Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland Functions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Where is the hypothalamus located in relation to the thalamus?
Immediately below the thalamus.
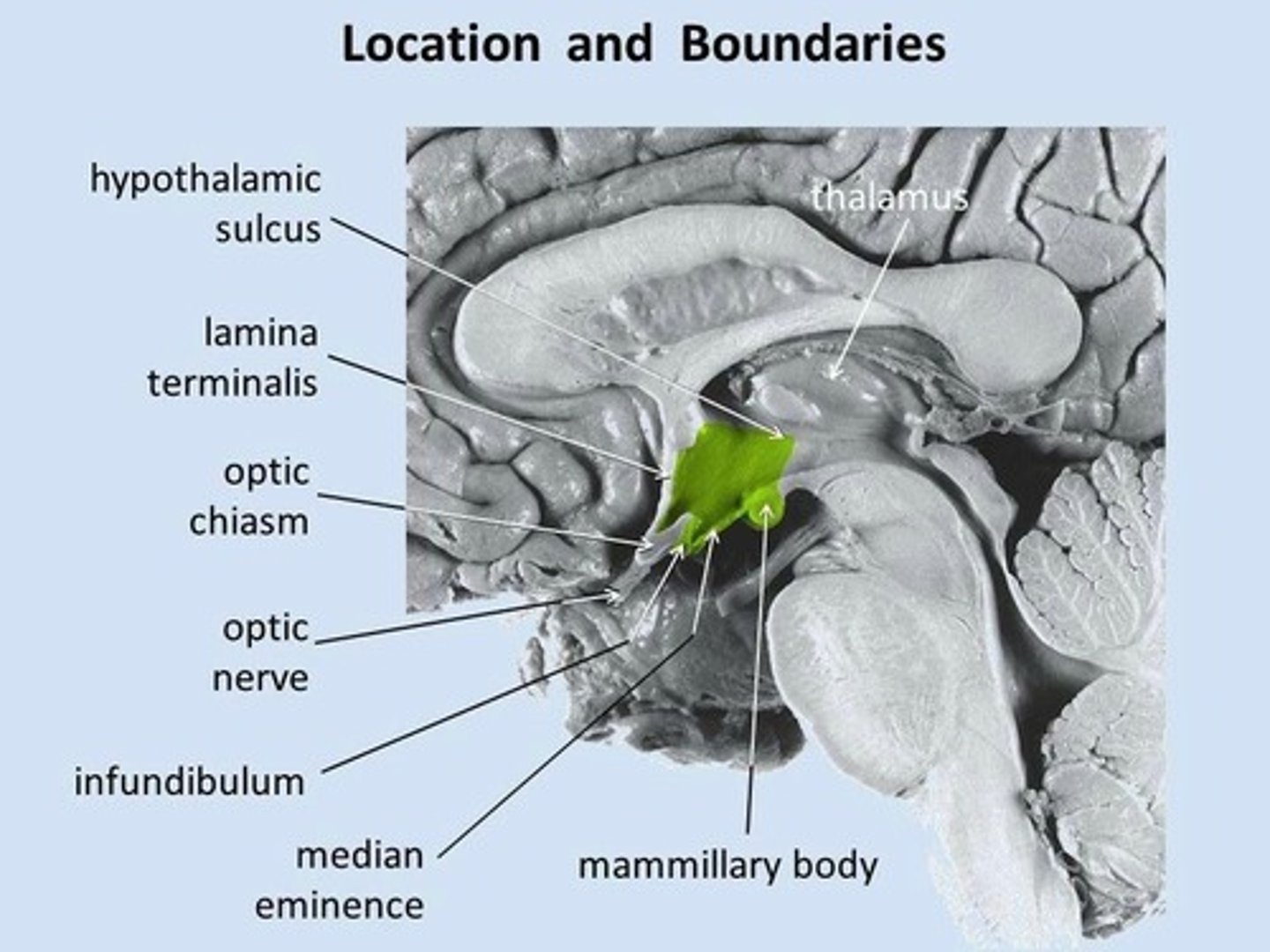
What percentage of brain volume does the hypothalamus occupy?
Less than 1%.
What vital function does the hypothalamus serve in the body?
It is key for homeostasis.
What structure connects the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland?
Infundibulum.
What is the diencephalon and what does it consist of?
A division of the forebrain between the telencephalon and midbrain, consisting of the thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus.
What is homeostasis?
The tendency towards stability in the body, monitored by changes in the internal and external environment.
How does the hypothalamus contribute to homeostasis?
It is the main visceral control and regulating center, controlling the autonomic nervous system and various bodily functions.
