure
Serological Pipette attached to an Electric Pipette Controller
these are the new types or new
sets of pipettes used in the modern day laboratories
Multichannel Pipette
identify

Serological Pipette attached to an Electric Pipette Controller
identify
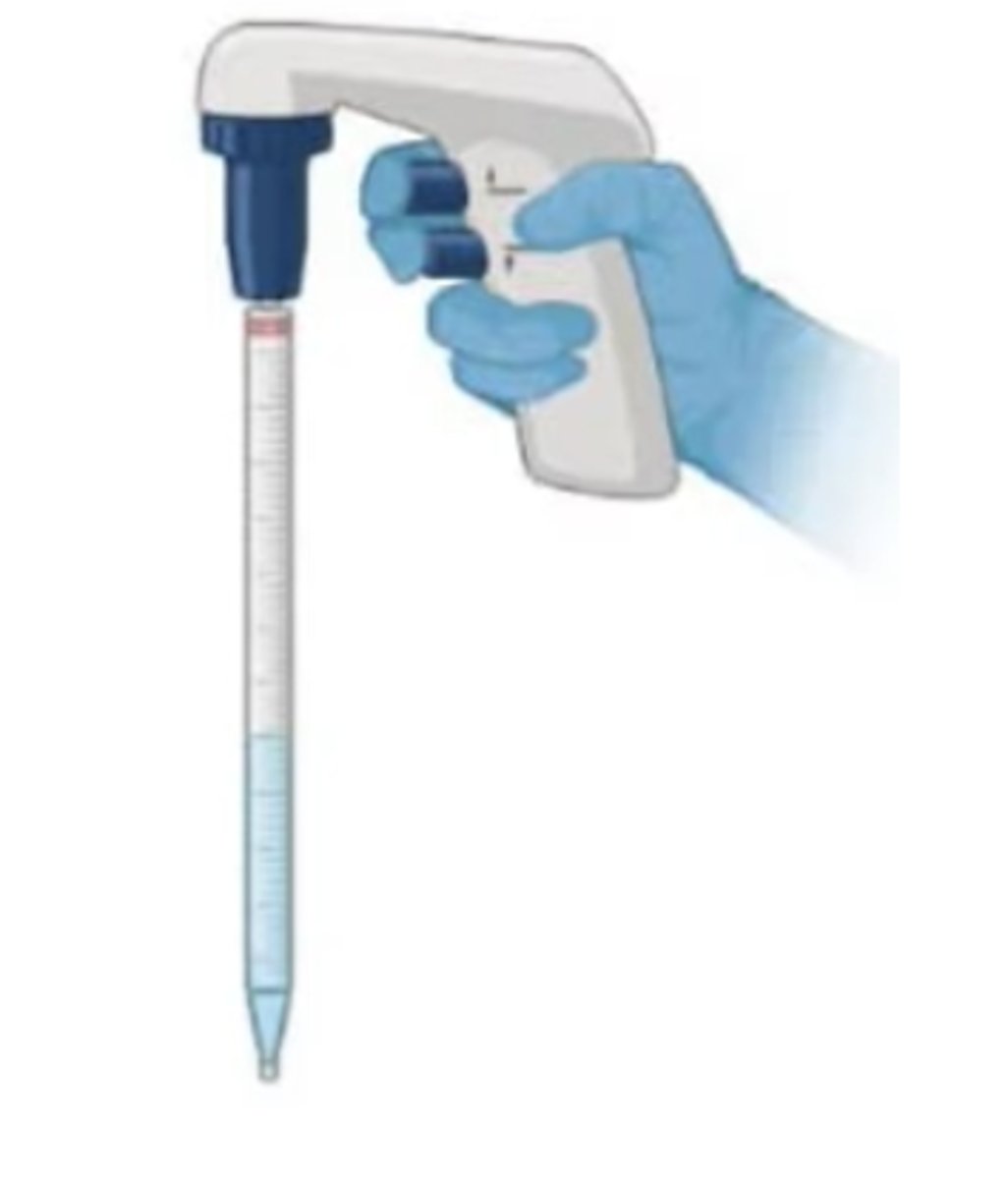
Serological Pipette attached to a Pipette Controller
identify

Serological Pipette attached to a Pipette Filler Bulb
identify

Pasteur Pipette
commonly used in the Laboratories to dispense small amounts of liquid solutions
Pasteur Pipette
rarely used in cases where accurate measurements are needed because we cannot dispense accurate volumes using pasteur pipettes
