ANA300 - Meninges and Cerebral Hemispheres
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Cerebral hemispheres are ______ separated by the _______
bilaterally paired, longitudinal fissure
Cerebral hemispheres are anatomically ______ but functionally ______
symmetrical, asymmetrical
Diencephalon is _______ buried within the cerebral hemispheres, including _____,_____ and ____
grey matter, thalami, hypothalamus, epithalamus
Brainstem includes the ____, _____ and ____
midbrain, pons, medulla
Brainstem contains vital ______, ______ ___
autonomic centres, cranial nerve nuclei, white matter tracts
Cerebellum consists of bilaterally paired ______, separated from the cerebral hemispheres by the _________
transverse fissure
Highly folded ____ and _____ increase surface area of the brain
sulci (grooves), gyri (bumps)
Particularly deep sulci are called _______
fissures
Variability in sulci and gyri between _____ and ____ of the same brain, however some consistency divides brain into ___—
brains, hemispheres, landmarks
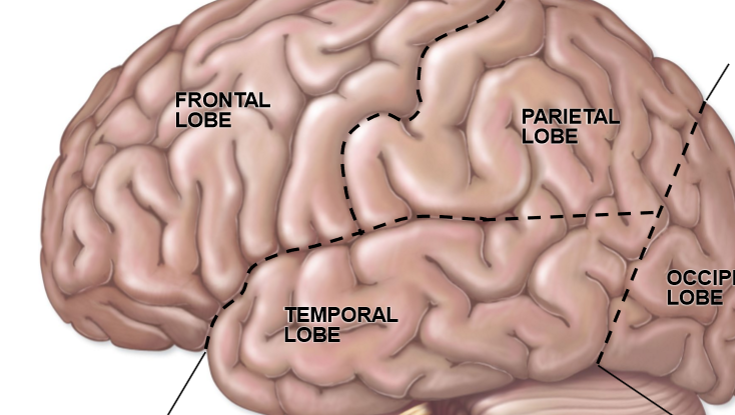
Left to right
Lateral fissure
Central sulcus
Parieto-occipital fissure
Preoccipital notch
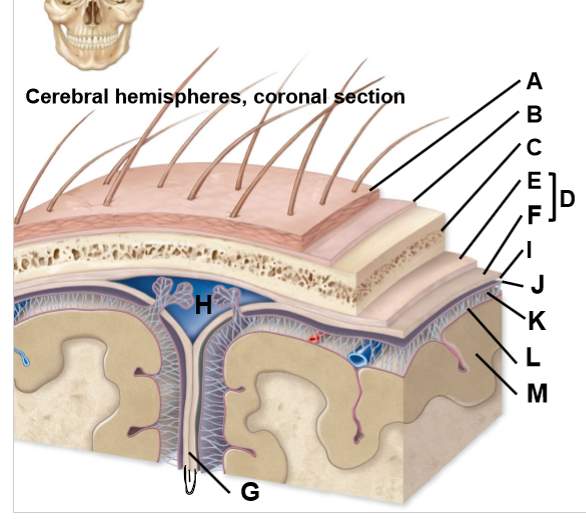
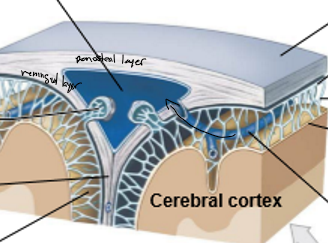
A-M
A: Skin
B: Periosteum
C: Cranium
D: Dura matter
E: Periosteal layer
F: Meningeal layer
G: Dural reflection
H: Dural venous sinus
I Subdural space (potential space)
J: Arachnoid matter
K: Subarachnoid space (contains CSF, BVs)
L: Matter
M: Cerebral cortex
A-F
A: Falx cerebri
B: Parietal lobe
C: Lateral fissure
D: Temporal lobe
E: Tentorium cerebelli
F: Cerebellum
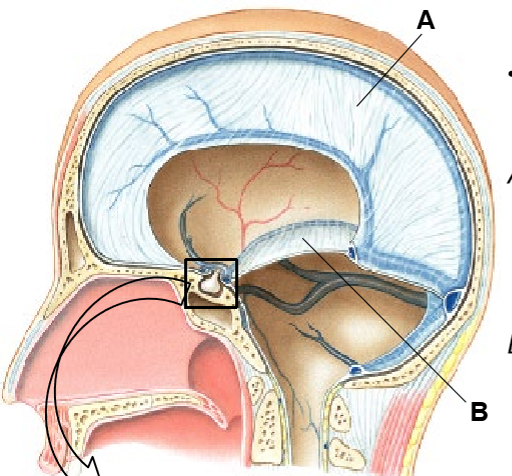
A-B
A: Falx cerebri
B: Tentorium cerebelli
The falx cerebri separates the _______
right and left cerebral hemisphere
Tentorium cerebelli separates the _______ of the _____ from the ______
