chemistry: covalent bonds
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
covalent bond
A chemical bond in which electrons are shared between atoms
covalent vs ionic bonds
An ionic bond is formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another while a covalent bond forms when electrons are shared between atoms.
molecule
A group of atoms bonded together
what is the difference of electronegativity between covalent and ionic bonds
A covalent bond has an electronegativity difference of less than 2.0, whereas an ionic bond has an EN difference of 2.0 or greater.
what elements are involved in a covalent bond?
two non-metals
what elements are involved in a ionic bond?
metal and nonmetal
what are the seven diatomic elements?
hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine
What do the prefixes (mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta, octa, nona, deca) mean?
One, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten
what are the prefixes used for?
They are used to indicate the number of atoms in molecules
What is the molecular formula for Ammonia
NH3
what are the water and carbon dioxide molecular formula
H2O and CO2
What are the molecular formulas for carbon monoxide, carbon tetrafluoride, and dihydrogen monosulfide?
CO, CF4, and H2S
How do the properties of molecular compounds differ from those of ionic compounds?
-Molecular compounds usually have low melting and boiling points
-ionic compounds have high MP and BP
-Molecular compounds usually do not conduct electricity when dissolved in water
-whereas ionic compounds do, and molecular compounds can be solid, liquid, or gas at room temp