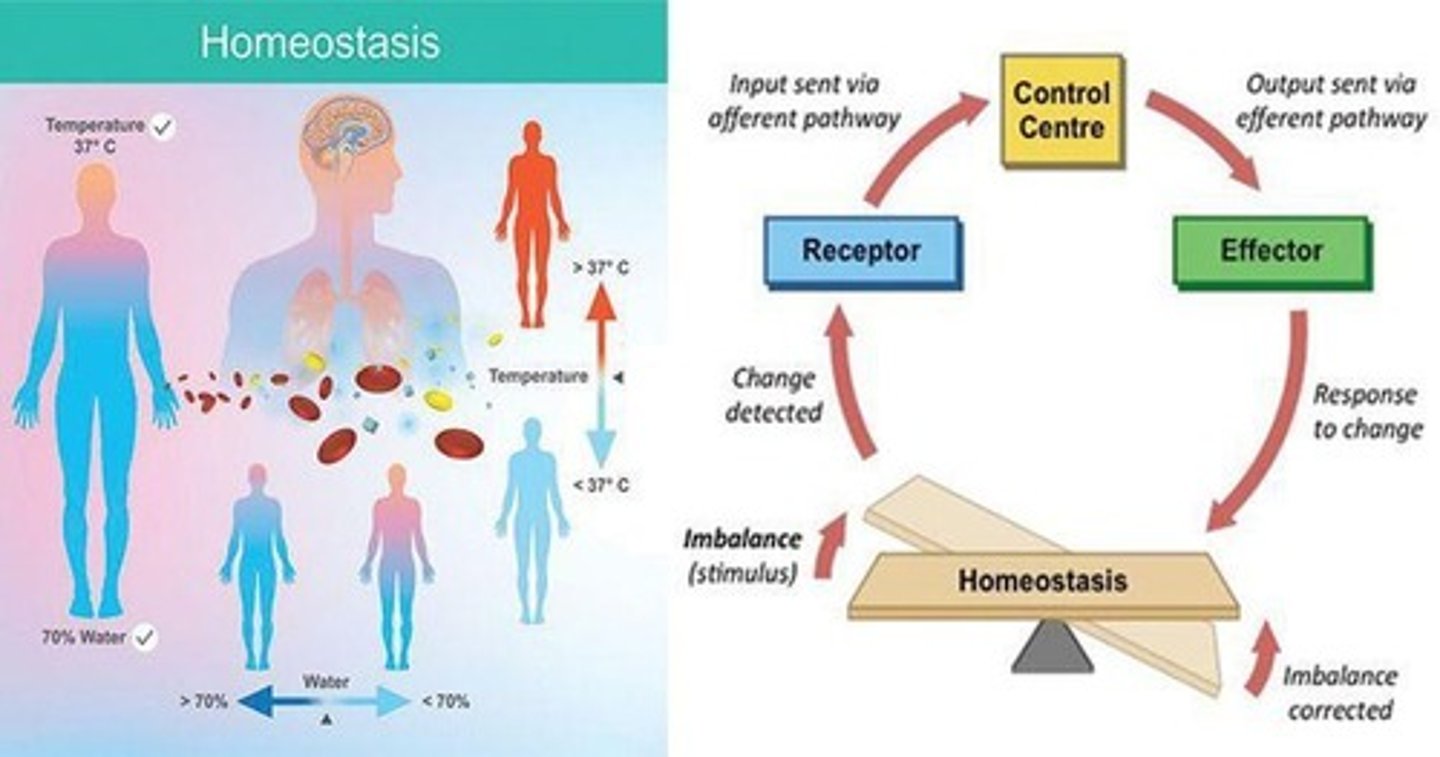
What are some functions controlled by the hypothalamus?
Blood pressure, heart rate, digestive tract motility, pupil size, and physical responses to emotions.
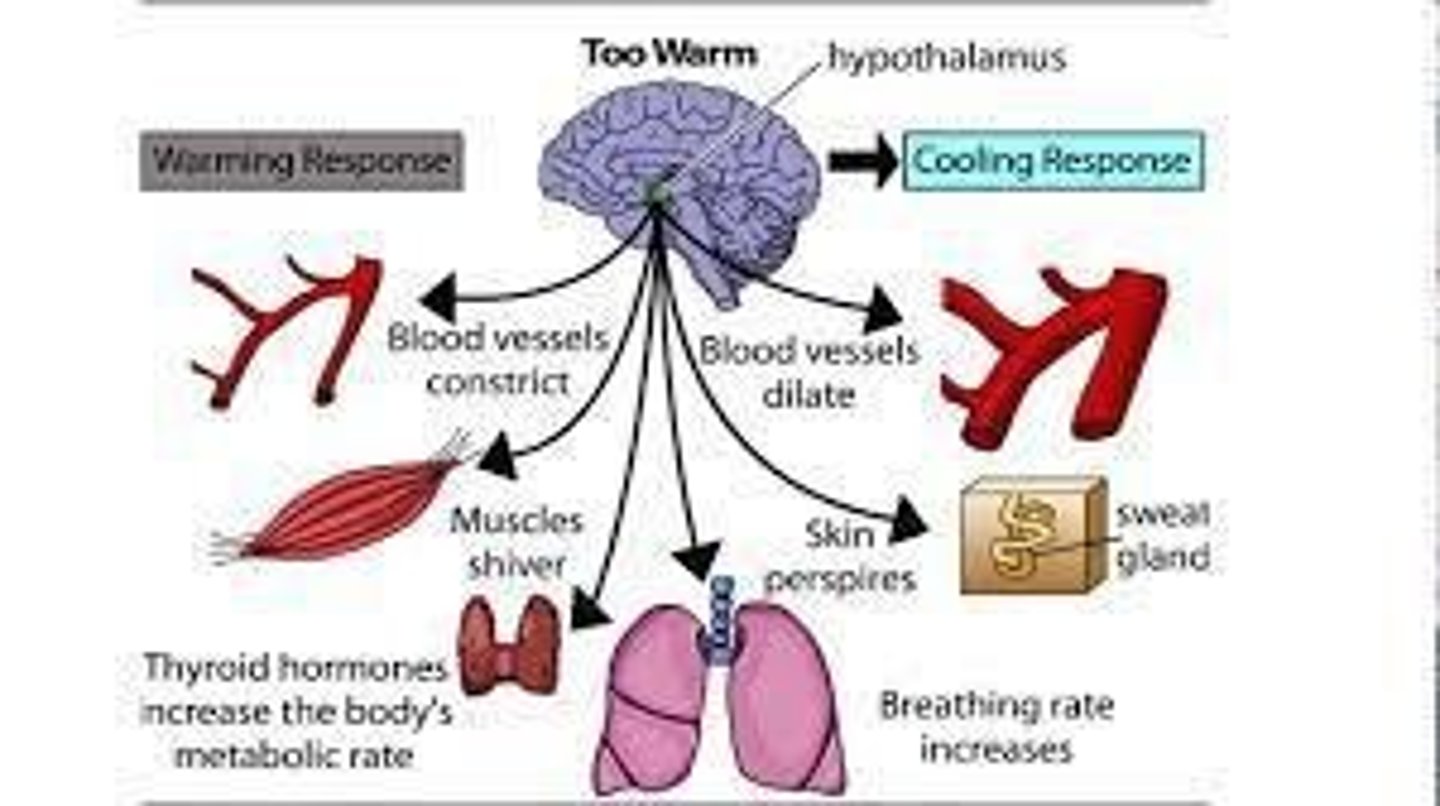
