Lesson 2: Body Structures & Organ Systems
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
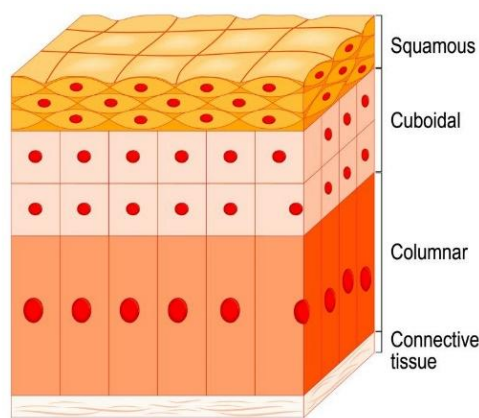
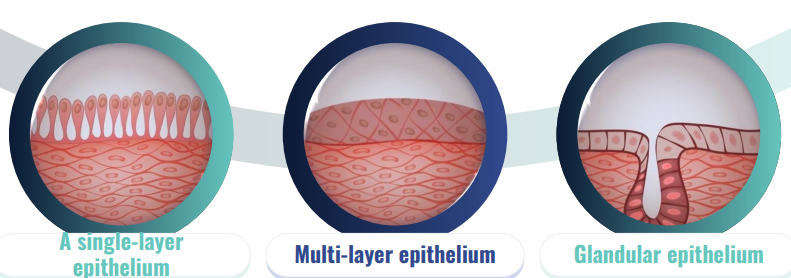
Epithelial Tissue
covers external body surfaces & lines internal body cavities, forming barriers & glands & playing roles in absorption & secretion
can be single, multi layer, or glandular
epithelial gland types
endocrine gland
exocrine gland
sweet gland


Connective Tissue
supports, protects, & binds organs to hold organs in place in their body cavities
includes cartilage, blood, bone, adipose tissue
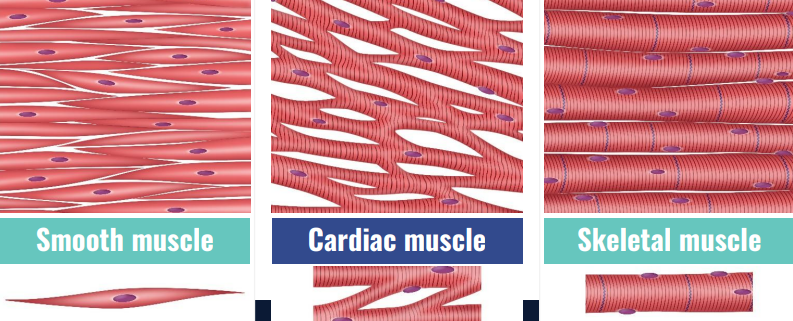
Muscle Tissue
contracts to allow body to move
includes skeletal, cardiac, & smooth muscles
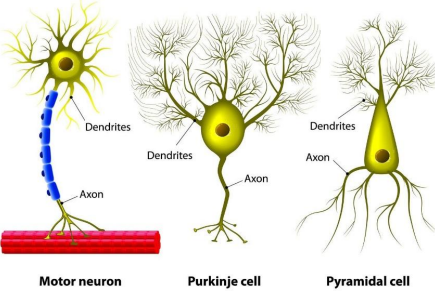
Nervous Tissue
composes brain, spinal cord, nerves
carries messages throughout the body to direct its activities
Anatomy
study of body structure
Physiology
study of body function
Pathology
study of disease
Level of Organization
chemicals > molecules > cells > tissues > organs > organ systems > organism
Which body systems are involved in protection, support, & movement?
Integumentary, Skeletal, Muscular
Which body systems are involved in coordination & control?
Nervous, Endocrine
Which body systems are involved in circulation & immunity?
Cardiovascular, Lymphatic
Which body systems are involved in energy supply & fluid balance?
Respiratory, Digestive, Urinary
Which body systems are involved in production of offspring?