occipital lobe, cerebrum, cerebellum
Falx cerebri in the ______ fissure and tentorium cerebelli in the ____ fissure
longitudinal, transverse
Top to bottom
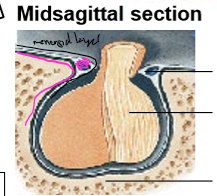
Diaphragma sellae (dural reflection around pituitary stalk)
Pituitary gland
Sella turcica of sphenoid
The diaphragma sellae stabilizes position of the ________ in the skull base
pituitary gland
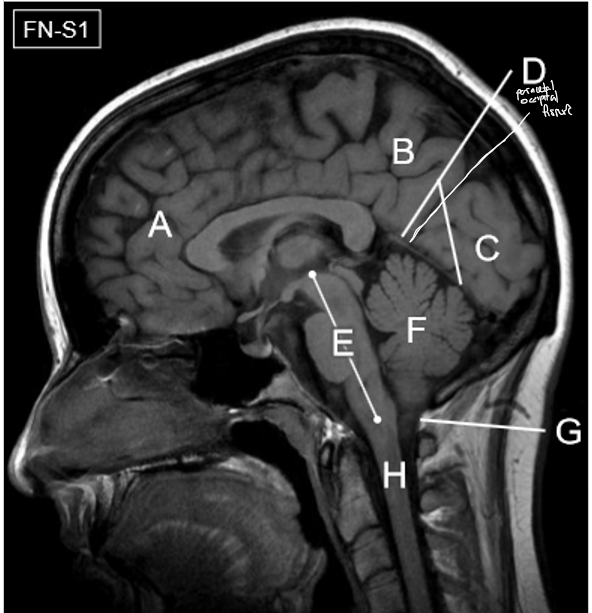
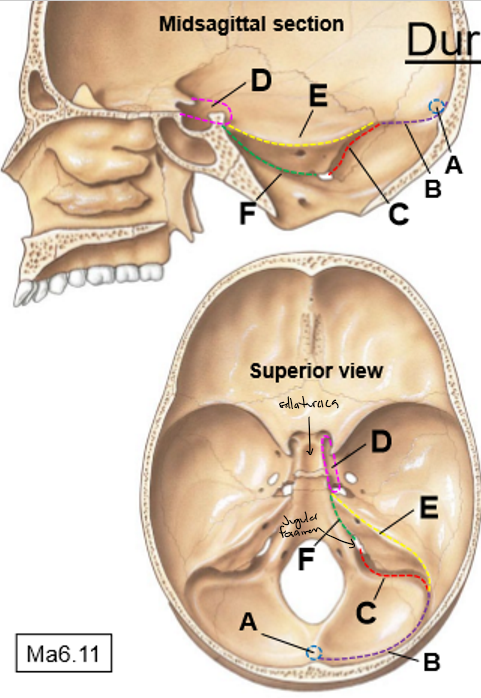
D-H
D: Tentorium cerebelli
E: Brainstem
F: Cerebellum
G: Foramen magnum
H: Spinal cord
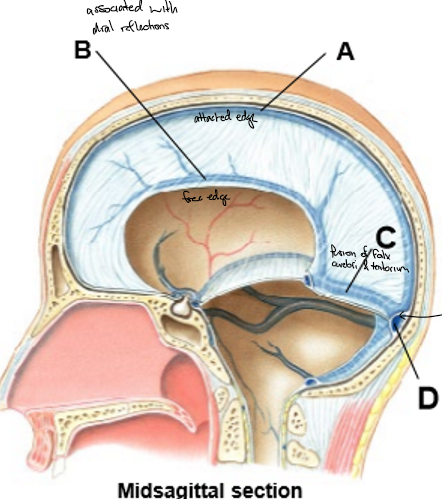
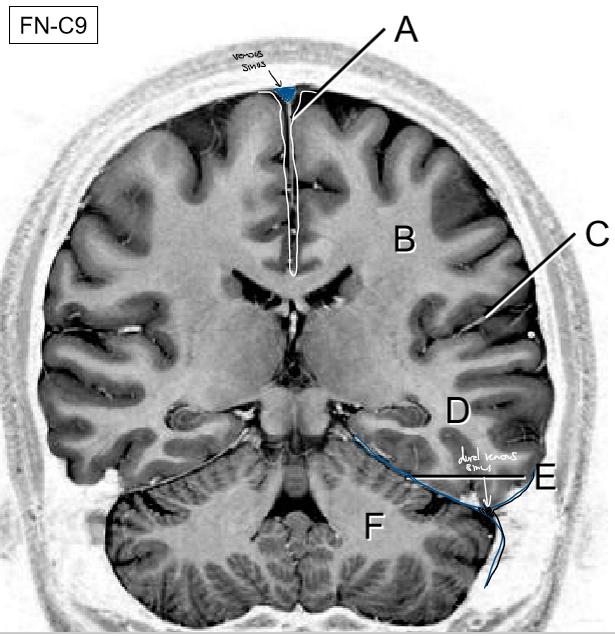
A-D
A: Superior sagittal sinus
B: Inferior sagittal sinus
C: Straight sinus
D: Confluence of sinuses
Dural venous sinuses drain venous blood from ________ into R/L ________
Cerebral veins, internal jugular veins
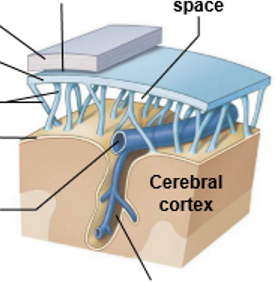
Outside-inside
Dura mater
Subdural space
Arachnoid mater
Subarachnoid space
Arachnoid trabeculae
Pia mater
Cerebral vein
Perivascular space
Outside-inside
Dura mater
Superior sagittal sinus
Subdural space
Arachnoid mater
Arachnoid granulation
Falx cerebri
Subarachnoid space
Arachnoid trabeculae
Pia mater
A-F
A: Confluence of sinuses
B: Transverse sinus
C: Sigmoid sinus
D: Cavernous sinus
E: Superior petrosal sinus
F: Inferior petrosal sinus
Sigmoid sinus runs to
jugular foramen
Cavernous sinus receives _______ from orbit
opthalmic veins
The ______ is a more direct root from cavernous to jugular foramen/sinus
Inferior petrosal sinus
The nervous system originates from a hollow, fluid filled tube; the ______
neural tube
Enclosed fluod-filled space, the _______ forms the _______ of the CNS
neural canal, ventricular spaces
Ventricular spaces contain _____ produced by the _____
CSF, choroid plexus