What are the primary functions of the hypothalamus?
Regulating body temperature, hunger, water balance, and sleep-wake cycles.
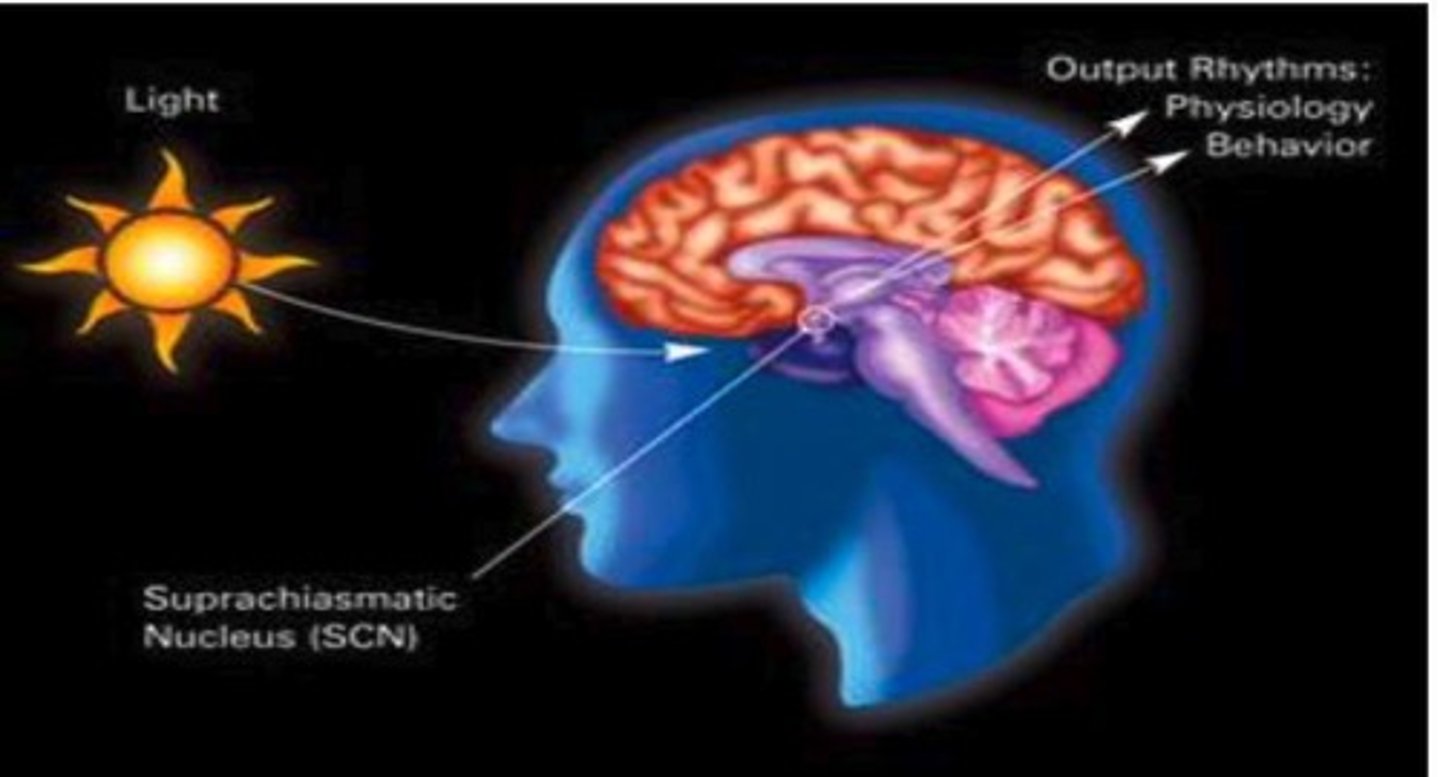
What is the suprachiasmatic nucleus?