-Ionic compounds are all solid at room temp
what is the exception to molecular compound properties?
network solids, which are molecular substances with very high MP and BP
What is the octet rule?
Many atoms tend to lose, gain, or share electrons in order to achieve the electron configuration of a noble gas. (Usually this means 8 valence electrons).
How many valence electrons does an atom from Group 13 have? How about Group 14? Group 15? Group 16? Group 17? Group 18?
3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8
How many electrons are shared in a single bond? A double bond? A triple bond?
2, 4, and 6
What is a Lewis structure (aka electron dot structure)?
A drawing showing the valence electrons in a molecule. Shared pairs (aka bonds) are usually shown as lines. Lone pairs (aka nonbonding pairs) of electrons are shown as dots.
What is a structural formula?
A Lewis structure that doesn't show dots. Just lines.
What is an unshared pair (aka lone pair)?
A pair of valence electrons that is not part of a covalent bond.
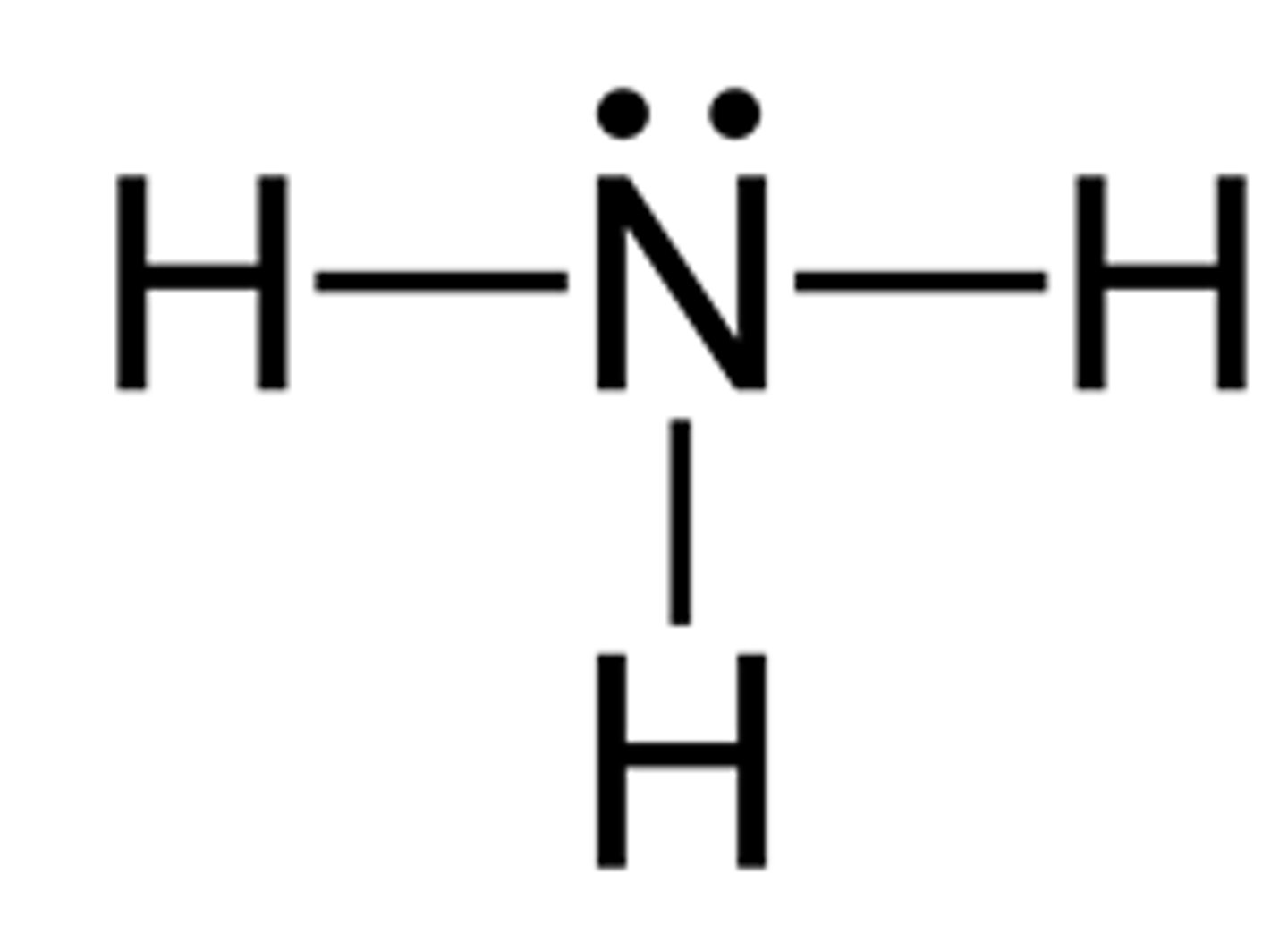
draw a lewis structure for ammonia
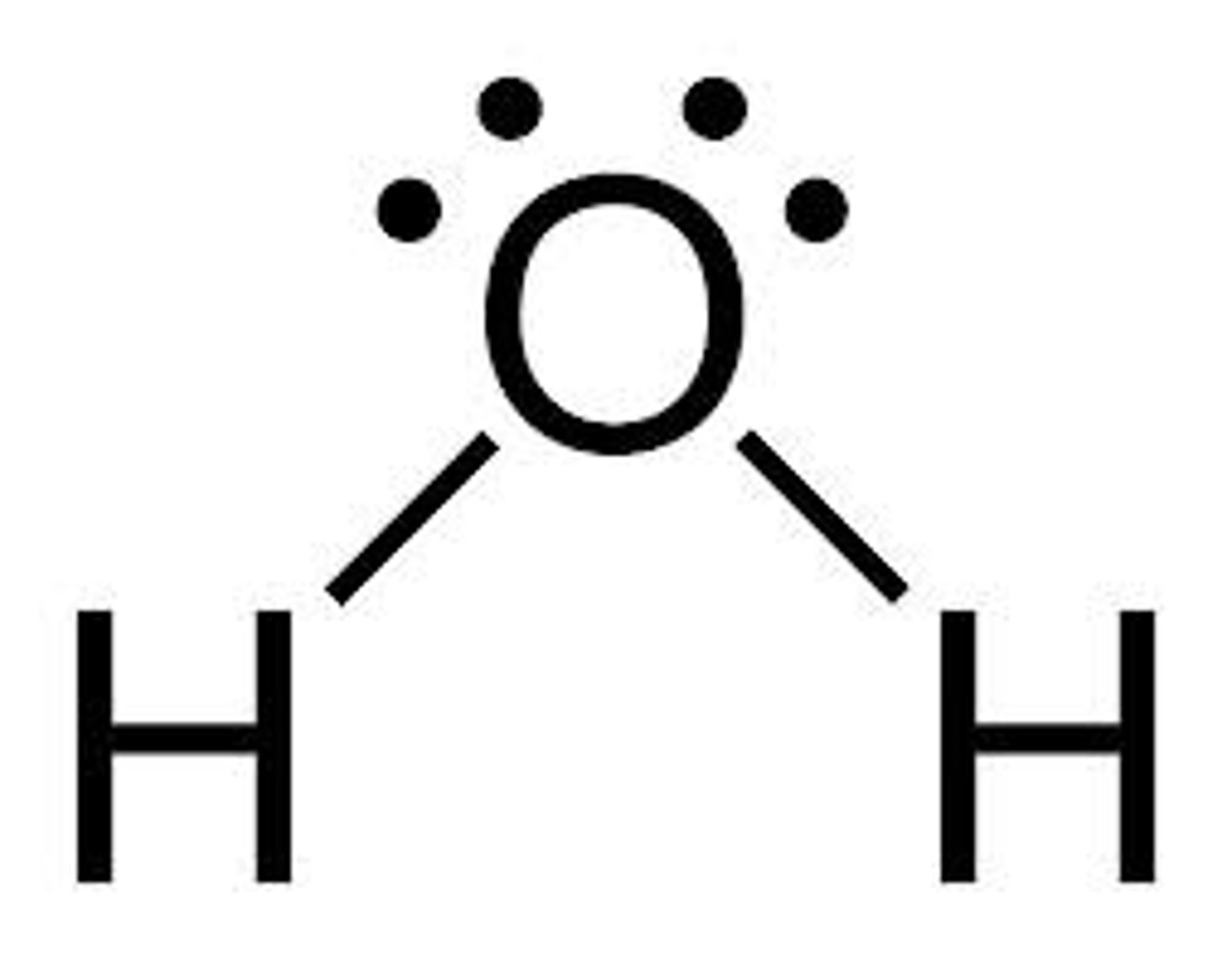
draw a lewis structure for water
draw a lewis structure for chlorine

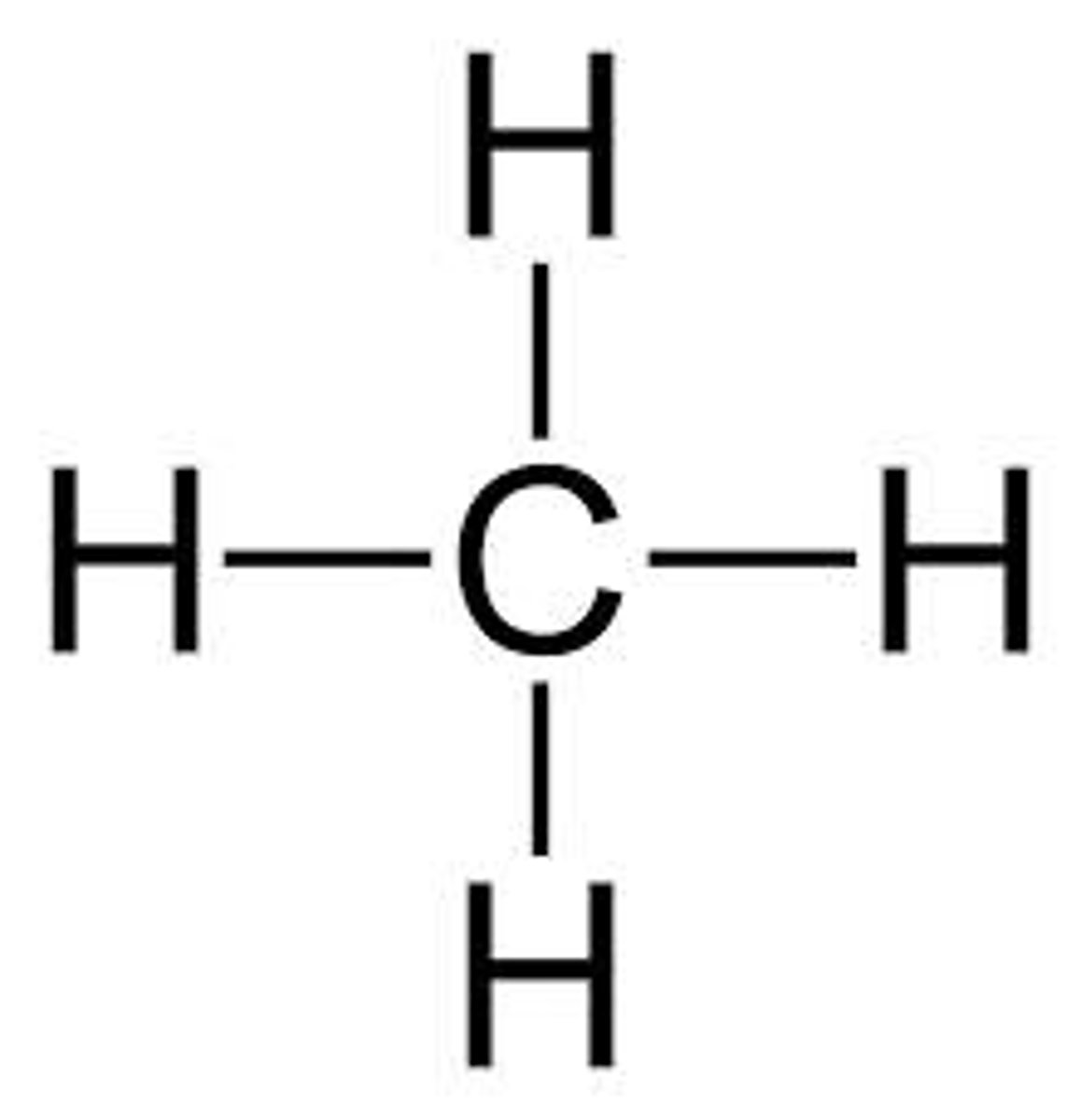
draw a lewis structure for methane (CH4)
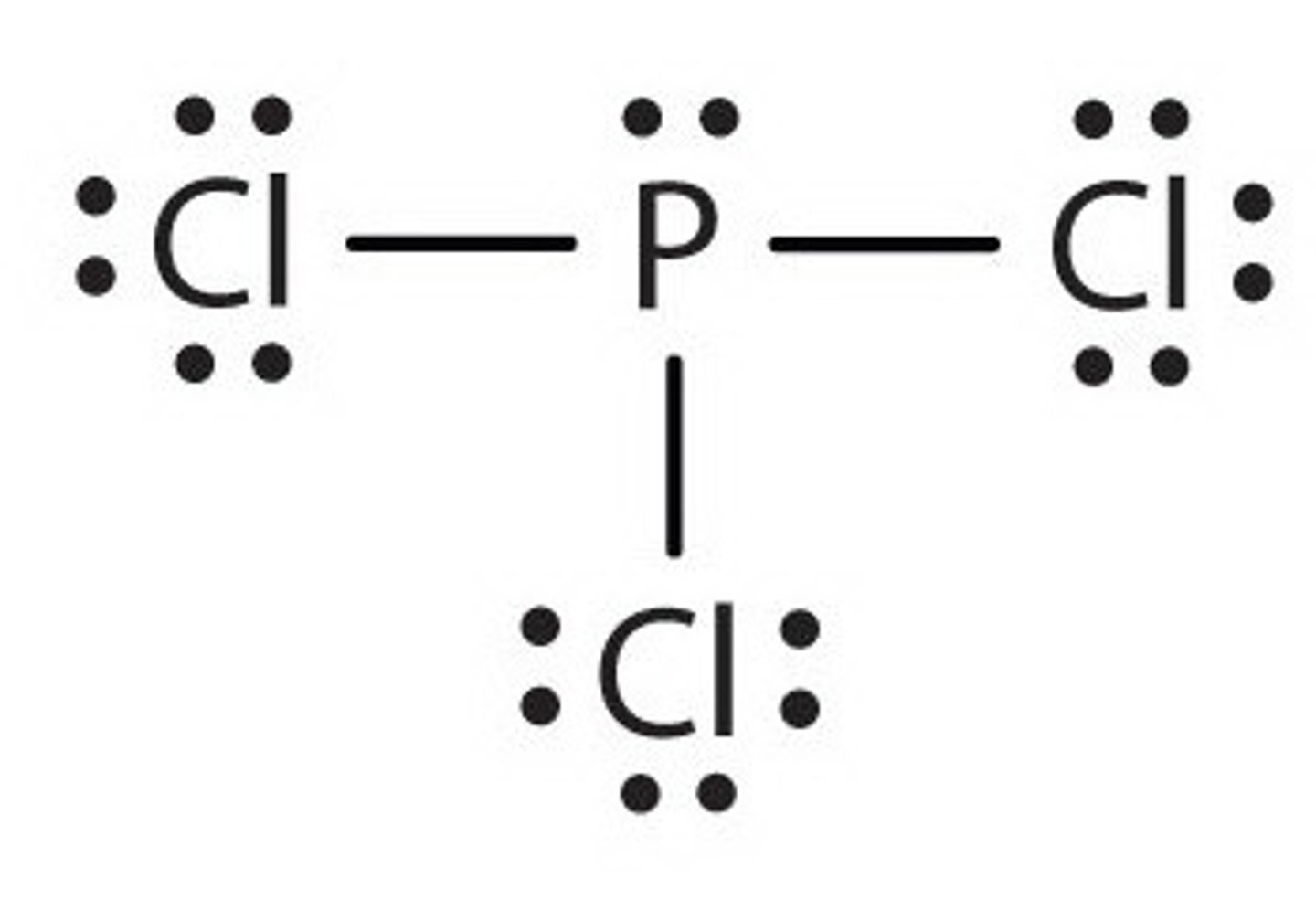
draw a lewis structure for phosphorus trichloride (PCl3)
How many bonds does each of these elements like to form: Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Carbon, Oxygen, and Halogens
1, 3, 4, 2, 1
Which of the following molecules has a triple bond?: I2,O2,N2
H2
N2
What is a coordinate covalent bond? How is it drawn?