__ between the_ cells of the choroid plexus forms the ___
TJs, ependymal, blood-CSF barrier
____ between the ___ cells of the cerebral BVs form the _______
TJs, endothelial cells, blood-ISF barrier
Capillaries in neural tissue are of the _____ type
continuous
BBB breakdown results in ____ permeability of brain capillaries and causes ______, which increases ______ and can act like a space occupying lesion
increased, vasogenic edema, intracranial pressure
In BBB imaging, seen with a _______ that doesn’t cross intact BBB
contrast agent
BBB breakdown occurs in ___, _______ and _____
tumors, arteriovenous malformations, inflammation
__________ are associated with the cerebra hemispheres
Bilaterally paired lateral ventricles
______ is associated with the diencephalon
third ventricle
______ is associated with the midbrain
Cerebral aqeduct
_______ is associated with the pons, medulla, cerebellum
fourth ventricle
The ________ is associated with the spinal cord
central canal
The ______ is usually blocked in pathology
cerebral aqueduct
The central canal opens ______ into the fourth ventricle
rostrally
The _____ has 3 openings into the subarachnoid space
fourth ventricle
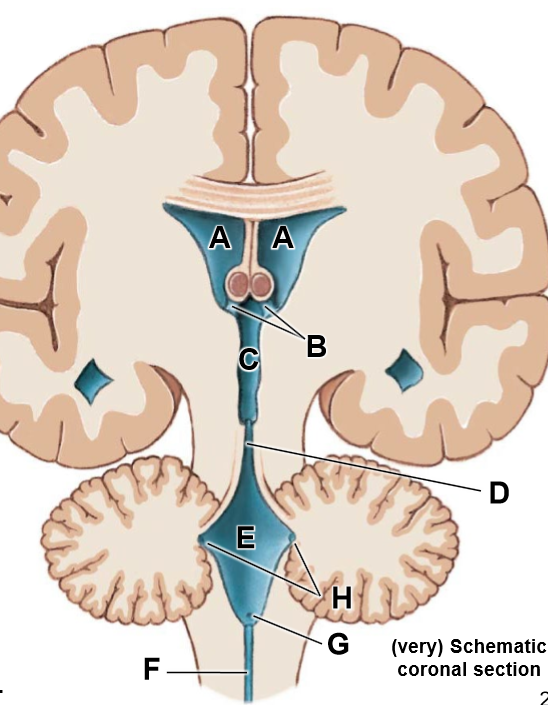
A-F
A: R/L lateral ventricles
B: Intraventricular foramen
C: Third ventricle
D: Cerebral aqueduct
E: Fourth ventricle
F: Central canal
G: Median aperture
H: Lateral apertures
Total volume of CSF is ~_______
150mL
We produce ______ of CSF/day and turnover ____
500mL, 3 times
CSF circulates through ____, enters the ______ via _______ apertures of the fourth ventricle
ventricles, subarachnoid space, median, lateral
CSF circulates in ______ space
subarachnoid
CSF is returned to venous blood via ________ in dural venous sinuses and along sheaths of _____ and ____ surrounding ____
arachnoid granulations, cranial, spinal nerves, lymphatics