A subnucleus of the hypothalamus involved in circadian rhythms.
What hormones does the hypothalamus control in the endocrine system?
Secretions of the anterior pituitary gland and production of posterior pituitary hormones.
How is the hypothalamus divided in a parasagittal plane?
Into three regions: supraoptic, preoptic, and tuberal.
What are the three areas of the hypothalamus in a coronal plane?
Periventricular, medial, and lateral.
What is the function of the anterior (supraoptic) nuclei of the hypothalamus?
Cooling the body, water balance, milk letdown, sleep cycle, and circadian rhythms.
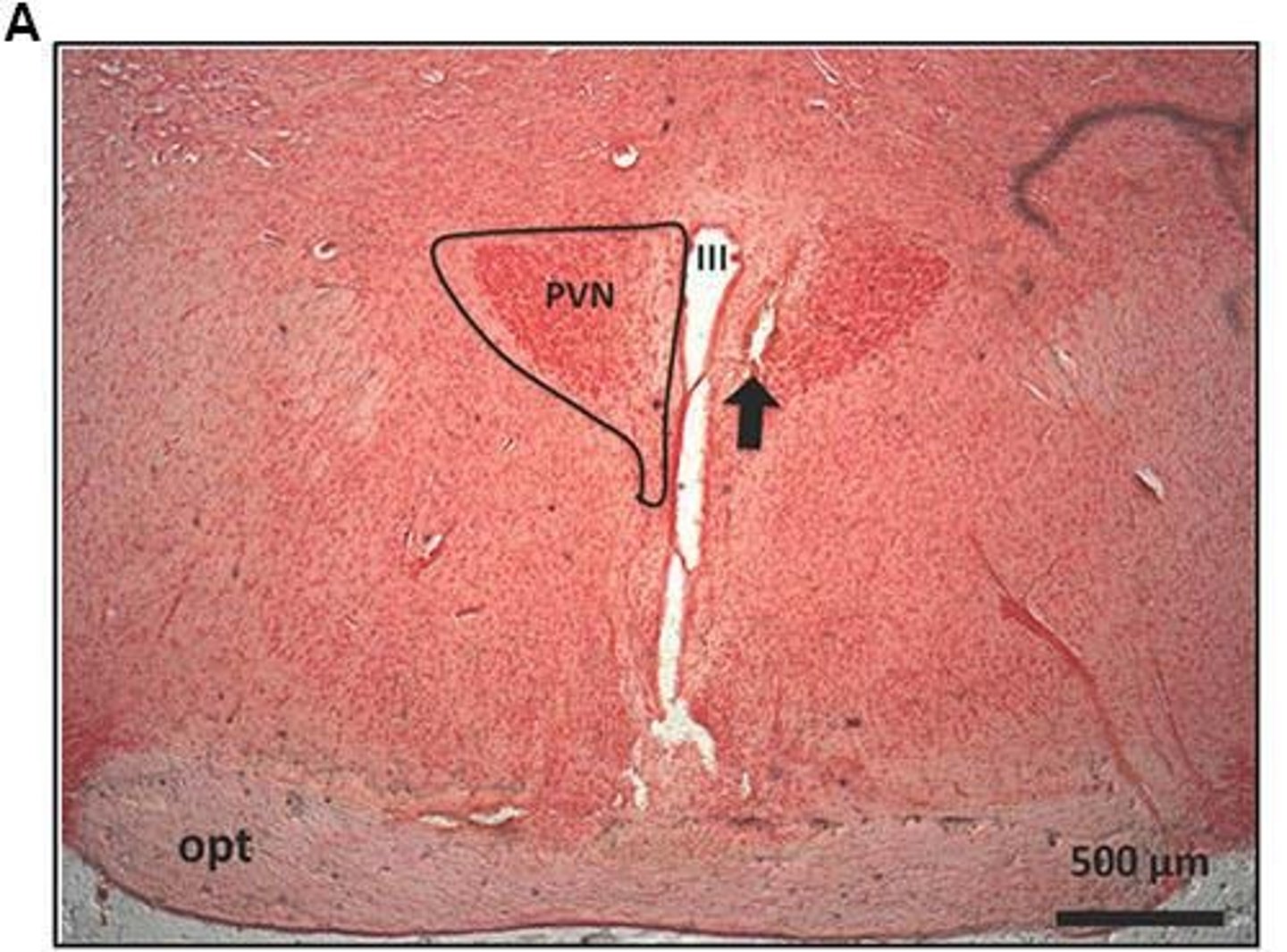
What does the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVH) secrete?
