STRUCTURES OF BACTERIAL CELL
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
TRUE
“Eu” means
NUCLEUS
“Karyo” means
EUKARYOTES
More complex and contain a true nucleus and membrane
bound-organelles
EUKARYOTES
Algae, protozoa ,fungi ,plants ,animals
80s
Number of ribosome in eukaryotes
70s
Number of ribosomes in Prokaryotes
1-10
size of Prokaryotic cell
10-100
size of Eukaryotic cell
0.02-0.3
size of virus
BINARY FISSION
replication of prokaryotic cell
MITOSIS/ MEIOSIS
replication of Eukaryotic cell
REQUIRES A HOST
replication of virus
PEPTIDOGLYCAN
cell wall of prokaryotic cell
VARIES (PLANTS/FUNGI)
cell wall of eukaryotic cell
VIRUS
Lack cellular structure, metabolism, and independent replication and requires a host
CAPSOMERS, NUCLEIC ACID CORE, CAPSID, ENVELOPE
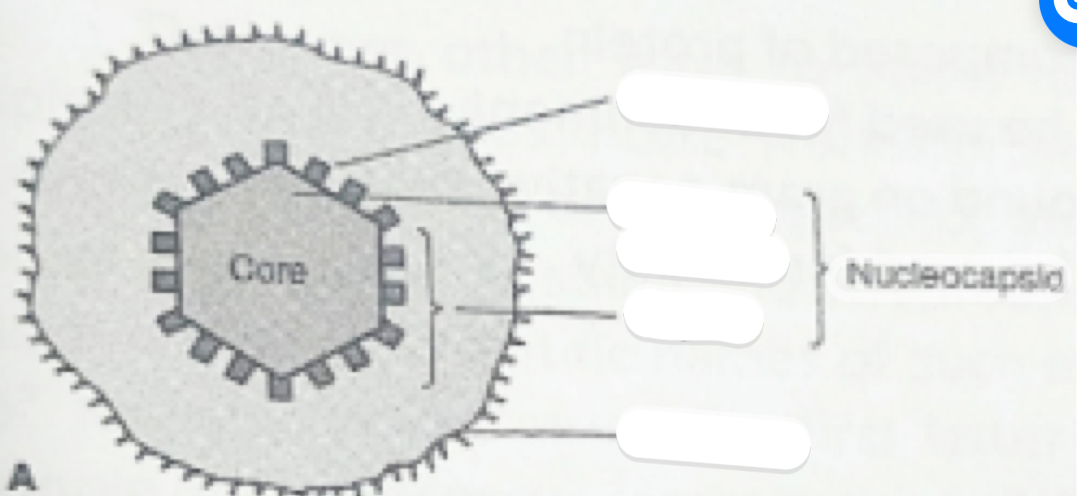
CYTOPLASM
The gel-like substance within the cell where metabolic activities and reactions occur.
NUCLEOID
Contains the bacterial chromosome; the region where the genetic material is located
GLYCOCALYX