Cerebral hemispheres receive ______ from, issue ____ to, the _______
sensory information, motor commands, opposite side of the body
The cerebral cortex is ______
grey matter
The subcortex is _____
white matter
Subcortical whit matter carries afferent information toward and efferent information away from _____________
neuronal cell bodies of cerebral cortex
Subcortical matter may be _____, ____ or ____ fibres
association, commissural, projection
Commissural tracts
Corpus callosum
Cross midline
Association fibres
Do not cross the midline
Projection fibres
Connect cerebral hemisphere with lower structure
Buried within the brain are ____ structures such as the ____ () and _____()
grey matter structures, basal nuclei (ganglia), diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus)
Movement is planned and initiated in
specific dedicated cortical areas
All sensory modalities reach the ____, most after a relay in the ____
cerebral cortex, thalamus
Each modality has an area dedicated to its ______ ()
perception, primary sensory cortexE
Each modality has an area dedicated to its _____, ()
interpretation, primary association cortexEa
In put from the various sensory modalities are integrated in the ____
multimodal association cortices
Primary motor cortex controls _______
voluntary, skilled movement
Area of the motor homunculus is _____ to precision of movement of the body part
proportional
The prefrontal cortex functions in the _____ and ______ of movement, and control of ____
programming, preparation, posture
Primary somatosensory cortex (Postcentral gyrus) controls _________
Perception of somatosensation
Area of sensory homunculus is _______ to the density of sensory innervation of a given body part
proportional
Somatosensory association cortex is responsible for interpretation of ____ and ______
