Science Study
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Solar System Structure
The Sun is at the center, with planets, moons, and other objects orbiting in elliptical paths.
Rocky Planets
Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars; these planets have solid surfaces.
Gas Giants
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune; these planets are primarily composed of gases like hydrogen and helium.
Natural Satellites
Moons that orbit planets, such as Earth's moon.
Artificial Satellites
Human-made objects that orbit Earth, like communication satellites.
Moonlight
The moon reflects sunlight, allowing us to see it at night; it does not produce its own light.
Phases of the Moon
The moon has different phases (new moon, full moon, etc.) based on its position relative to Earth and the Sun.
Tides
Caused by the moon’s gravitational pull on Earth's oceans.
Moon Phases Sequence
New Moon, Waxing Crescent, First Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon, Waning Gibbous, Last Quarter, Waning Crescent.
Aboriginal Knowledge
Stars and moon phases are used to predict weather, animal behavior, plant cycles, and tidal changes.
Day and Night
Caused by Earth’s rotation.
Seasons
Result from Earth's tilt as it orbits the Sun.
Leap Years
Account for the extra 0.25 days in a year.
Eclipses
Occur when the Earth, moon, and Sun align, resulting in solar and lunar eclipses.
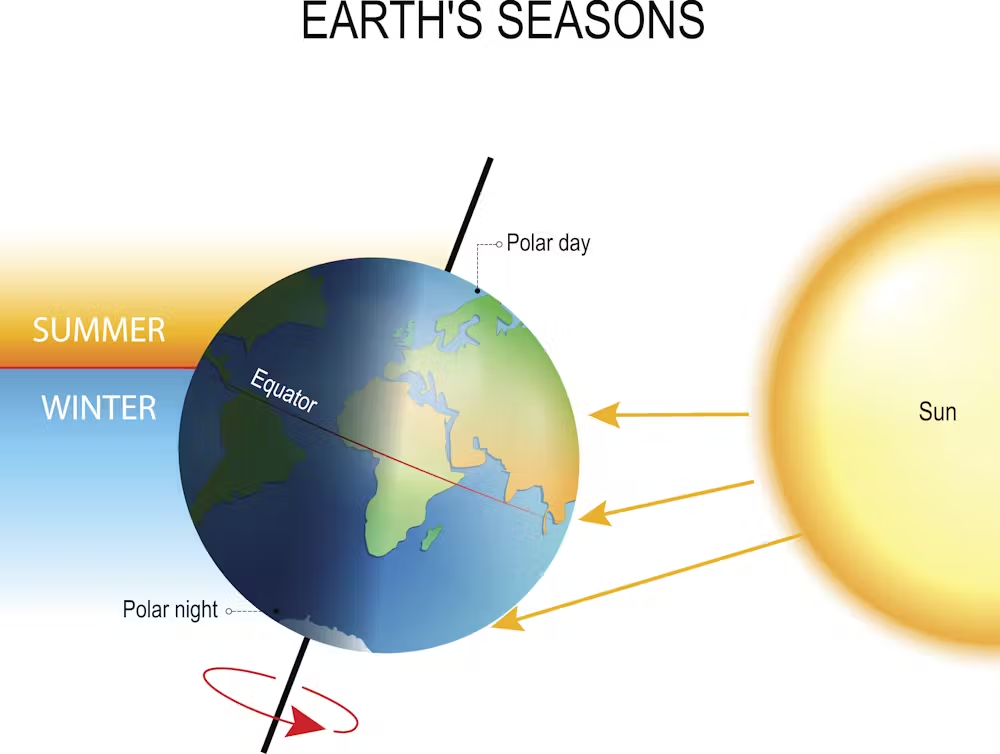
Earth's Tilt
The tilt of the Earth is 23.5 degrees, which causes seasons.
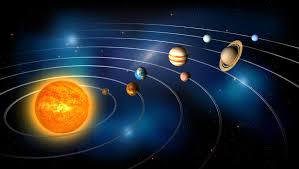
Heliocentric View
The model in which the Sun is at the centre of the universe.
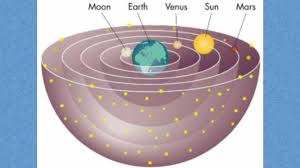
Geocentric view
The model in which the Earth is at the centre of the universe.
Penumbra
where you experience a partial eclipse
Umbra
Where you experience a Total Eclipse