Oxytocin, vasopressin, and CRF/CRH.
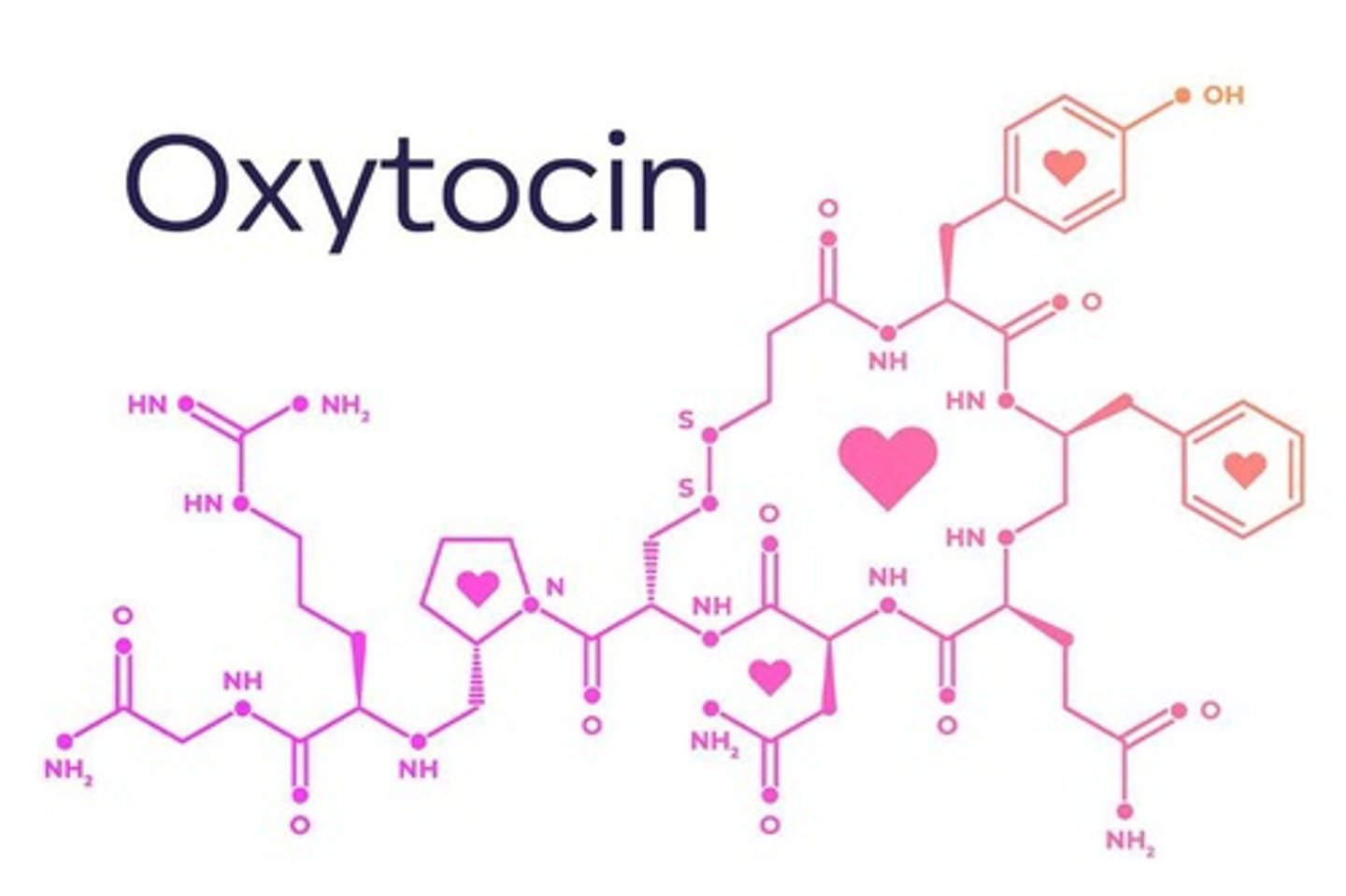
What role does oxytocin play in the body?
Involved in social bonding, empathy, reproduction, childbirth, and milk production.