Pasteur Pipette
identify

Serological Pipette
has two continuous rings or two etched rings near the top of the pipette
Serological Pipette
knowing that it has two etched rings that means the last drop of liquid should be expelled into the receiving vessel making it a blowout type of pipette
Serological Pipette
identify
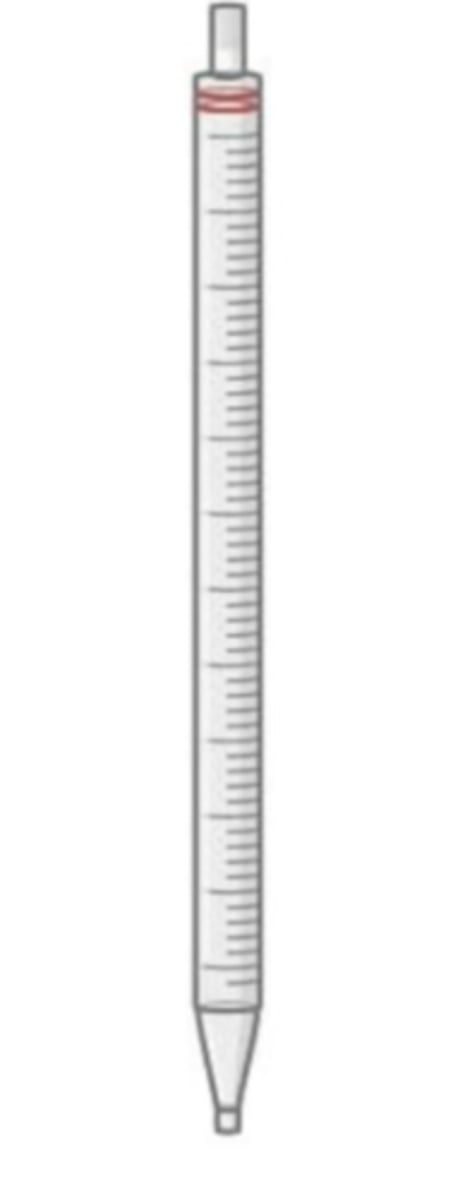

it is a to deliver Blowout Measuring type of pipette
What is the complete classification of serological pipets?
Semi-automated micropipette
this type of pipet is used to dispense minute or very little samples as low as one micrometer (μm).
