Joints and microscopic anatomy of bone
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What’s another name for joints?
Articulations
3 types of Joint Types
Fibrous, Cartilaginous, and Synovial
What makes a synovial joint synovial?
It has to have articular cartilage, capsule (enclose the joint), reinforcing ligaments.
6 synovial Joints
Ball + Socket, gliding/plane, pivot, saddle, condyloid, and hinge
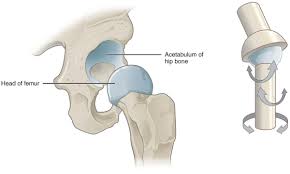
Ball and Socket
Femoral Head and Acetabulum
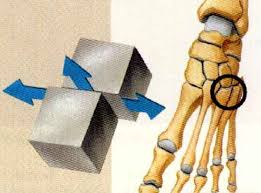
gliding/plane
between inter-carpals, inter-carpals, and the common vertebrae
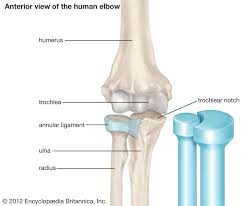
Pivot
Atlas/axis and radius on ulna
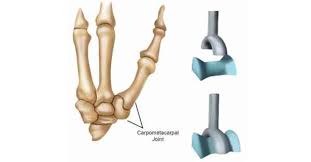
Saddle
Clavicle + Sternum, between trapezium and 1st metacarpal
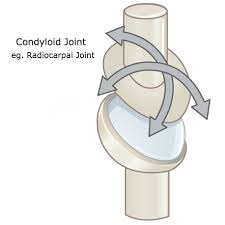
Condyloid
Metacarpals to proximal phalange, radius to Scaphoid, and occipital to atlas
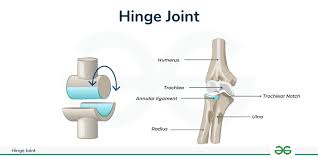
Hinge
Elbow, knee, interphalangeal, tibia to talus
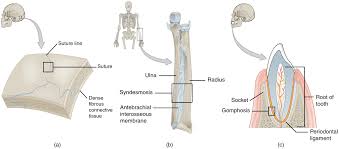
Fibrous
Sutures and teeth
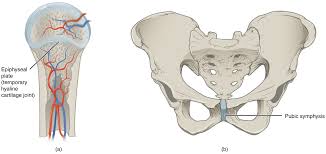
Cartilaginous
Vertebrae
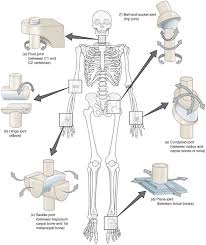
Synovial
All movable
3 types of cartilage
Hyaline, elastic, and fibocartilage
Hyaline
Ribs, synovial joints, trachea, and nose
Elastic
Ear lobes and epiglottis
Fibocartilage
Knee, vertebrae, pubis
Embryonic Skeleton
Mostly made out of cartilage (hylaine) and slowly replaced by bone through a process called endochondral ossification.