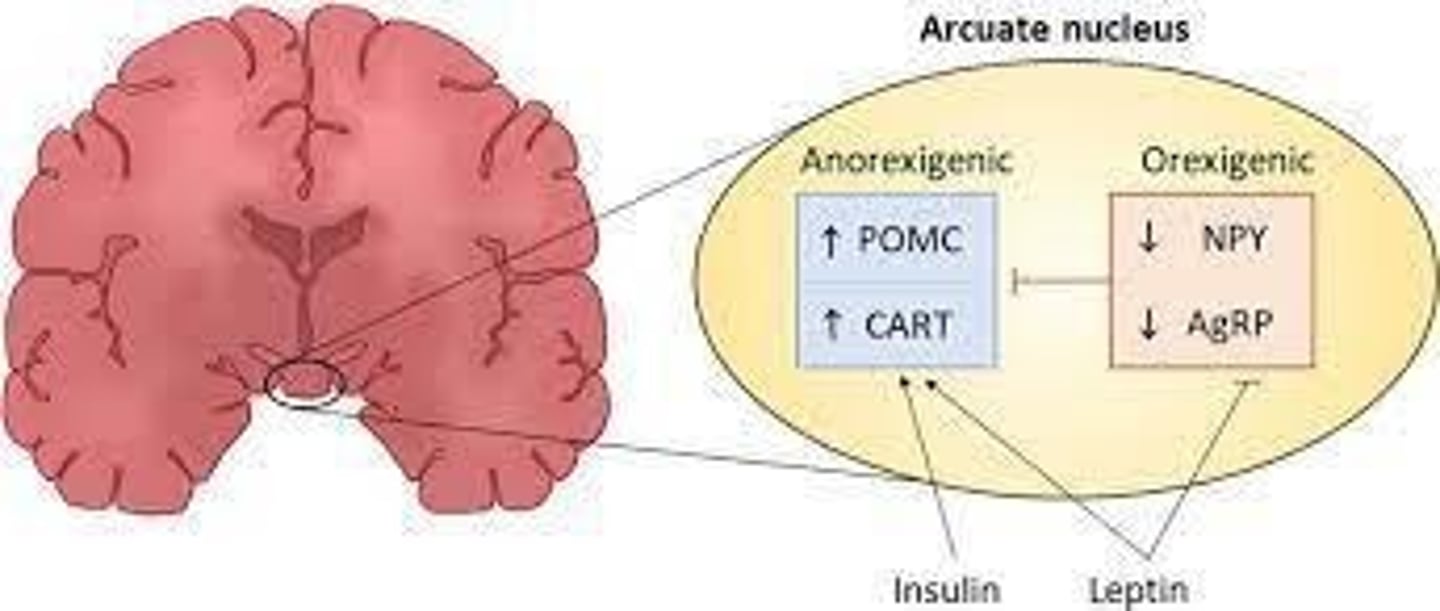
What functions do the tuberal nuclei serve?
Feeding, satiety, and sexual behavior.
What hormones are found in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus?
NPY, AgRP, POMC, CART, kisspeptin, substance P, MSH, somatostatin, GnRH.
What are the effects of hypothalamic damage?
Severe body wasting, obesity, sleep disturbances, dehydration, and emotional imbalances.
What happens to appetite when there are lesions in the lateral part of the hypothalamus?
Animals lose their appetite and may starve in the presence of food.
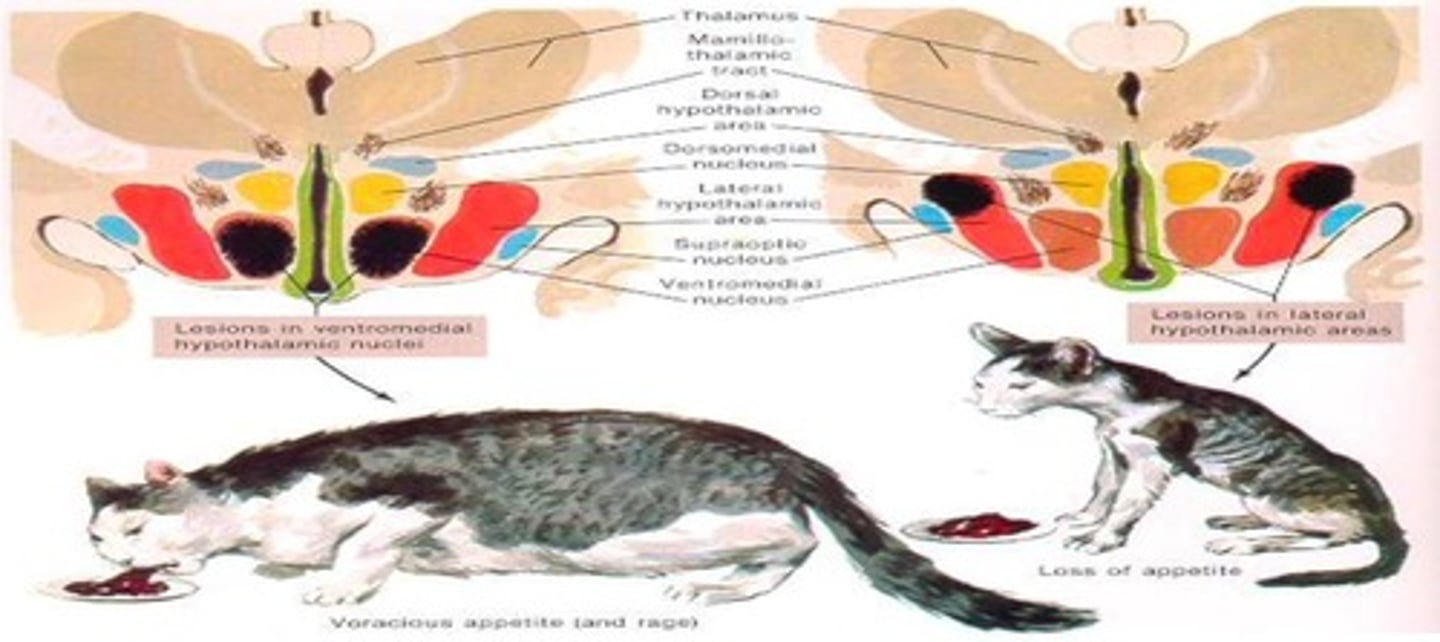
What occurs when there is a lesion in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus?