Semi-automated micropipette
identify
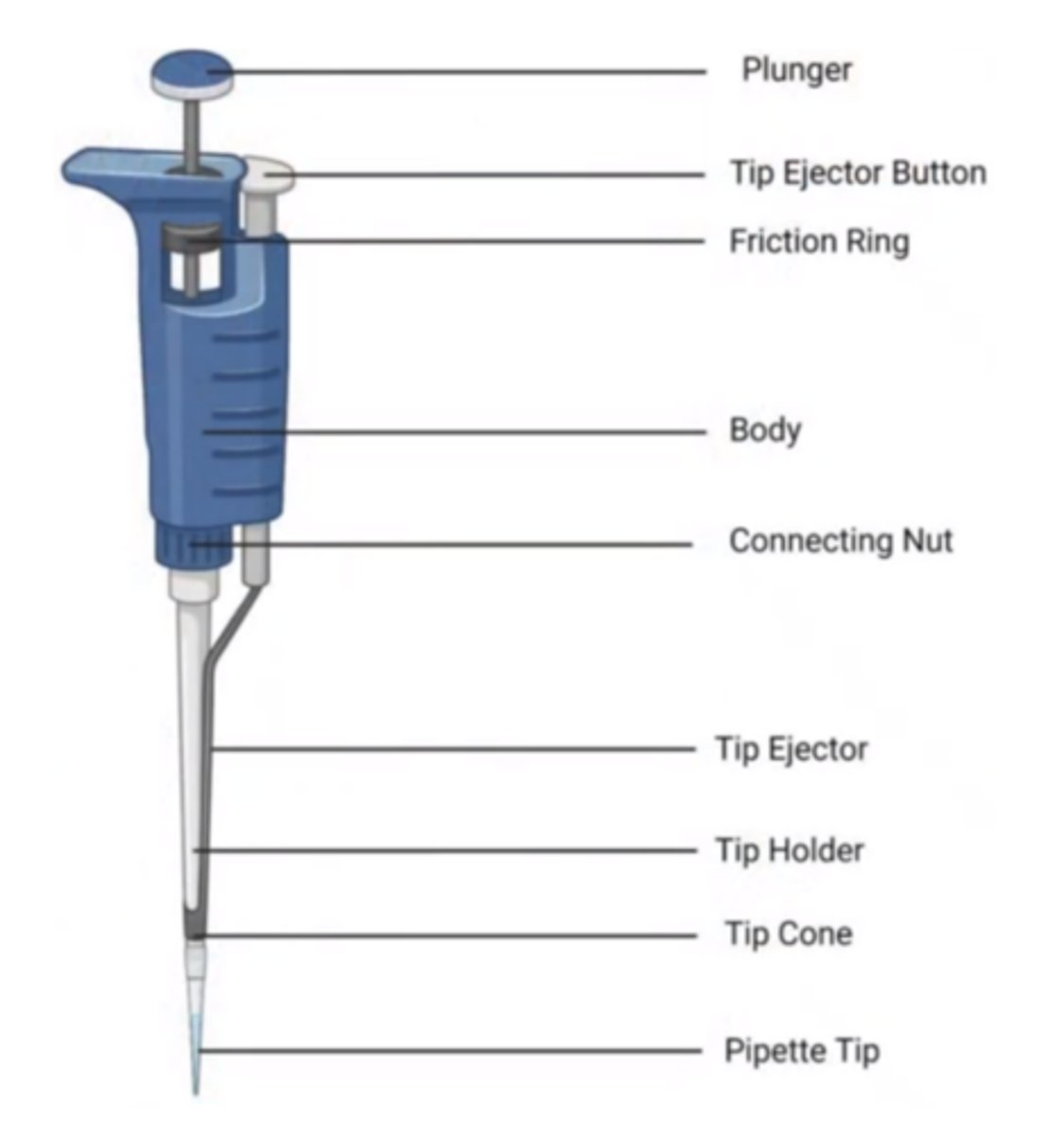
Plunger
where you need to push in order to aspirate the fluid that is found in the pipette tip
Tip Ejector Button
what you need to press or to push so that the pipette tip can be removed from the tip cone
Body
they are connecting knots or knobs
Tip Ejector
The one that will push the pipette tip out
Tip Cone
Where you need to attach the pipette tip
- Design
- Draining Characteristics
- Type
3 types of pipette classification
- To Contain
- To Deliver
2 categories under the Design classification
- Blowout
- Self-draining
2 categories under the Draining Characteristics classification
- Measuring
- Transfer
2 categories under the Type classification
To Contain (design)
Types of pipettes that could hold or contain a particular volume but does not dispense the volume that is indicated.
To Contain (design)
Also referred to as "rinse-out pipette.”
Mercury
Calibrating medium of To Contain Design
- Micropipettes
- Long Levy Type
- Sahli's Pipette
To Contain (design) examples
To Deliver
Will dispense the volume indicated.
To Deliver
Designed to drain by gravity
To Deliver
They must be held vertically with the tip placed against the side of the container and must not touch the liquid in it.