Reproductive
Integumentary System
skin and associated structures (oil glands, sweat glands, hair, nails)
protection, sensory perception, temperature regulation
Skeletal System
bones & joints
support, protection, movement
Muscular System
skeletal muscles
movement, support, protection, heat generation
Nervous System
brain, spinal cord, nerves
sensory perception, coordination & control of responses, memory, language skills, reasoning
Endocrine System
endocrine glands
secretion of hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, behavior, reproduction
Cardiovascular System
heart & blood vessels
supply of oxygen & nutrients to tissues, removal of metabolic waste
Lymphatic System
lymphatic vessels & nodes
aid in circulation, immunity, & transport of digested fats
Respiratory System
lungs & breathing passages
ventilation of lungs & exchanges of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body & the atmosphere
Digestive System
digestive organs from mouth to anus, including esophagus, stomach, intestine; accessory organs (salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas)
food intake, breakdown of good into usable nutrients, absorption of nutrients into the circulation, & elimination of undigested waste
Urinary System
kidneys and organs that transport and store urine: ureters, bladder, urethra
elimination of soluble waste materials and water
Reproductive System
sex glands (ovaries, testes) and organs associated with transport of germ cells (eggs, sperm) and gestation (uterus)
production of offspring
Aging Effects
Gradual changes occur in all body system
Some changes are harmless (wrinkles & gray hair)
Some changes may result in injury and disease
Decreased kidney function
Loss of bone mass
Formation of deposits within blood vessels
Homeostasis
Body’s maintenance of internal balance
Regulated variables must be kept with a narrow range
Body temperature
Volume and composition of body fluids
Blood levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Blood pressure
Negative Feedback
keeps body conditions within a normal range by reversing any upward or downward shift
components of a negative feedback loop are sensor, control center and effector
Sensor measures the level of the variable
Control center compares sensor inputs with set point
