lecture 13 lab med exam 3
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Send the patient home with supportive care
A 34-year-old male with no known past medical history presents to the clinic with 4 days of sore throat, cough, runny nose, and hoarseness. His wife has similar symptoms which began a few days before his. His symptoms came on gradually. He denies fever, shortness of breath, skin rash, or chest pain. On exam, you note erythema in the posterior pharynx without evident exudate. There is no notable lymphadenopathy. He is afebrile and his vitals are stable. He is breathing comfortably. Which of the following is the appropriate next step in management?
Obtain a rapid strep test in the office
A 34-year-old male with no known past medical history presents to the clinic with 2 days of sore throat. His symptoms began acutely and he notes as associated fever (Tmax at home 101.5F). He feels like his entire neck is swollen and tender. He denies chest pain, shortness of breath, dysphagia, stiff neck, and cough. On exam, you note pharyngeal erythema with visible tonsillar exudate as well as significant posterior cervical lymphadenopathy. He is noted to have a fever of 38.5C in office but his vitals are otherwise stable. He is breathing comfortably on exam. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Transport patient to the emergency room
A 34-year-old male with no known past medical history presents to the clinic with 2 days of sore throat. He says the pain is severe and isolated to the left side of his throat. He has also noted a fever and cough and describes some "trouble breathing". Upon exam, you note that he is speaking in a muffled voice and drooling copiously. Inspection of the oropharynx reveals a uvula that is deviating to right and left sided tonsillar bulging. He is febrile to 39C, HR= 125, RR=20, BP 135/95, O2 89% on RA.
group A beta hemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis
what is the most common bacterial pharyngitis
acute onset sore throat and anterior cervical lymphadenopathy
what are some key symptoms of group A beta hemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis
- post strep glomerulonephritis
- rheumatic heart disease
what are complications of group A beta hemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis
- acute onset
- upper respiratory symptoms typically absent
- tonsillar exudates
- cervical lymphadenopathy
features that suggest streptococcal pharyngitis
rapid antigen detection test
which is a high specificity moderate high sensitivity thats available in office for group A beta hemolytic streptococcus pharyngitis
do further testing
if they are a high risk patient and rapid antigen detection test comes back negative what should you
throat culture
Higher sensitivity/specificity compared to RADT but longer turn-around time
strep NAAT
•Highest sensitivity, moderate specificity (false-positives) but not always available
throat culture or NAAT
due to the RADT giving false negatives, if you are still suspicious of them having group A beta hemolytic strep what should you order
- pt at higher risk of complications from GAS
- pts with contact in a high risk populations (immunocomprimised)
- young adults in dorms
- if in an area with endemic rheumatic heart fever
- if clinical suspicsion of GAS is high
if RADT is negative you should always do a throat culture or NAAT in patients if they have the following
The patient should be tested for strep with either a throat culture or rapid strep test and treated if positive
An 18-year-old male with a past medical history of anxiety presents to the clinic for evaluation of a sore throat. He reports an acute onset of symptoms around 3 days ago. He has had a runny nose and congestion but no cough or fever. On exam you note tonsillar exudates and an erythematous posterior pharynx but no lymphadenopathy. Which of the following is true?
- absence of a cough
- anterior cervical
- fever
- tonsillar exudates
- age
which are 1 point for the center criteria
0
A 46-year-old female presents to the clinic for evaluation of sore throat. Her symptoms began gradually around 6 days ago. She denies cough and fever. She is afebrile and her vitals are stable. On physical exam, you note mild erythema of the posterior pharynx, and no lymphadenopathy is present. Physical exam otherwise unremarkable. What is her Centor Score?