Distilled Water
Calibrating medium of To Deliver pipette
Serological pipettes, Mohr pipettes,
Volumetric pipettes, Ostwald-Folin pipettes
Examples of To Deliver pipettes
Blowout
Has 2 continuous rings or two etched rings located near the top of the pipette or the area where we attach the pipette bulbs or the safety bulbs for suction of the fluid.
Blowout
This means the last drop of liquid should be expelled into the receiving vessel through blowing out.
- Serological
- Ostwalk-Folin
2 examples of blowout pipettes
Self-draining
No ring markings located at the top of the pipettes.
Self-draining
Draining is by gravity
Self-draining
Tip of the pipette should not touch be in contact with the accumulating fluid in the receiving vessel during drainage in order for us not to disrupt the free-flowing fluid and to have an accurate measurement of the fluid being dispensed.
Measuring/ Graduated Pipettes
Long, cylindrical tubes drawn out to the tip and are calibrated in uniform fractional volume measurements.
- Mohr
- Serological
Examples of Measuring/ Graduated Pipettes
Volumetric/ Transfer Pipettes
Very distinct in appearance because they're shaped like rolling pins with a large belly
Neck
Blunt end of the Volumetric/ Transfer Pipettes
Tip (where you will dispense the solution
Tapering end of the Volumetric/ Transfer Pipettes
- Volumetric
- Ostwald-Folin
Examples of Volumetric/ Transfer Pipettes
sedimentation principle
Principle: The centrifuge utilizes the _____ due to gravitational force.
centrifugal field
The centrifugation technique uses a ____ to separate the different particles that are suspended in a liquid medium. These are put in the centrifuge rotor either in bottles or tubes.
Sedimentation
____ is a process whereby gravity causes the suspended particles to separate from the fluids. This suspended substance may consist of either powder or clay like particles.
Centrifugation
A process in which centrifugal force is used to separate solid matter from a liquid suspension.
- Separate serum or plasma from blood cells.
- Separate supernatant from a precipitate.
- Separate two immiscible liquids.
- To expel air
4 uses of the Centrifuge
- Rotor
- Shield
- Motor
3 principles of centrifuge
Lid
most important part of the centrifuge because it is used to cover you from any hazards, aerosols, oreven mechanical hazards such as broken tubes from flying out from the centrifuge.
Rotor
- Holds the tubes, bottles, or even blood bags if we use a refrigerated centrifuge in the Blood Bank department.
- This contains liquids that are for centrifuge
drive shaft
Different rotor types and sizes can also be interchangeable with one another, can be mounted on the ____ which connects to the motor and the motor provides the power to turn the rotor.
cabinet
Usually, a ___ surrounds and supports these parts and also protects the operator should a tube break or any metal parts fail while the centrifuge is running.
operating controls and indicator dials
The ___ and ___ for speed and time are mounted on the cabinet.
brake system
Most centrifuges have a ___ to bring the rotor to a stand-still shortly after the run is finished.
- Mass
- Speed
- Radius
Centrifugal force depends on 3 variables:
RCF = 1.118 x 10^-5 x r x (rpm)^2
The speed of the centrifuge is related to the relative centrifugal force (RCF) by the following equation:
Horizontal-head or Swinging-bucket centrifuge
Allows the tube to attain a horizontal position in the centrifuge when spinning and a vertical position when head is not moving.