Effector increases or decreases activity to alter the level of the regulated variable.
Signals carry information between the components.
Barriers
Maintain distinct environments.
Plasma membrane separates the intracellular and extracellular fluids.
Skin/mucous membranes separate the inside of the body from the outside.
Flow
The movement of a substance from one area to another
Examples: blood flow, diffusion, air flow
Gradient
A difference in a specific physical or chemical value between two areas
Examples: pressure, temperature, concentration
Resistance
Factors that inhibit flow down a gradient
Examples: barriers, friction
Standard Anatomical Position
standardized posture used as a reference point in the medical and anatomical sciences to describe the locations and relationships of body parts to each other. In this position, the body stands upright and faces forward
feet: slightly apart & flat on ground, pointing forward
arms: positioned at sides w/ palms facing forward, placing thumbs outward
head & eyes: facing forward, maintaining level gaze
torso: upright & facing forward, aligning w/ head & lower limbs
ensures clarity and consistency across various medical fields
eliminates ambiguity in the description of body parts, making it easier for professionals to communicate about physical examinations, surgical procedures, and anatomical analysis
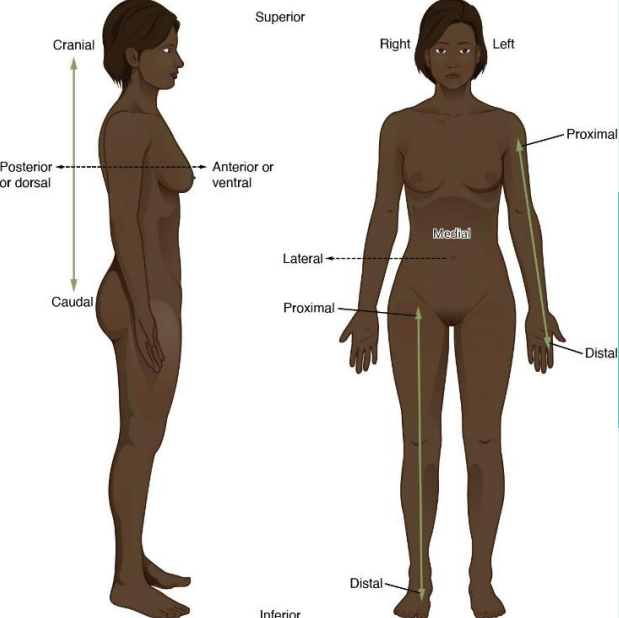
Directional Terms
used to describe the locations of structures in relation to each other
Superior (Cranal)
body part located above or toward the head end of the body
ex: chest is superior to the abdomen
Inferior (Caudal)
opposite to superior, refers to a body part that is below or toward the feet
ex: stomach is inferior to the chest
Anterior (Ventral)
refers to the front or forward part of the organism
for a human in the standard anatomical position, the chest is on the anterior side
Posterior (Dorsal)
describes the back or direction toward the back of the body
ex: spine is posterior to the chest
Medial
something is closer to the midline or median plane of the body, which divides the body into left and right halves
ex: heart is medial to the lungs
Lateral
opposite of medial, away from the midline of the body
ex: arms are lateral to the chest