somatosensation, conscious awareness of the contralateral half of the body
Visual cortex located on either side of the ________ in the ____ lobe, functions in _______
calcarine fissure, occipital, visual perception
Visual association cortex is the remainder of the _____ lobe
occipital
Role of visual association cortex
Interpretation of visual images in the context of past experience
Lesion causes deficit in visual interpretation and recognition
Primary auditory cortex located in the ____ within the ________
temporal lobe, lateral fissure
Role of primary auditory cortex
Conscious perception of sound
Tonotopic (pitch) map of cochlear duct
Auditory association cortex is located in the _______
adjacent portions of the temporal lobe
Sensory speech area (____) in the _____
Wernicke’s area, dominant area
The non-dominant hemisphere of the sensory speech area, interprets _____ ()
prosidy (musical components of language)
Motor speech area located in ______ anterior to ______
portions of frontal lobe, precentral gyrus
Motor speech area (aka. ______)located in the _____ (usually the __) hemisphere only
Broca’s area, dominant, left
The non-dominant hemisphere of the motor speech area, interprets ___
prosidy
The gustatory cortex is located in the _______
inferior part of postcentral gyrus and insula
Gustatory cortex interprets
conscious perception of taste
Olfactory complex located in the _____ and responsible for _______
temporal lobe, conscious perception of smell
Multimodal association cortices include the ______ and ________
Prefrontal cortex, inferior portions of parietal lobe
Prefrontal cortex integrates information from _________, responsible for ________
various association cortices, high intellectual functions
Inferior portions of parietal lobe are the interface between ______, ____, and _____ association cortices