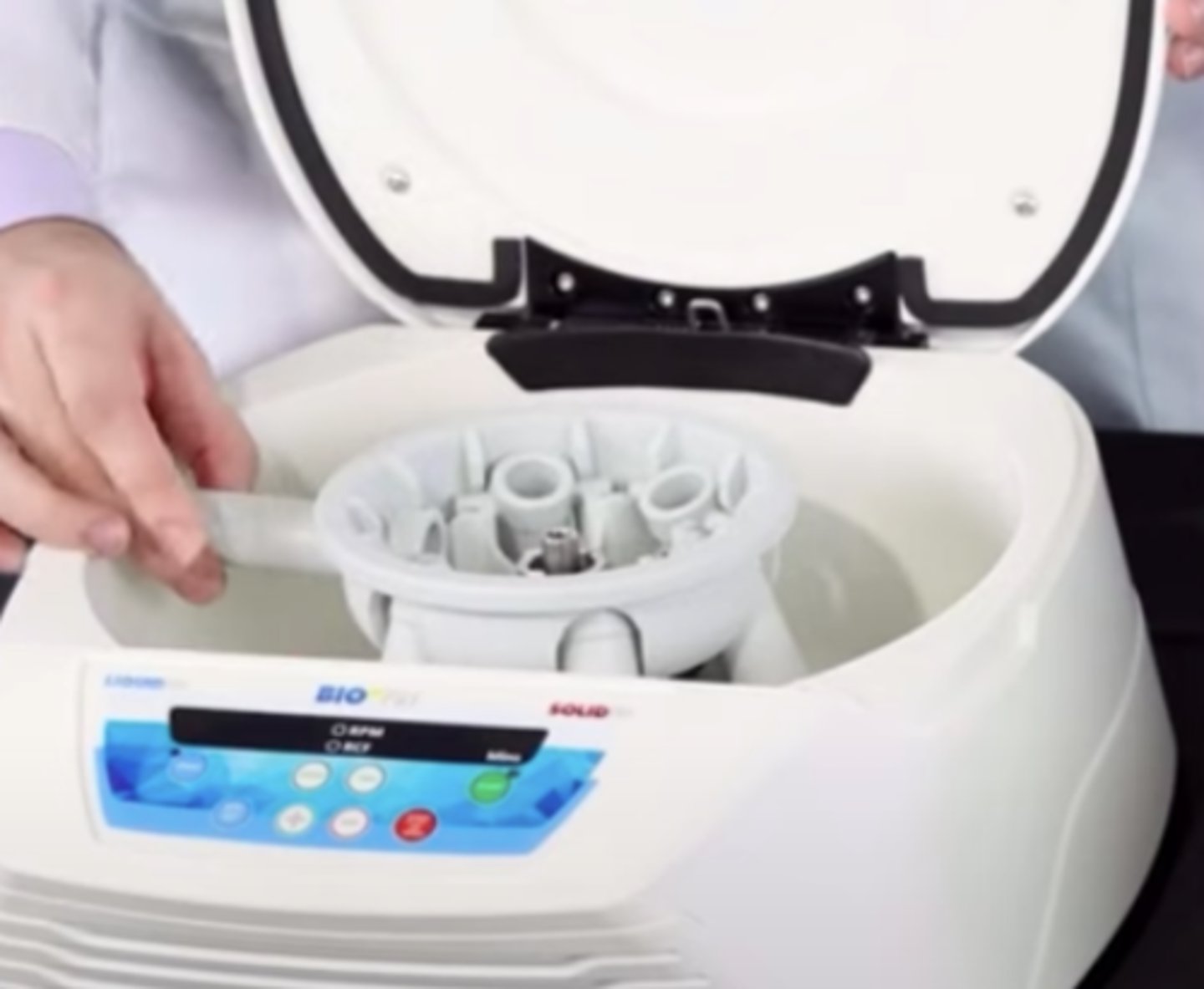

Horizontal-head or Swinging-bucket centrifuge
when it is moving, it will have a horizontal position as shown in the picture below. It will then stand vertically when the centrifuge in unused or when it is not moving.
Fixed-angle or Angle-head Centrifuge
Holds the tubes at a specified angle, usually 25 to 50 degrees, to the vertical axis of rotation.
25 to 50 degrees,
Fixed-angle or Angle-head Centrifuge holds the tubes at a specified angle, usually ___ to ___ to the vertical axis of rotation.
Fixed-angle or Angle-head Centrifuge
These are the common centrifuges that we use here in the laboratory.