Conservative care; no testing or antibiotics
A 46-year-old female presents to the clinic for evaluation of sore throat. Her symptoms began gradually around 6 days ago. She denies cough and fever. She is afebrile and her vitals are stable. On physical exam, you note mild erythema of the posterior pharynx, and no lymphadenopathy is present. Physical exam otherwise unremarkable. How do you treat this patient?
lxodes scapularis
what is the tick that lymes disease is due to
walking in the woods in the spring or summer
when would you be at highest risk for getting lymes disease
24 hours
how long must the tick be feeding for it to transmit to us
Borrelia burgdorferi
what is the gram negative spirochete that causes lymes disease
bulls eye lesions (erythema migrans)
what is the clinical presentation of early localized disease from lymes disease
<30 days
what is the time frame to be considered early localized disease in lymes disease
- carditis (AV block)
- cranial nerve palsy (CN VII)
- disseminated rash
what are some side effects from early disseminated disease
days to weeks from bites
what is the time frame to be considered early disseminated disease
- arthritis
- neurological symptoms
what are symptoms from late disseminated disease
months to years from the bite
what is the time frame to be considered late disseminated disease
Early Localized Lyme Disease
what stage of lymes disease is this

early disseminated disease
what stage of lymes disease is this
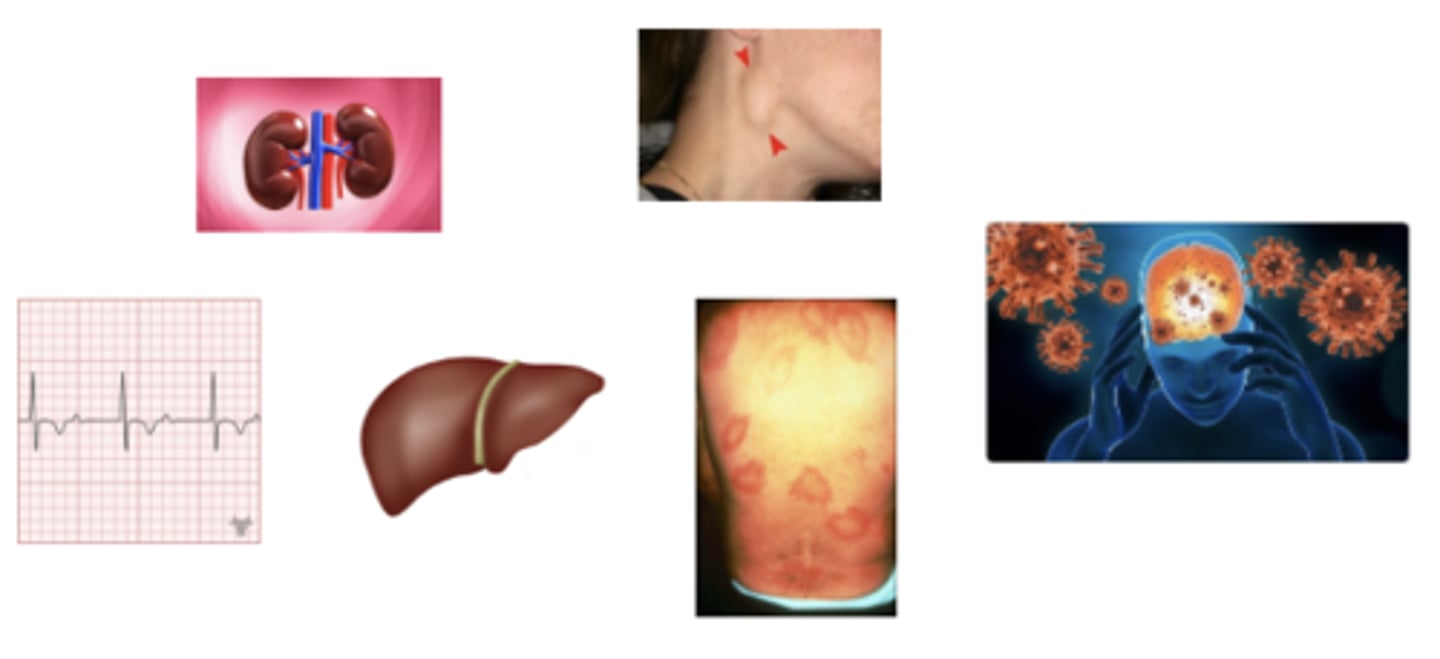
late disseminated disease
what stage of lymes disease is this
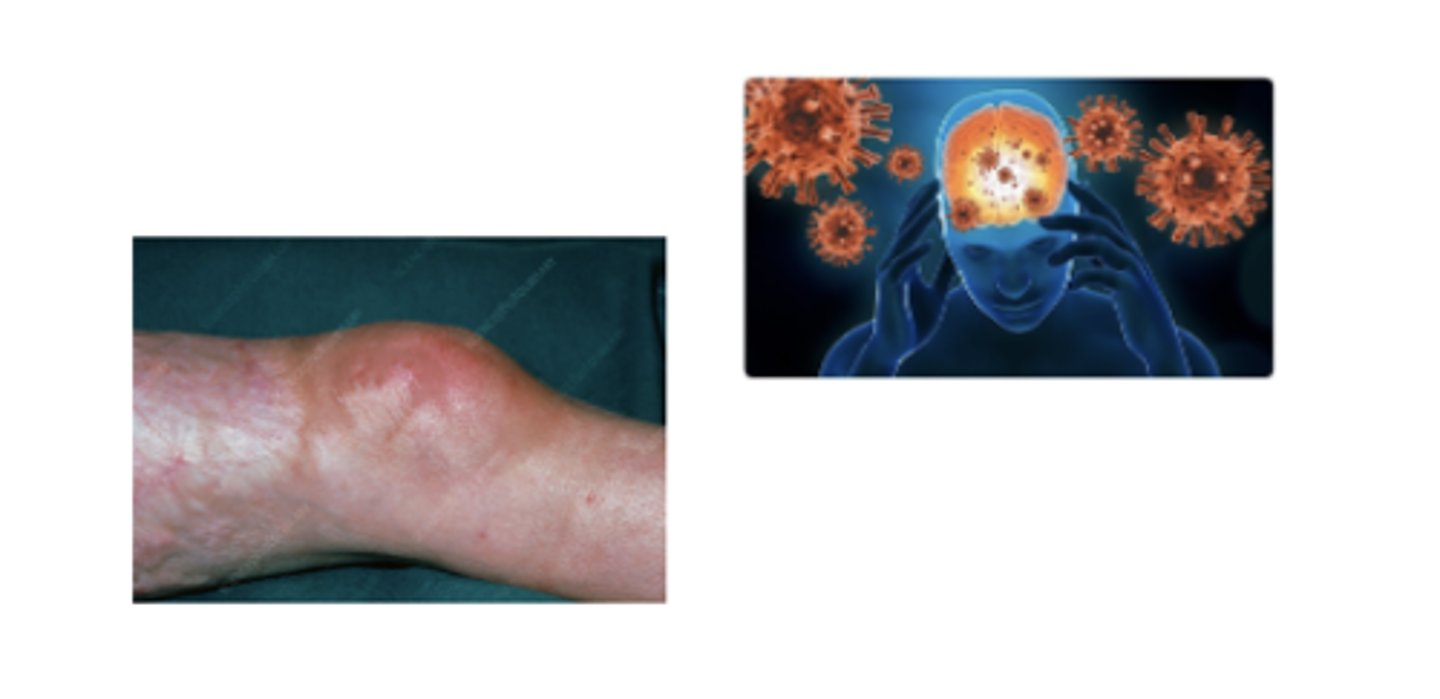
clinical
what is the diagnosis for early localized lyme disease
frequent false negatives
why are seroligies not recomomned for early localized lyme disease
ELISA and western blot for confirmation
how can you diagnose early disseminated or late lymes disease
detects antibodies to B burgoderderi
what can the ELISA testing tell you for lymes disease
its a confirmatory test used after the ELISA that detects the specific components f B burgoderderi
what can the western blot testing tell you for lymes disease
The patient should be treated empirically with an antibiotic that covers spirochete infection
A 38-year-old female presents to the clinic for evaluation of a rash. She noted a rash on her right calf that started 8 days ago. She has been applying OTC antifungal cream with no response. On physical exam you note a bulls-eye lesion on her right calf (pictured below) but is otherwise unremarkable. She reports having been camping in Vermont 2 weeks ago. She denies fatigue, headache, myalgia, chest pain, shortness of breath, vision changes, weakness. An ECG, CBC, and CMP are all unremarkable. Which of the following is true?