somatosensory, visual, auditory
The basal nuclei includes the (4)
Caudate
Putamen
Globus pallidus/pallidum
Substantia nigra, subthalamus
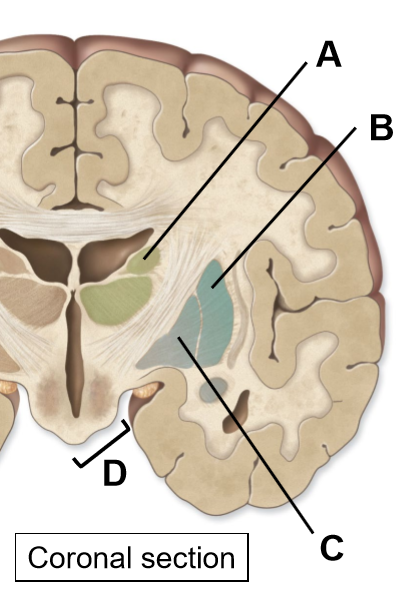
A: Caudate
B: Putamen
C: Globus pallidus
D: Substantia nigra
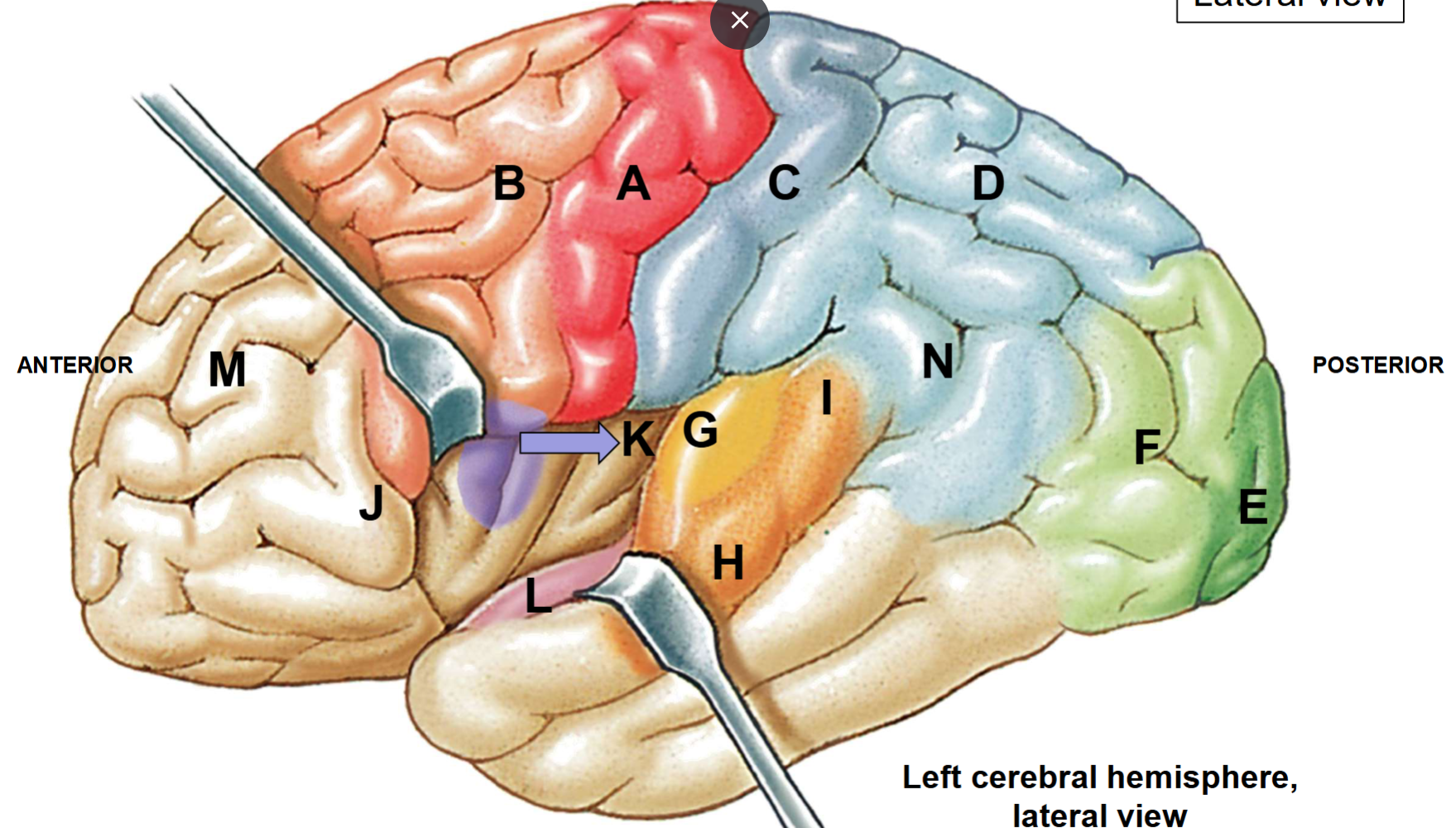
A-N
A: Primary motor cortex
B: Premotor cortex supplementary motor area
C: Primary somatosensory cortex
D: Somatosensory association cortex
E: Primary visual cortex
F: Visual association cortex
G: Primary auditory cortex
H: Auditory association cortex
I: Sensory speech area
J: Motor speech area
K: Primary gustatory cortex
L: Primary olfactory cortex
M: Prefrontal cortex
N: Inferior portions of parietal lobe
Basal nuclei functions in _____
normal voluntary movement
Basal nuclei is not directly connected to _____, therefore doesn’t directly _____
spinal cord, control movement
Diseases of basal nuclei present with
Hypokinesis (without paralysis) or hyperkinesis
Altered posture and muscle tone
Altered cognition, behavioural disturbances
ie. Parkinsons
Sensory nuclei of the thalamus
Vision (lateral geniculate nucleus)
Hearing (medial geniculate nucleus)
Somatic sensation, conscious proprioception, taste (ventral posterior)
Motor nuclei of thalamus
Associated with basal nuclei and cerebellum
Movement planning and control (VA, VL)
Limbic nuclei of the thalamus control ____, ___ ()
Emotions, mood, (anterior group)
Association nuclei in the thalamus integrates _____ and connects with _____
sensory information, association cortices
Intrinsic and diffuse projecting nuclei influences levels of ______
arousal
Hypothalamus maintains homeostasis via _____ and ___ means in response to ____ and __ input
neural, hormones, interoceptive, limbic
Hypothalmamus regulates:
Reproductive
autonomic and instinctive functions
Food/water intake