A polysaccharide layer that protects the cell, aids in adherence, and prevents desiccation
CAPSULE
A tightly packed glycocalyx that protects bacteria from phagocytosis and aids in pathogenicity
CELL WALL
Provides structure, protection, and shape to the cell; made of peptidoglycan in bacteria
PLASMA MEMBRANE
A selectively permeable membrane that regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell and facilitates metabolic reactions
RIBOSOME
Protein synthesis occurs here
PILI
Hair-like structures that aid in attachment and DNA transfer during conjugation
FIMBRIAE
Short, thin projections that help bacteria adhere to surfaces and host cells
FLAGELLA
Long, whip-like structures that provide motility
SPORES
Highly resistant structures formed under adverse conditions for survival; protect genetic material
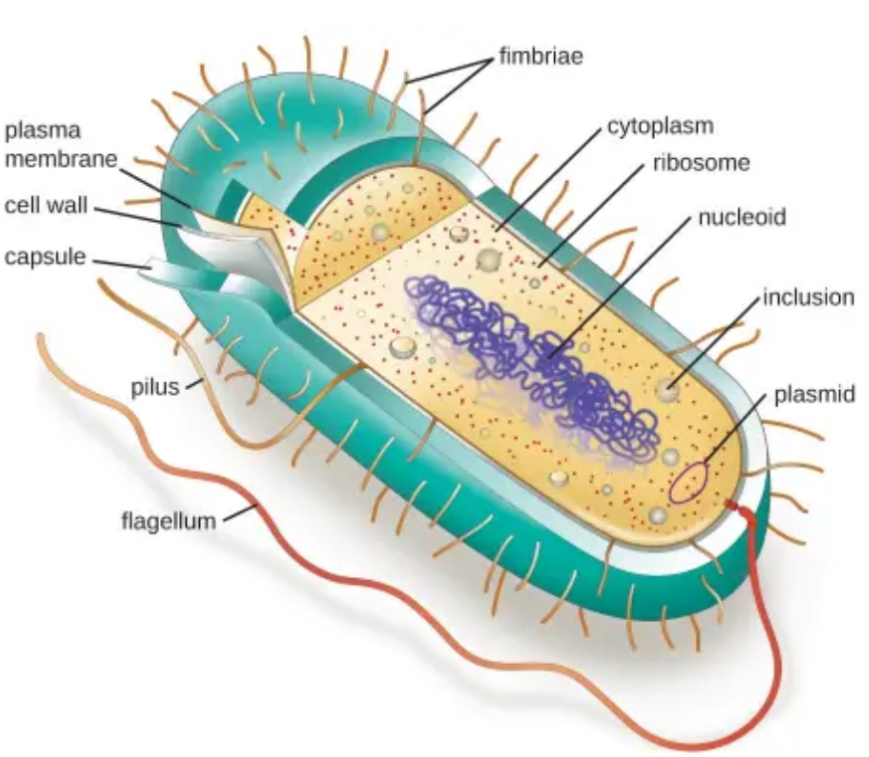
PROKARYOTES
Very Simple cells and do not have complex system of membranes and organelles
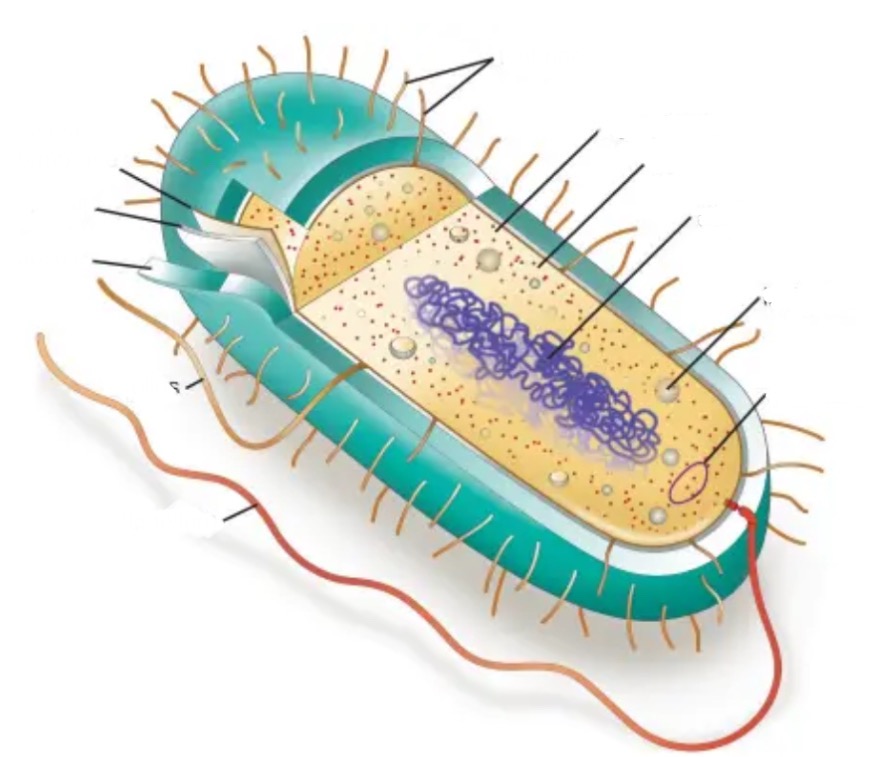
PROKARYOTES
Bacteria and Arachea