Proximal
used in reference to the limbs and denotes a position in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or the trunk of the body
ex: elbow is proximal to the wrist
Distal
Opposite of proximal, further from the point of attachment or further from the trunk
ex: fingers are distal to the elbow
Superficial (External)
position closer to or on the surface of the body
ex: skin is superficial to the muscles
Deep (Internal)
something that is more internal or closer to the core of the body than another structure
ex: lungs are deep to the rib cage
Central
denote the center of the body or a body part
ex: central nervous system refers to the brain and spinal cord which are central to the body’s functions
Peripheral
occurring or located away from the center
often refers to the nerves and blood vessels that are not central
Ipsilateral
structures occurring on the same side of the body
ex: right arm injury and a right leg injury are ipsilateral
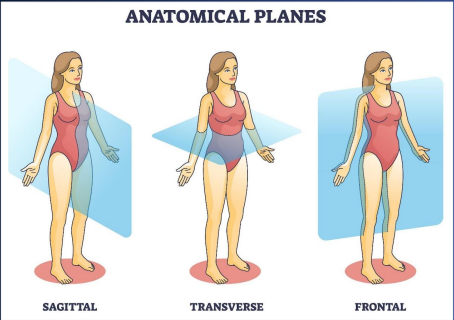
Body Planes & Sections
imaginary lines drawn through the human body to specify the spatial relationships of structures and to guide dissection and medical imaging
allows healthcare professionals to describe the location of injuries or diseases accurately, conduct precise medical interventions, and interpret medical images correctly
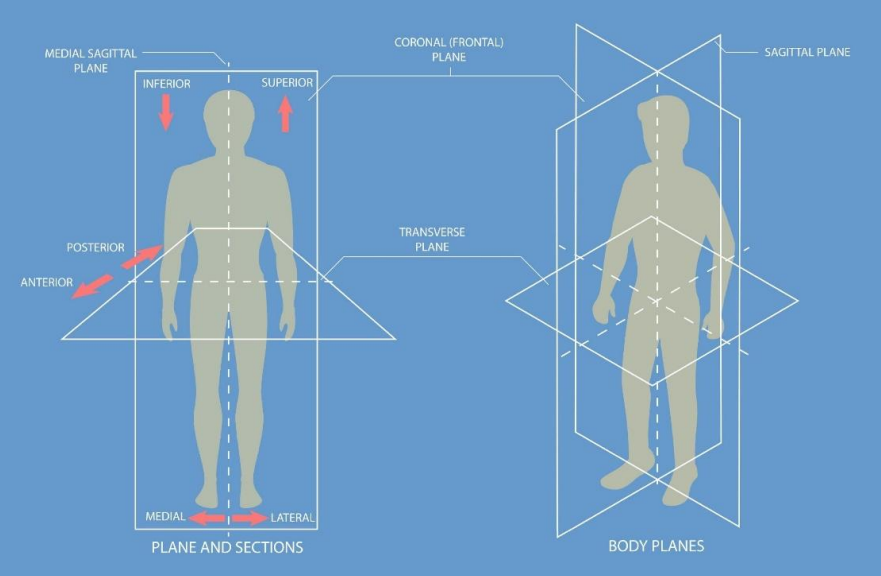
Frontal (Cronal Plane) [front & back]
runs vertically but divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) sections
runs perpendicular to the sagittal plane and parallel to the face
used to view the front and back parts of the body and is often used in both clinical and diagnostic settings, such as in X-rays or CT scans to examine the chest or abdominal cavities
Sagittal Plane [left & right]
runs vertically through the body, dividing it into right and left sections
if it divides the body into two symmetrical halves, it is called the median or midsagittal plane
any sagittal plane that does not pass through the midline and divides the body into unequal right and left sides is called a parasagittal plane
used in imaging techniques to view lateral sections of the body, such as in MRIs or during neurological examinations to assess the left and right hemispheres of the brain