Animals do not feel satisfied and continue to eat, leading to obesity and rage.
What is the effect of lesions on the anterior nucleus of the hypothalamus?
Causes hyperthermia due to its role in cooling the body.
What is the role of the suprachiasmatic nucleus in sleep?
It receives input from the retina to control sleep and circadian rhythms.
What are circumventricular organs?
Areas in the brain without a blood-brain barrier that communicate between the CNS and peripheral blood.
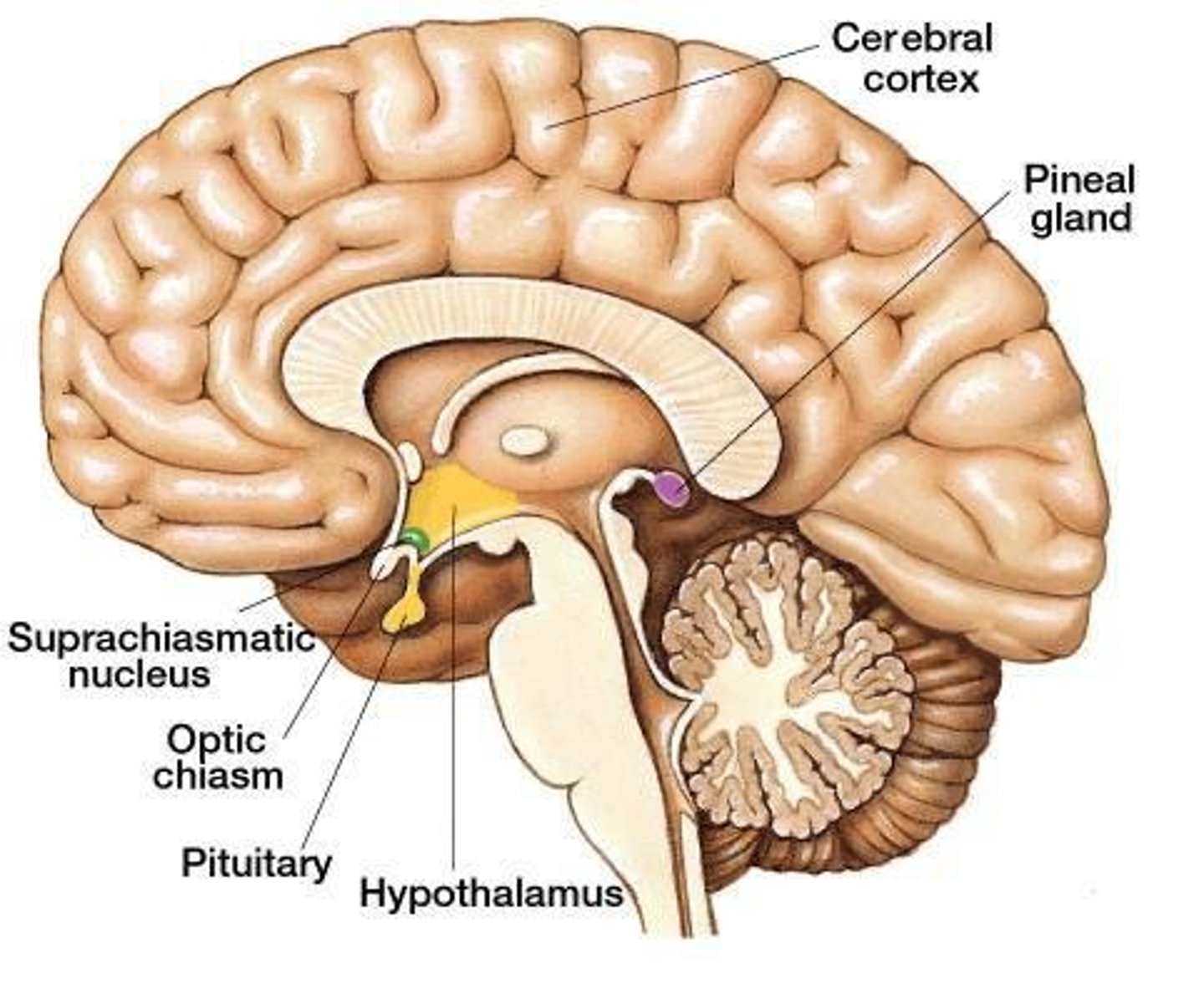
What is the pituitary gland often referred to as?