Horizontal-head or Swinging-bucket centrifuge
The pellets or the pelleted material will form at the bottom of the conical centrifuge tube.
Fixed-angle or Angle-head Centrifuge
The tubes processed will form a sedimentation on the side so this could be problematic if the solids get caught in the angle of the tube.
Swinging-bucket rotors
The ____ offer a more superior sedimentation location means that this is the best choice for centrifuging samples
Fixed-angle or Angle-head Centrifuge
____ offer valuable features that often make them a more desirable choice due to their simple and efficient tube spacing, which is why they can hold a greater quantity of tubes compared to that of the swinging-bucket counterpart.
Fixed-angle or Angle-head Centrifuge
it is more practical for high throughput applications especially in the laboratory since we are dealing with a lot of samples—that’s why it is preferable to have a fixed angle centrifuge.
Ultracentrifuge
Are commonly used to separate lipoproteins.
Blood Bank
Refrigerated ultracentrifuges are the ones used in ____.
cracks
Steps in operation of a centrifuge:
Step 1: Inspect the centrifuge bottles and tubes for ___ before use.
aerosol
A centrifuge can spin at such high speeds, a liquid sample can easily become an ___ if it is not properly contained.
broken or cracked tubes
Cracked tubes can fracture at high speeds or at the very least, leak liquid into the rotor. Discard ___ or ____ to prevent them from accidentally being used in the future.
Cap
Steps in operation of a centrifuge:
Step 2: ____ tubes with the proper lid.
cap or lid
Tubes that have been specified for use with the centrifuge have a proper ___ or ___ that seals the tube.
aerosol
- Using a different lid or covering such as saran wrap or foil can easily lead to spills within the centrifuge.
- Making an ___ of your sample can be hazardous to your health and the environment.
precious sample
Not capping the tubes with the proper lid can lead to the loss of ___
Wipe the outside of the tube
Steps in operation of a centrifuge:
Step 3: ____ with disinfectant before placing it in the centrifuge.
spills or aerosol
T/F:
You want to limit any possible ___ or ___ formation of your sample.
wipe down the sample
The best prevention is to _____ with a proper disinfectant before the spin begins.
However, due to the business in the laboratory, this might be overlooked but it is really best that we wipe the outside portion of the tube before starting the spinning.
label
Steps in the operation of a centrifuge:
Step 4: Clearly ___ tubes for identification
Mislabelling or misidentification
____ or ____ of the sample is a grave offense in the laboratory.
F
You may know how you placed your tubes into the centrifuge before they started spinning, but at the end of the spin you will not be able to tell them apart.
T/F:
You may know how you placed your tubes into the centrifuge before they started spinning, but at the end of the spin you will be able to tell them apart.
label the tube directly
Make sure you put some sort of label on each tube, so you know which sample is which that’s why it is best to _____ instead of using a sticker since a sticker can fall off during the spin making identification difficult.
counterbalance
Steps in the operation of a centrifuge:
Step 5: Make a ___ for the centrifuge tube you want to put in the centrifuge.
aren't equal masses opposite
At high speeds, a centrifuge can easily become unbalanced if there _____ to each other in the rotor.
masses
Remember to balance the ____ of the tubes, and not the volumes.
permanent damage of the centrifuge and can be hazards
Unbalanced tubes can lead to ___ and ___ if the rotor breaks free from the rest of the centrifuge.
Balancing
____ also is extremely important at higher centrifugation speeds, many centrifuges will automatically turn off if it senses an unbalanced load.
firm, level surface
Steps in the operation of a centrifuge:
Step 6: Place the centrifuge on a ____.
Relocate
_____ the centrifuge to a more stable place if it is sliding around or the counter underneath is sagging to avoid destroying the centrifuge because it's very expensive.
proper rotor
Steps in the operation of a centrifuge:
Step 7: Choose the ____ to use at the speed you need.
rotor
The ____ is a piece that spins your sample.