The patient should be tested for Lyme Disease initially with ELISA testing
A 28-year-old male presents to the clinic for evaluation facial paralysis. He states that around 6 weeks ago he noticed a rash on his back but didn't think anything of it as it resolved after a week or two. However, a few weeks later he began to feel profound fatigue as well as muscle aches and occasionally can feel an irregular heart beat. This morning, he noticed that the left side of his face was "drooping" and he couldn't form an even smile. He is an avid rock-climber and often spends time outdoors in Western North Carolina. He denies smoking or IVDU. On exam, you note left-sided facial drooping but otherwise his exam is unremarkable. An ECG is as below. Which of the following is true?
H pylori
Bacteria which infects/colonizes the gastric mucosa and causes chronic inflammation
H. pylori
what bug is the most common cause of peptic ulcer disease
gastric ulcer cancer and lymphoma
what does H pylori increase your risk of
usually asymptomatic
what are the symptoms of H pylori
antibiotics and confirm complete eradication
what is the treatment for H pylori
endoscopy with biopsy of H pylori
what is the gold standard to diagnose nonerosive gastrictis H pylori
endoscopy with biopsy urease test
what is the second line diagnostic study for nonerosive gastrictis H pylori besdies
endoscopy with biopsy urease test
which diagnostic study for H pylori IS affected by ppi use
endoscopy with biopsy urease test
which diagnostic study for H pylori has more frequent false negatives
urea breath test
what is the most commonly used diagnostic study for H pylori
urea breath test
this test can tell when H. pylori converts urea into labeled carbon dioxide and is affected by recent AB use
serologic antibodies
this diagnostic study for H pylori does not distinguish active vs past infection and cant be used to check eradication
stool antigen test
Can confirm active infection and eradication after bx for H pylori
- All tests are fairly sensitive and specific ASIDE from serologic testing
- For tests affected by PPI, PPI should be discontinued 1-2 weeks prior to testing
- If there are “other” indications for EGD, perform EGD + biopsy for histology vs. EGD + urease
- If no indications for EGD, r/o H. Pylori with breath test or stool antigen
what are the rules for H pylori testing
if the patient is high risk
when should you use an EDG instead of stool or breath testing for H pylori
Clostridiodes difficile Infection
Toxin producing bacteria that colonizes the healthy GI tract AND causes antibiotic-associated colitis.
antibiotic therapy
what is a common cause of C diff
- Non-toxigenic forms of C. Diff can colonize the GI tract
- These strains do not produce toxin an do not cause disease
what is the cause of diagnosis and managment complications for C diff
EIA for GDH antigen
Detects GDH antigen found of C. diff cell surface and is Not a toxigenic strain specific
EIA for toxins A and B
diagnostic stool test that detects toxins A and B and is toxigenic strain specific
C diff NAAT/PCR
diagnostic stool test for c diff that is toxigenic strain specific and is sensitive but also detects asymptomatic carriers (false positive)
must only test those with greater than 3 liquid stools in 24 hours
what is the rule of testing C diff NAAT/PCR
when there is an acute onset with clinical significant diarhea
when should you test for C diff
test GDH and Toxin A/B then further test it with NAAT
what is the first step for stool testing for C diff
Perform NAAT to further diagnose
A 47-year-old female presents with 6 days of watery diarrhea. She reports 6 bowel movements a day and even wakes up at night to have a bowel movement. She notes crampy LLQ abdominal pain. She denies hematochezia, melena, fever, nausea, vomiting. She takes no OTC medications or supplements. No sick contacts. No recent travel. She took clindamycin for a dental abscess 10 days ago but otherwise has been healthy. She is afebrile and hemodynamically stable. You obtain a GDH antigen and Toxin A and B test. GDH antigen is positive but Toxin A and B are negative. Which of the following is the best next step in her management?
+1
how many points do you get for center criteria if you are less than 15
-1
how many points do you get for center criteria if you are older than 45