The 'master gland' of the endocrine system.
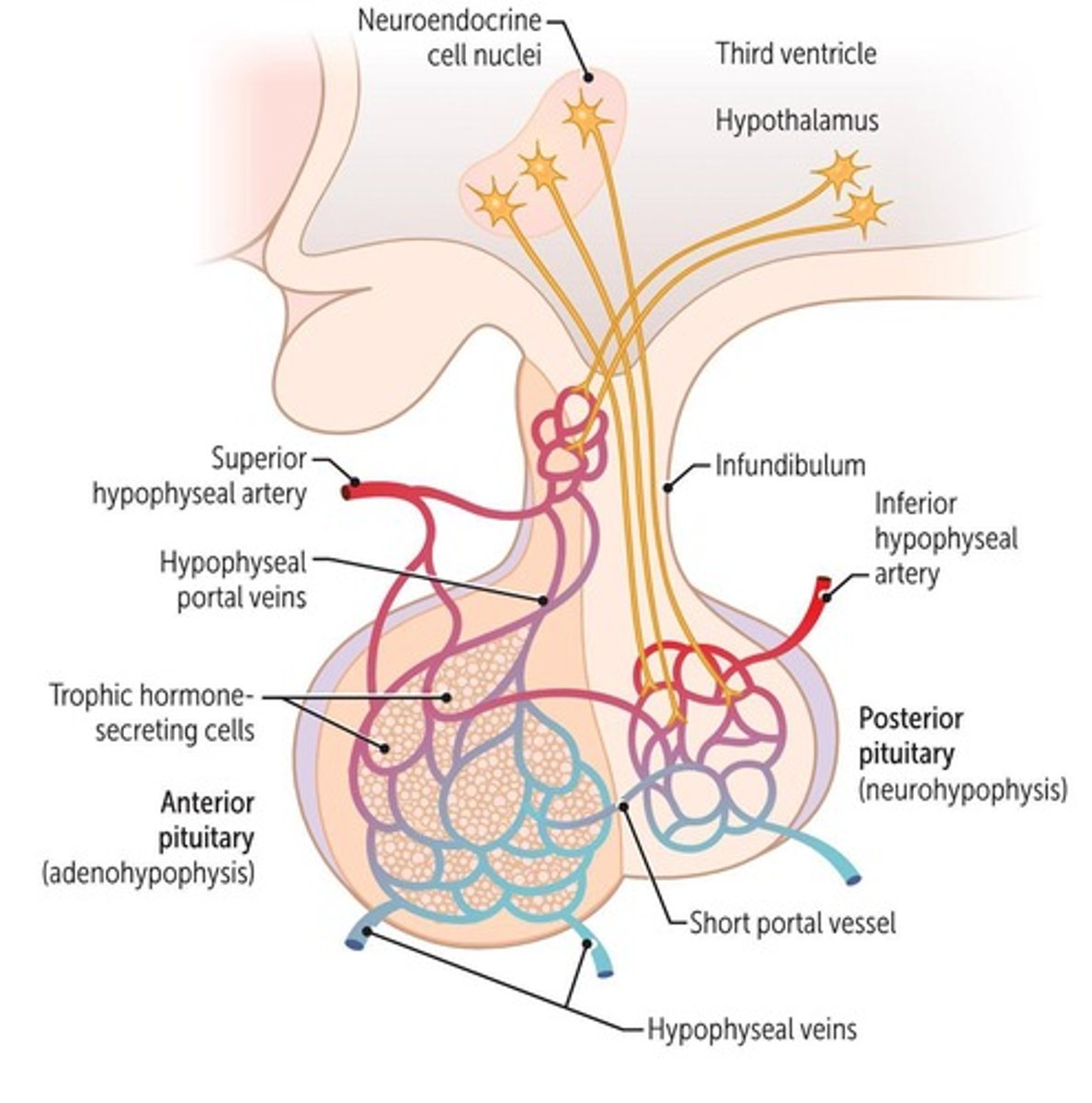
What are the two parts of the pituitary gland?
Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary) and neurohypophysis (posterior pituitary).
What hormones are produced by the anterior pituitary?
ACTH, TSH, FSH, LH, GH, and PRL.
What hormones are stored and released by the posterior pituitary?
Oxytocin and vasopressin.
What is Cushing's disease?
A condition caused by increased ACTH production due to a tumor on the pituitary, leading to increased cortisol production.