A pair of shared electrons that comes from one atom. In other words, one atom donates both electrons to form the bond, rather than each atom donating one electron.
What are resonance structures? How are they drawn?
Resonance structures are multiple valid Lewis structures that can be drawn for the same molecule. A double-headed arrow is used to show resonance structures
Which of the following has a coordinate covalent bond?: N2, CO2, CO, NH3
CO
If a molecule has an odd number of valence electrons, what does that tell us about its Lewis structure?
One of its atoms will have an unpaired electron. In other words, the octet rule must be violated.
What is bond energy?
amount of energy required to break a bond
Which type of bond is strongest: single, double, or triple?
triple
Common shapes for molecules
Linear, tetrahedral, trigonal planar, trigonal pyramidal, bent
Tetrahedral shape conditions
Central atom bonded to two other atoms, no lone pairs
Linear shape conditions
Central atom bonded to two other atoms, no lone pairs
Trigonal planar shape conditions
Central atom bonded to three other atoms, no lone pairs
Trigonal pyramidal shape conditions
Central atom bonded to three other atoms, with a lone pair
Bent shape conditions
Central atom bonded to two other atoms, with one or two lone pairs
VSEPR
Valence shell electron pair repulsion
Explanation of VSEPR theory
Pairs of valence electrons repel each other. This is true whether the pairs are bonding or nonbonding. Because of the repulsion, the electron pairs will arrange themselves on opposite sides of the atom, forming symmetrical shapes.
Trigonal planar central atom condition
False. If it has a lone pair, it will be trigonal pyramidal.
Effect of molecular shape on properties
Absolutely true!
Polar Bond
Electrons shared unequally between atoms.
Electronegativity
Atom's tendency to attract electrons.
Tug of War Analogy
Atoms pull on shared electrons, affecting polarity.
Partial Charges
Unequal electron sharing creates positive and negative regions.
Van der Waals Forces
Includes dipole-dipole interactions and dispersion forces.
Dispersion Forces
Intermolecular forces present in all molecules.
Dipole-Dipole Interactions
Attraction between partially positive and negative poles.
Hydrogen Bonds
Strongest intermolecular force, 5% strength of covalent bonds.
Intermolecular Forces
Determine states of matter and molecular shapes.
Molecular State Variation
Different states due to varying dispersion forces.
Network Solid
Giant molecule with all atoms covalently bonded.
Carbon Tetrafluoride
Nonpolar due to symmetrical tetrahedral shape.
Electronegativity Difference
Greater than 0.4 indicates a polar bond.
Lewis Structure
Diagram showing electron arrangement in molecules.
Molecule Polarity
Not always polar despite having polar bonds.
Strength of Dispersion Forces
Increases with the number of electrons.
Diatomic Molecules
Two atoms bonded, affecting physical states.
Sigma bond
Symmetrical molecular orbital around atomic nuclei axis.
Pi bond
Molecular orbital from side-by-side p orbital overlap.
Orbital hybridization
Mixing atomic orbitals to form equivalent hybrids.
sp hybrid orbitals
Formed from one s and one p orbital mixing.
sp2 hybrid orbitals
Formed from one s and two p orbitals mixing.
sp3 hybrid orbitals
Formed from one s and three p orbitals mixing.
Linear shape
Shape created by two sp hybrid orbitals.
Trigonal planar shape
Shape created by three sp2 hybrid orbitals.
Tetrahedral shape
Shape created by four sp3 hybrid orbitals.
Strength comparison
Sigma bonds are stronger than pi bonds.
Length comparison
sp hybrid orbitals are longer than p orbitals.
network solids
solids in which all of the atoms are covalently bonded to each other