epiphyseal line
Growth plate
2 types of bone material
Compact and Spongy bone
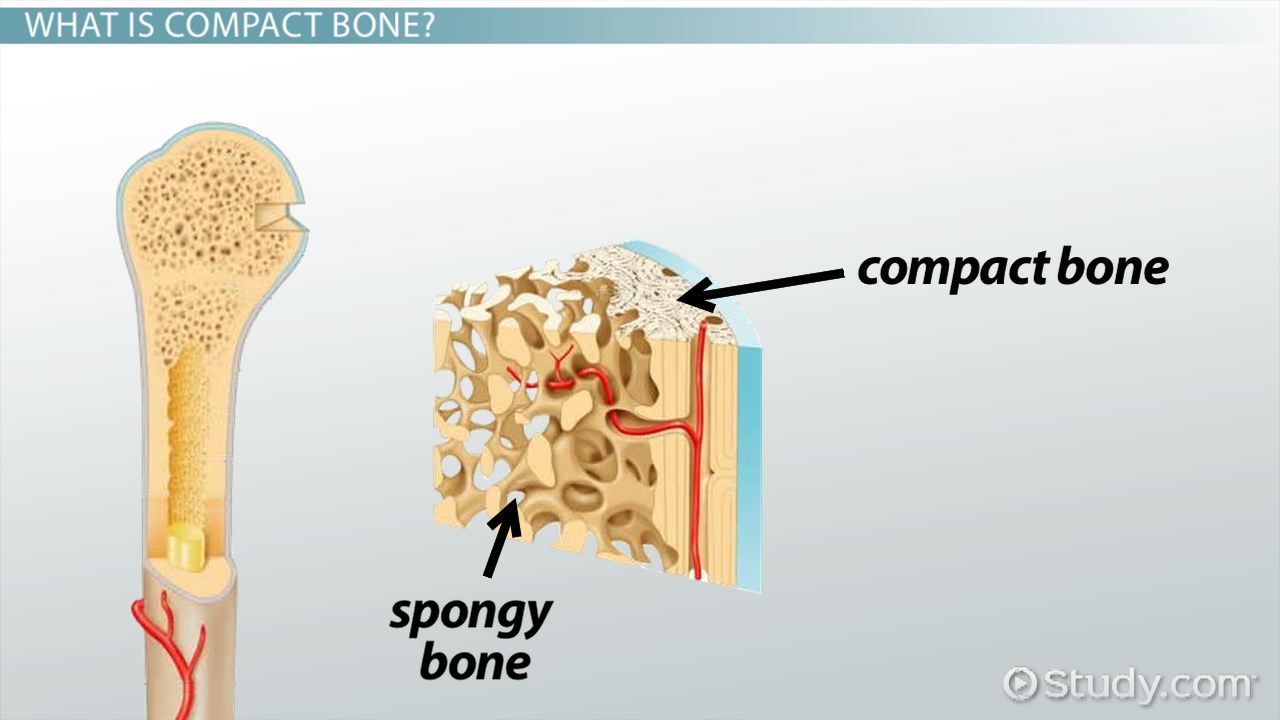
Compact
dense and strong, typically found in diaphysis
Spongy Bone
(cancellous) porous, and weaker - found in ephysis
Red Marrow
found in the epiphysis - it makes red blood cells (but makes all 3 blood cell types)
Yellow Marrow
In core diaphysis - often associated with immune cell formation
Osteoblasts
Bone builders, cells that deposit new bone material, and takes materials like calcium from the blood and put it into the bone
Osteoclasts
Breaks down bone and putting it into the blood stream
Adults
Have a balance between oblast and oclast function
Juveniles
oblast > oclast
Elderly (esp. post-menopause)
oclast > oblast
Wolff’s Law
Weight-bearing exercise simulates oblasts
Strong Bones
Vitamin D helps absorption of calcium (sunlight)
estrogen (linked directly)
To oblast function and more estrogen equals more oblast activity
4 Stages of Bone Fracture Repair
Hematoma, Soft Callus, Hard Callus, and remodeling
Hemoato
First Phase, white blood cells prevents the risks of infection
Soft Calus
Phase 2, cartilage builders form soft callus and acts as a temporary bridge
Hard Calus
Phase 3. osteoblasts is added between the fracture building the extra tissue
Remodeling
Phase 4, sends osteoblasts to break down extra tissues for the bones
Hyperparathyroidism
overactive parathyroid gland
Pagets
Accelerated turnover of bone material
Rickets
Less/no vitamin D
Craniosynostosis
Premature fusing of skull
Scoliosis
Sideways curvature of the spine
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Autoimmune Joints
Bursitis
Inflammation of bursae sac
Osteoarthritis
Bone on bone, due to cartilage wearing down
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Imperfect growing of bone, brittle bone disease
Leukemia
Cancer of bone marrow
Klippel-Feil Syndrome
Fusion of cervical vertebrae
Fibrous Dysplasia
Bone salt replaced by fibrous scar-like tissue
What regulates the calcium in your body?
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
What are the three hormones that regulate calcium?
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), Vitamin D, and Calcitonin