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane [Up & Down]
runs horizontally from right to left, dividing the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) parts
perpendicular to both the sagittal and frontal planes
essential in cross-sectional imaging, frequently utilized in CT scans and MRI to provide a cross-section view of the body, particularly useful for examining structures in the abdomen and chest
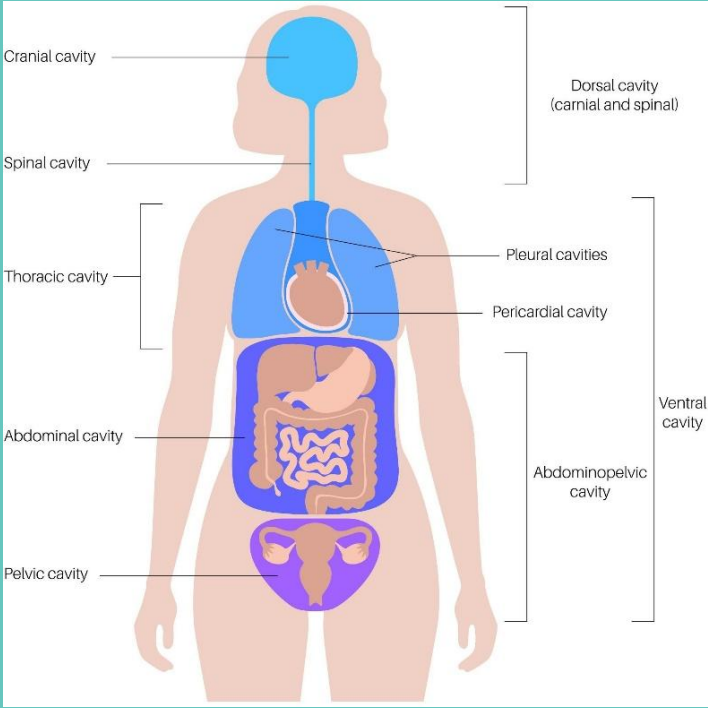
Body Cavities
body is organized into major compartments that help protect internal organs and allow them to function properly. These are primarily divided into the dorsal (posterior) and ventral (anterior) cavities
Dorsal Cavity
Located along the body's back, houses the brain and spinal cord within the cranial and vertebral canals, respectively, forming the central nervous system's protective enclosure
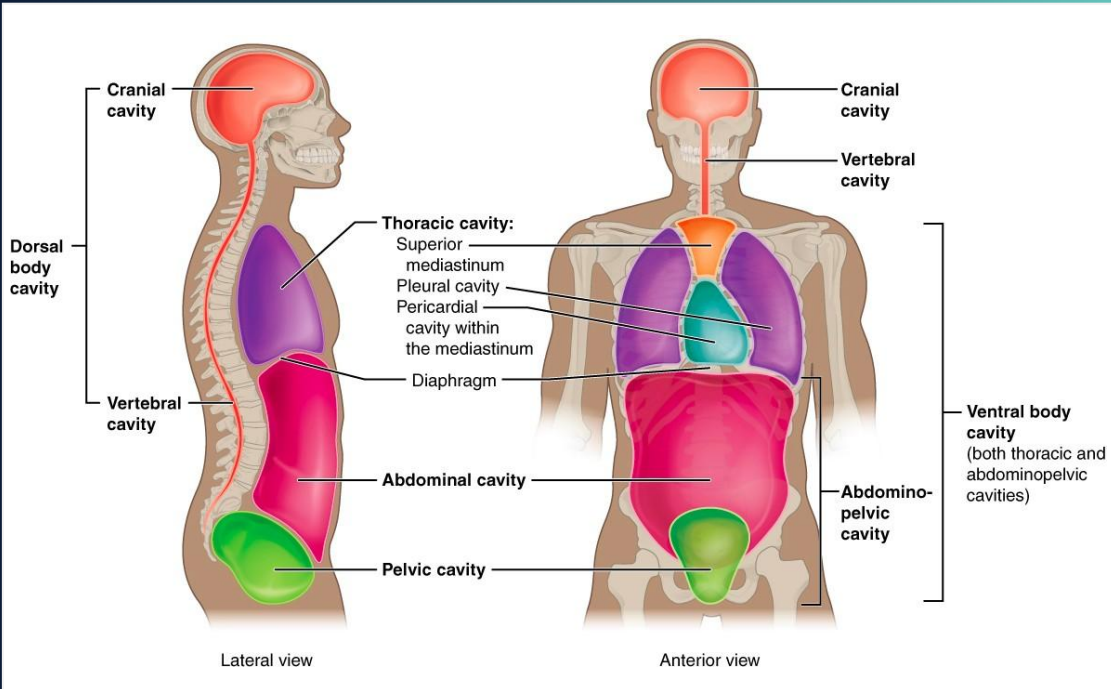
Ventral Cavity
situated at the front, the ventral cavity includes the thoracic cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity
provides a flexible space that accommodates the expansion and contraction of organs
crucial for organ protection and function, enabling organs like the heart, lungs, and stomach to operate without impacting each other or surrounding tissues
structural organization is fundamental for understanding how the body functions in health and in medical treatments
Thoracic Cavity
Contains the heart and lungs, protected by the ribcage yet flexible enough to allow for breathing and heartbeats
Abdominopelvic Cavity
encompasses the abdominal and pelvic areas, housing organs like the stomach, intestines, liver, bladder, and some reproductive organs
supports digestive, excretory, & reproductive functions by allowing organs to change size and shape during their activities
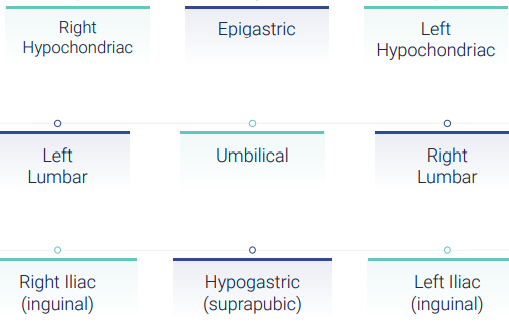
9 Abdominal Cavity Regions
subdividing the abdominopelvic cavity using two horizontal and two vertical lines
horizontal lines: upper horizontal line (subcostal line) is drawn just below the ribs, and the lower horizontal line (transtubercular line) is drawn just above the pelvis
vertical lines: lines drop vertically from the midpoint of each clavicle (collarbone), typically aligning with the nipples in a forward-facing individual
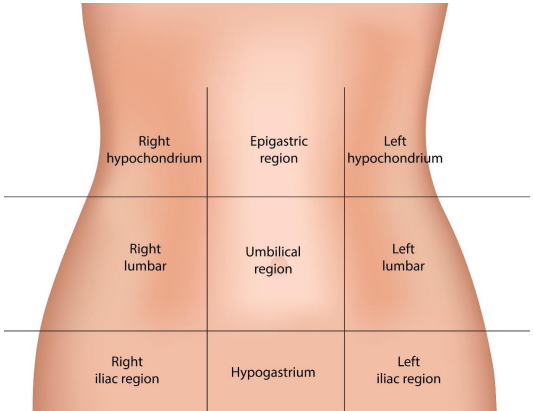
4 Abdominal Cavity Quadrants
useful in emergency settings or initial evaluations, where a quick determination of the location of pain, discomfort, or other symptoms is necessary
single vertical line and a single horizontal line intersect at the umbilicus (navel), dividing the abdomen into four quadrants
left upper quadrant (LUQ)
right upper quadrant (RUQ)
left lower quadrant (LLQ)
right lower quadrant (RLQ)
Oblique Plane
planes pass through the body at an angle
not parallel to the standard sagittal, coronal, or transverse planes
particularly useful in surgical procedures or imaging techniques that require a more specific angle to better view or treat a particular area
each plane offers a unique perspective and is chosen based on the specific diagnostic or therapeutic needs of the medical situation
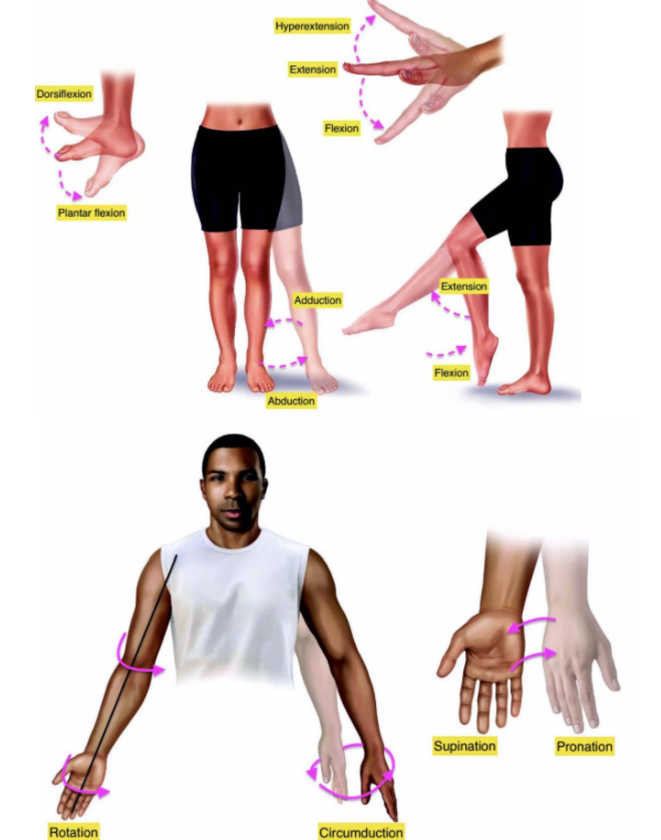
Anatomical Body Movements
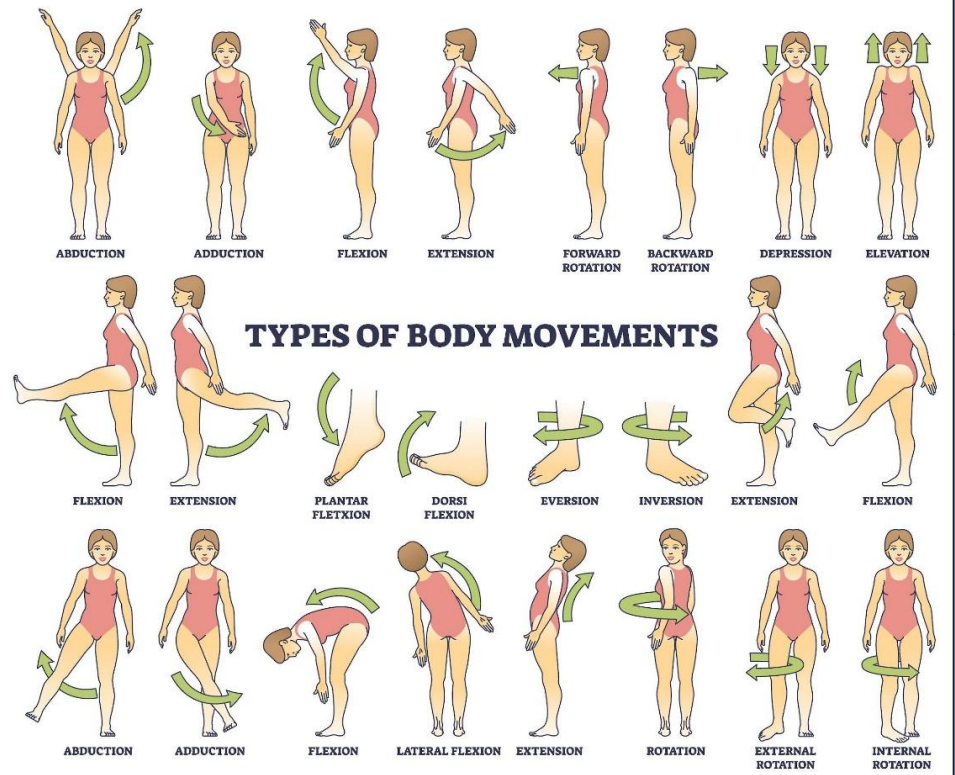
Flexion
Bending a body part or decreasing the angle of a joint
Straightening a body part or increasing the angle of a joint
Hyperextension
Extending a body part past the normal anatomical position
Dorsiflexion
Pointing the toes up
Plantar Flexion
Pointing the toes down
Abduction
Moving a body part away from the midline of the body
Adduction
Moving a body part toward the midline of the body
Rotation
Twisting a body part—for example, turning your head from side to side
Circumduction
Moving a body part in a circle—for example, moving your arm in a circular motion
Pronation
Turning the palm of the hand down or lying face down
Supination
Turning the palm of the hand up or lying face-up
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot medially
Eversion
Turning the sole of the foot laterally
Retraction
Moving a body part posteriorly
Protraction
Moving a body part anteriorly
oste/o
bone
myo
muscle
neur
nerve
derm
skin
cardi/o
heart
vasc/o
veins & arteries
hem/o or sangu
blood
angi/o
blood vessels
ven/o or phleb/o
veins
aort
aorta
cardi/o
arteri/o
arteries
enceph
brain
rhino
nose
myringo or tymphan
eardrum
odont or dento
tooth
crani
skull
opthalm or oculo
eye
oto
ear
lingu
tongue
hepat/o
liver
cholecyst
gallbladder
esoph/a
esophagus
colo
large intestine
gastr/o
stomach
ileo
small intestine